Team:UT-Tokyo/Sudoku experiments
From 2010.igem.org
(→Terminator leak) |
|||
| Line 182: | Line 182: | ||
= Parts Making = | = Parts Making = | ||
| - | == Terminator leak(Parts) == | + | == Terminator leak(Parts Making) == |
| - | == Phage MS2(Parts) == | + | == Phage MS2(Parts Making) == |
[[Image:Sudoku_MS2-make_2.jpg|200px|thumb|How to make MS2 parts]] | [[Image:Sudoku_MS2-make_2.jpg|200px|thumb|How to make MS2 parts]] | ||
| Line 213: | Line 213: | ||
| - | == Location sequence(Parts) == | + | == Location sequence(Parts Making) == |
== Hin == | == Hin == | ||
Revision as of 00:29, 28 October 2010


Sudoku
Introduction System Modeling Experiments Perspective Reference
Experiments
Assay
2. Phage MS2
Parts Making
1. #Terminator leak(Parts Making)
3. #Location sequence(Parts Making)
4. #Hin
5. #flpe
Detail Note Book
Assay
Terminator leak
To construct 4C3 leak-switch, which is indispensable to determine the numbers when solving Sudoku, the following system is required: do not express enough amount of Cre gene that has two or more terminators on the upstream, and express enough amount of Cre gene that has only one terminator there. For this purpose, it is neccessary to use appropriate terminator.
The aim of terminator leakiness assay is to make sure whether our terminator is appropriate or not. We measured the fluorescence of GFP expressed when Cre protein recombine DNA construct. When the fluorescence of expressed GFP depends on the existence of Cre gene in this construct, our system works properly. However, in the first trial, the fluorescence of GFP cannot be observed in our construct. We considered whether lox sequence, cre coding sequence or both of them have some errors, and performed some experiments to make sure our hypothesis. As a result, it elucidated that lox sequence is not functional.
INDEX
Profiling of the gene expression by T7 RNA polymerase
Verification of the recombination activity of Cre protein
Verification of the activity of the lox sequence in our construct
Verification of the activity of the Cre protein in our construct
Profiling of the gene expression by T7 RNA polymerase
Experiment one
First, we did some experiments to profile the gene expression by T7 RNA polymerase. The part 1-24 (T7 promoter – GFP unit) plasmid was transformed to BL21 (DE3) strain, and incubated on the LB plate at 37 oC.One colony was isolated and cultivated in two LB mediums. One sample was added IPTG (final conc. 1mM) and incubated at 37 oC. The samples were centrifuged and the supernatant were removed. We checked fluorescence from pellets on our eyes.
- DE3 strain is one of the E.coli strain which codes the gene of T7 RNA polymerase at the downstream of lac operon on its genome.
As a result, we could not observe the increasing of the GFP flourescence by addition of IPTG.The cultivated bacteria without the addition of IPTG turned green and those with the addition of IPTG did not turn green.
From this result, the following possibility was suggested. Green bacteria without the addition of IPTG → T7 RNA polymerase was expressed weakly and transcribed the mRNA coding gfp. White bacteria with the addition of IPTG → Overexpressed GFP made inclusion body.
Experiment two
From the previous result, we expected that reduced IPTG concentration will prevent the formation of inclution body and performed experiment 1 in low IPTG concentration.We checked the GFP fluorescence of both samples on our eyes.
The GFP fluorescence of both samples were measured and there was no difference between the two samples .
It was suggested that BL21(DE3) is not proper to control the expression of gene expression.
We desided to use Rossetta (DE3) pLysS, that can repress the activity of the leaked T7 RNA polymerase.
Experiment three
The plasmid containing part 1-24 was transformed to Rosetta (DE3) plysS.
Experiment four
We improved the protocol to the following.
We used full growth samples preserved in glycerol made in experiment three. We added samples I-V into LB medium and cultured at 37oC. One colony was isolated and cultured in LB medium in duplicate. We added IPTG into one and cultured at room temperature. Then we observed green fluorescence. (The concentration of IPTG was 0.1mM)
As a result, we confirmed that IPTG is able to induce expression in samples I-III. Regarding IV, a small amount of green fluorescence was detected in the sample without IPTG too. We were not able to detect any green fluorescence in V whether IPTG was added or not.
Experiment five
We assayed how the fluorescent intensity of GFP changes over time for sample 1, the sample we were able to induce in the previous assay..
I:The plasmid containing part 1-24 transformed to Rosetta (DE3) plysS
When the OD reached 0.6, we added IPTG to a final concentration of 0.1 mM.
We measured the fluorescence and graphed the results:
Result
We observed fluorescence without IPTG. However, fluorescence intensity was half compared to that after IPTG induction.
Experiment Six
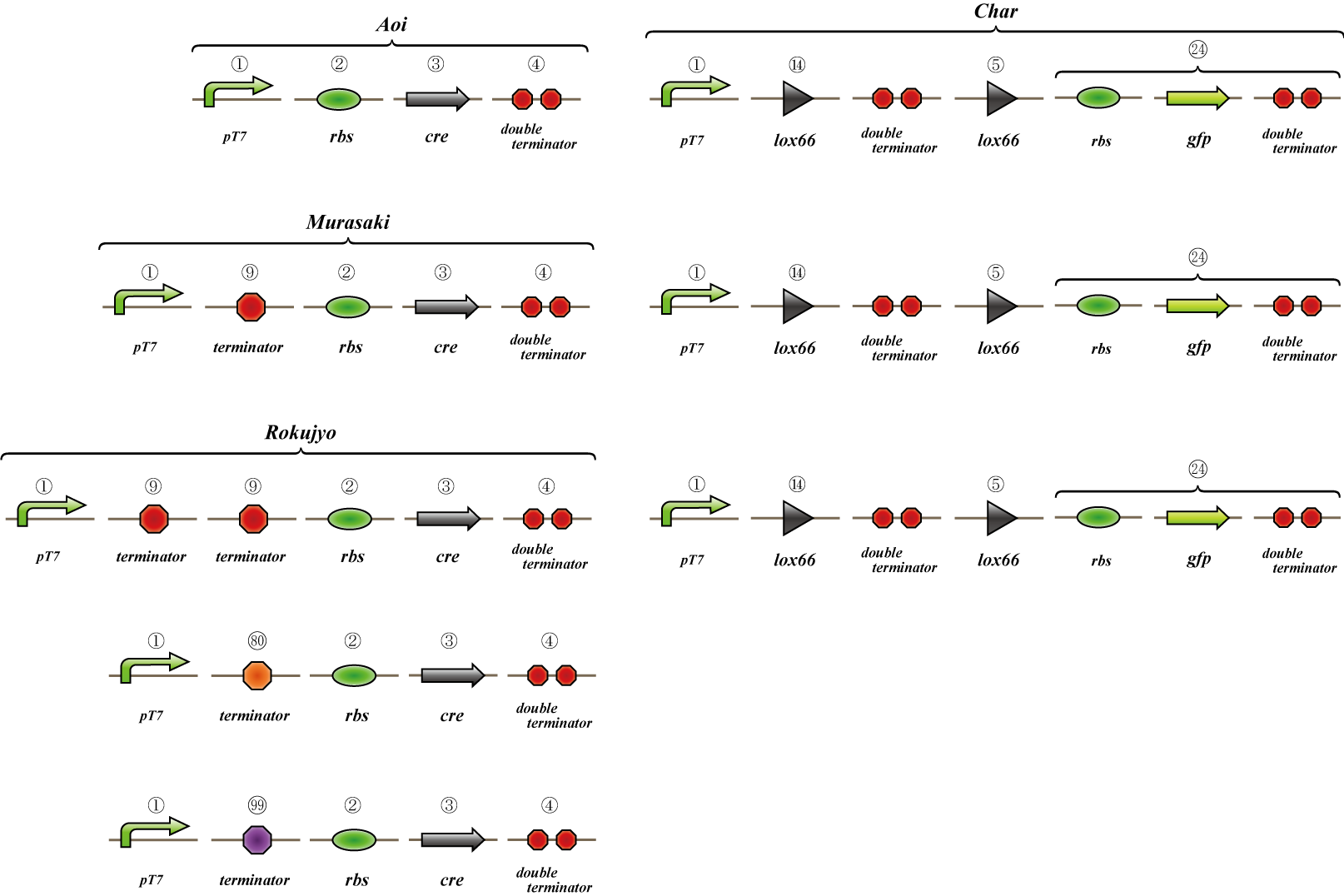
We make four constructs. The first, “Aoi,” does not have a terminator between the promoter and the ribosome binding site. The second, “Murasaki,” has one terminator, and “Rokujo” has two terminators. “Char,” the fourth, expresses GFP when the lox sites are recombined. We combine these to make three units. 1. Aoi + Char unit 2. Murasaki + Char unit 3. Rokujo + Char unit
Cre protein is placed downstream of the RBS.
The terminator is placed between the two lox sites. GFP is expressed when terminators between the lox sites are excised by the Cre protein.
GFP is expressed when the terminators between the lox sites are excised by Cre protein.
A terminator exists between the promoter and the rbs, so cre is not translated. However, this terminator is leaky and transcribes a small amount of cre, so the terminators are gradually excised and GFP is expressed.
Terminators exist between the promoter and the rbs, so cre is not translated. The terminator is not excised and GFP is not expressed.
We transformed E.coli containing Char, Aoi&Char, Murasaki&Char and Rokujo&Char to Rosetta(DE3) plyS.We cultured these and measured the fluorescence intensity of GFP after IPTG induction.
With Char, we were not able to observe GFP fluorescence because terminator is not excised in this construct.(negative control)
With Murasaki & Char, IPTG induces the expression of Cre and the terminators are gradually excised, so the ratio of plasmids able to produce GFP increases.
Therefore, the intensity of GFP fluorescence increases gradually.Murasaki & Char express Cre at low levels, so the terminator is excised infrequently.Therefore, the intensity of GFP fluorescence increases slowly.
With Rokujo & Char, Cre is seldom expressed, so the intensity of GFP should be similar to that of Char.
Result
We were only able to observe fluorescence native to bacterial proteins. We deciphered this result as the following.
The sequence of our parts were identical to those reported on the registry, so the possibility of errors in our sequence was eliminated.
1. We used BBa_I71801(lox66)and (lox71)BBa_I718017 as our lox sites. There is the possibility that these sequences were dysfunctional.
2. We used BBa_J61047 as our Cre protein. There is the possibility that the sequence of this Cre protein was incorrect and Cre is dysfunctional.
Phage MS2
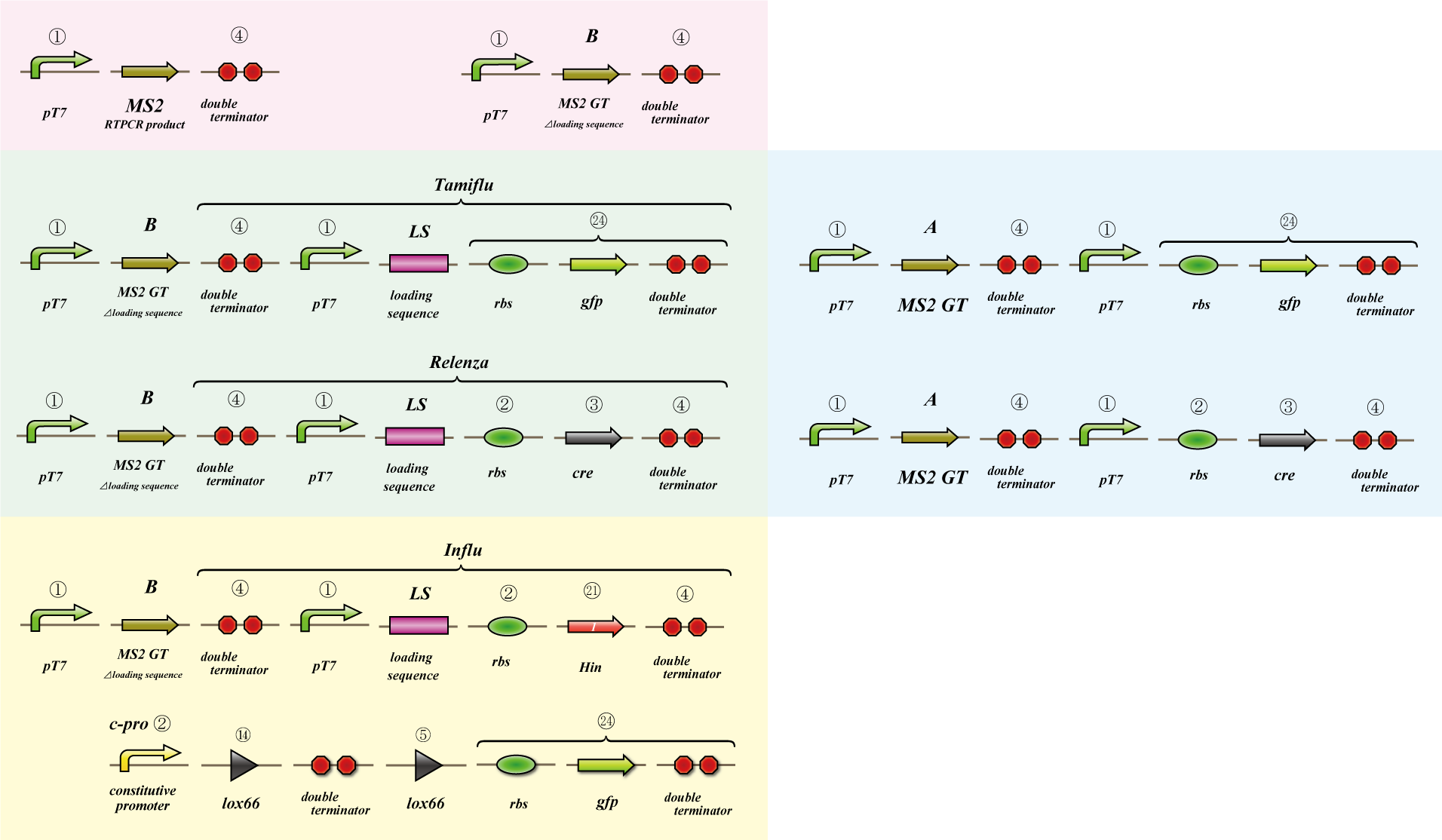
We use MS2 phage to transmit information of location and number. The expression of the phage should start after 4C3 leak switch turns on. MS2 phage transport RNA which has loding sequence, so we knock out self assembly and made our E.coli translate loading seaquence at another point. To check whether transportion go correctly, we made assay.
i. Phage expression assay (red region)
Check whether RT-PCR product can be translated into MS2 phage.
ii. Packaging assay (blue & green region)
MS2 phage package RNA which has loading sequence. Using this character, we check whether RNA which has loading sequence and other coding region (gfp, cre) can be packaged correctly.
iii. Infection assay (yellow & green region)
We make the assay, which express gfp only when cre protein is expressed correctly. By using this part, we check whether E.coli can be infected with the MS2 phage made in assay ii as the fluorescence of gfp.
Location sequence
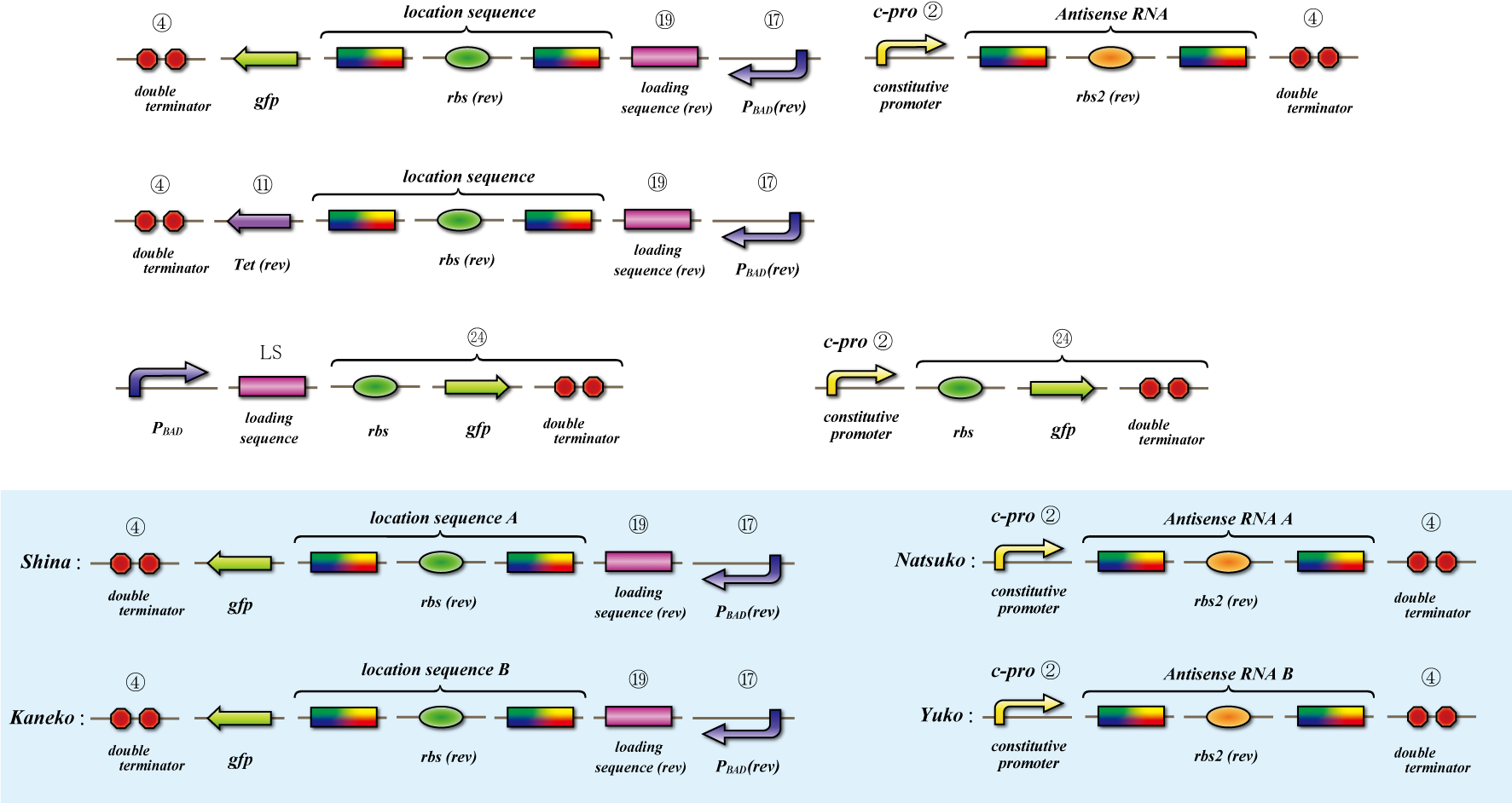
The object of the assay is to test whether antisense RNA used in our construct works or not. In order to block the unnecessary information transformed by the virus from the other grid, we use antisense RNA to block ribosome to bind the region around the ribosome binding site (rbs) and prevent the expression of protein. In our construct, information is carried by virus and antisense RNA is transcribed constantly inside the cell. Once the unnecessary information was transformed, the antisense will come and shut out all the RNA chain excluded by virus. In this assay, we used pBAD as the promoter to start translating grid information which will be transformed by virus in our construct. The strength of the promoter depends on the concentration of arabinose. On the other hand, we used c-pro as the promoter to start translating antisense RNA. This c-pro is the strongest constitutive promoter submitted in igem parts. In assay I, we examined the relative strength of pBAD (with eight different concentration of arabinose) and c-pro. By using the proper concentration of arabinose which was determined by assay I, in assay II, we inspect observe whether our antisense RNA works or not. In these two assay, gfp was used as a reporter protein.
Parts Making
Terminator leak(Parts Making)
Phage MS2(Parts Making)
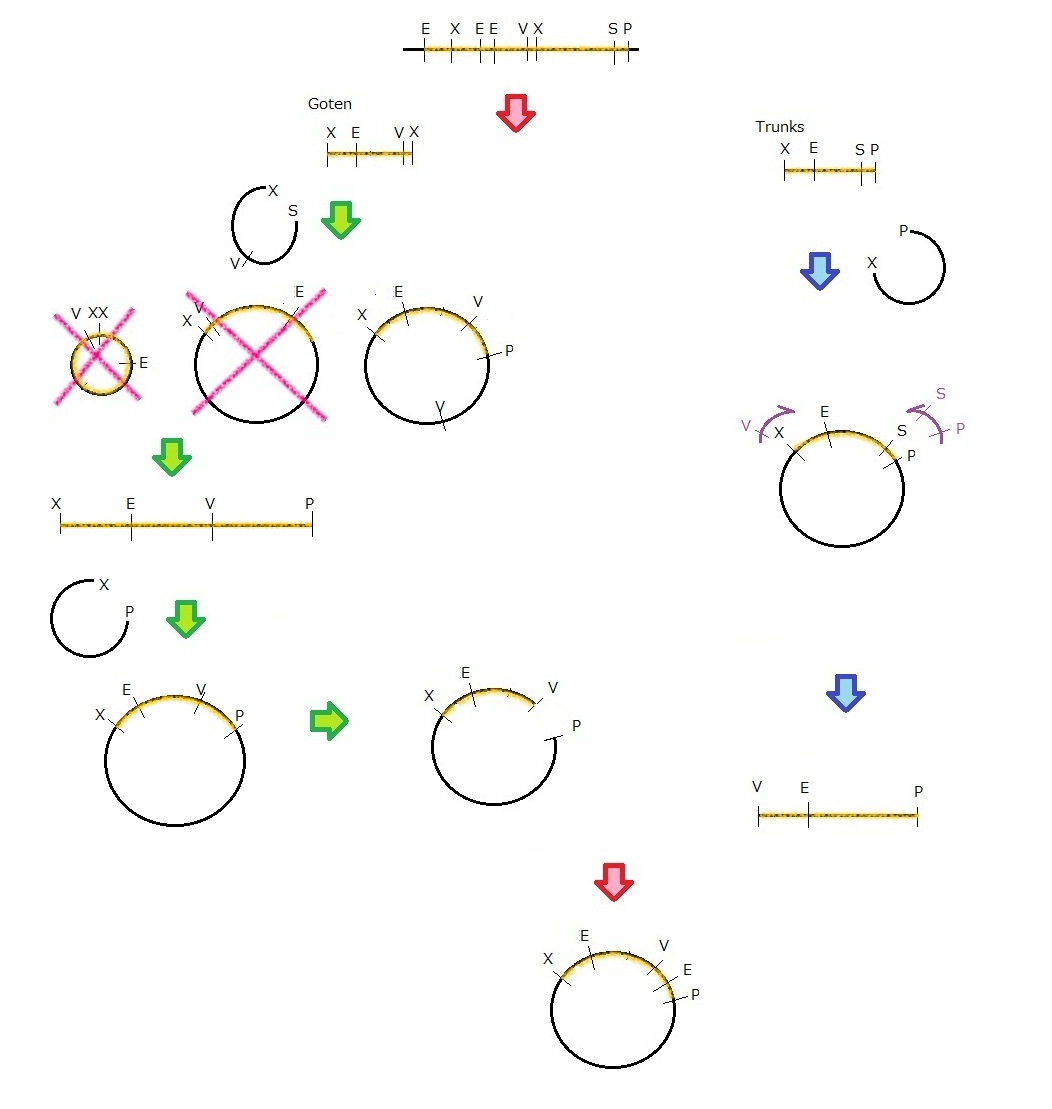
We get MS2 gene RT-PCR product. This original product include a lot of restricted enzyme site: two EcoRI site, two XbaI site and one VspI site.
To run our project, we don’t have to remove EcoRI site in the region. So we modified XbaI site by PCR as the following method:
1. We divided RT-PCR product into two parts by XP enzyme digestion:
E-X-E-E-V-X -> “Goten”
X-S-P -> “Tranks”
(named from the famous animation, "DRAGON BALL")
2. Insert is ligated with the vector, chloramphenicol-tolerance:
Goten -> EX vector
Tranks -> XP vector
3. Tranks -> PCR adding V-X region
4. Each part -> VP enzyme digestion, ligation each other
Location sequence(Parts Making)
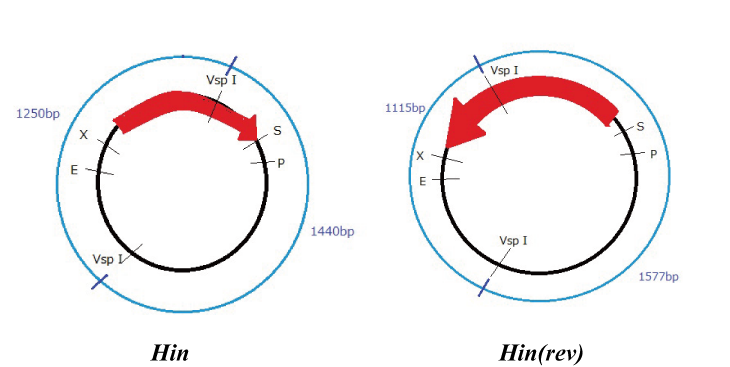
Hin
Parts making (reverse)
We get Hin parts from HQ (BBa_J31000).
We use this part as the form of reverse, so we made this part reverse by PCR.
To check PCR is done correctly, we did VspI digestion.
Expression check
To check whether flpe works correctly, we made assay shown in Fig, similar to the assay of flpe check.
The top construct is a nagative control. GFP can't be expressed because of the double terminators.
The bottom construct express GFP when Hin works correctly. When Hin is expressed correctly, Hin recognaize the hix site and double terminator which terminates the expression of gfp is removed, so GFP may be expressed.
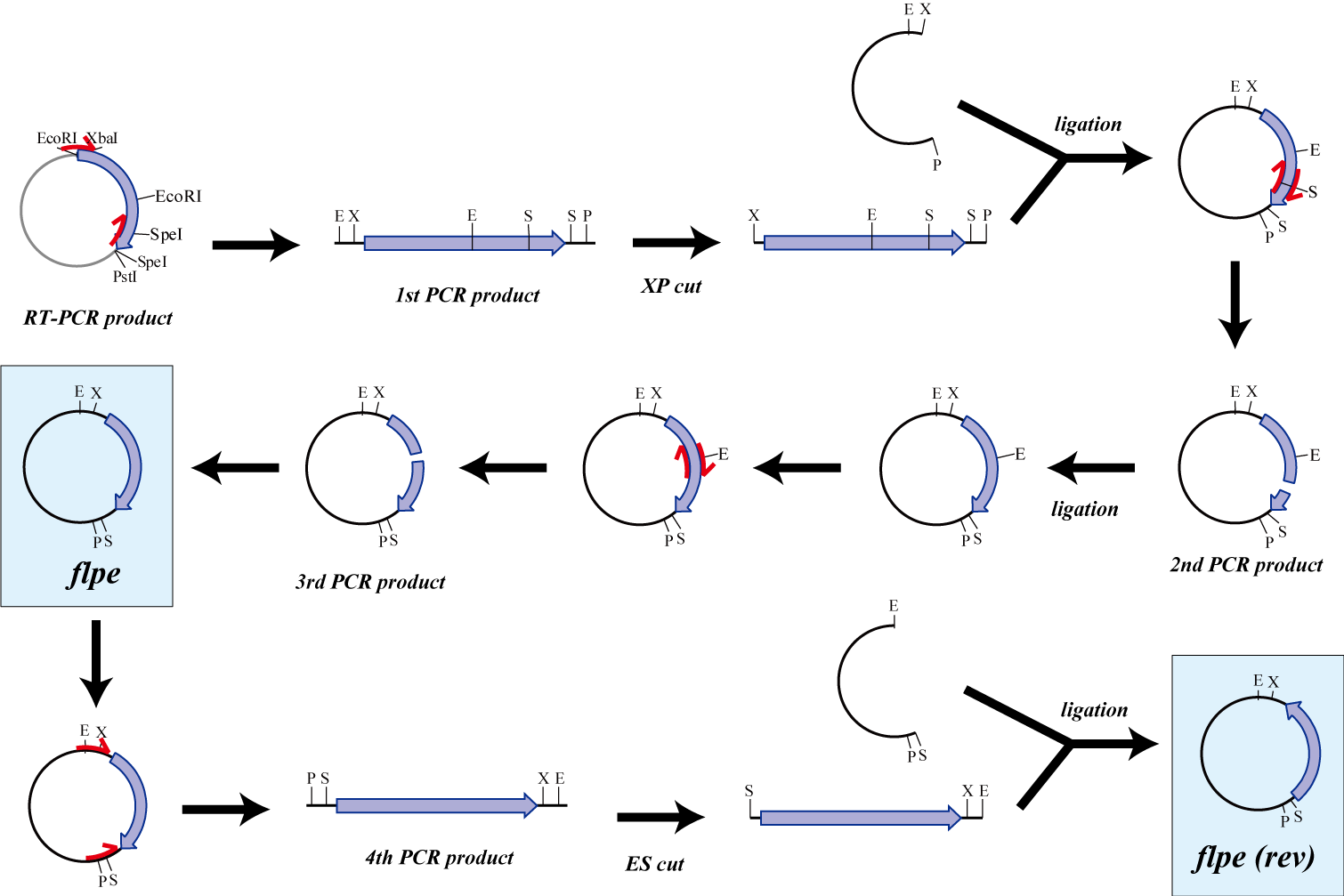
flpe
The original flpe include two restriction enzyme sites(EcoRI, SpeI).
We modified this flpe by PCR:
1st PCR : cloning
-> ligation with vector
-> 2nd PCR : modified SpeI site
-> 3rd PCR : modified EcoRI site
We use this part as the form of reverse, so we made this part reverse by PCR.
Expression check
To check whether flpe works correctly, we made assay shown in Fig.
The top construct is a nagative control. GFP can't be expressed because of the double terminators.
The bottom construct express GFP when flpe works correctly. When flpe is expressed correctly, flpe recognaize the frt site and double terminator which terminates the expression of gfp is removed, so GFP may be expressed.
Parts list
| Number | Name | Link to BioBrick | Plate coordinate | Vector | Code length |
| 1 | T7 promoter |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_I712074 BBa_I712074] | plate1-6N | pSB1AK8 | 46bp |
| 2 | rbs |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0030 BBa_B0030] | plate1-1H | pSB1A2 | 15bp |
| 3 | cre recombinase |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_J61047 BBa_J61047] | plate1-5D | pSB1A2 | 1037bp |
| 4 | double terminator |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0014 BBa_B0014] | plate2-24C | pSB1AK3 | 95bp |
| 5 | lox66 recombinase site |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_I718017 BBa_I718017] | plate1-17J | pSB1A2 | 34bp |
| 6 | Kan resistance (rev) |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_J31002 BBa_J31002] | plate1-2K | pSB1A2 | 816bp |
| 7 | rbs (rev) |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0014 BBa_B0014] | plate1-1J | pSB1A2 | 15bp |
| 8 | lox71 recombinase site |
order-made | --- | --- | 34bp |
| 9 | single terminator |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B1006 BBa_B1006] | plate1-4H | pSB1AK3 | 39bp |
| 10 | constant express promoter |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_J23119 BBa_J23119] | plate1-18A | pSB1A2 | 35bp |
| 11 | Tet resistance (rev) |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_J31006 BBa_J31006] | plate1-1N | pSB1A2 | 1191bp |
| 12 | hixC |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_J44000 BBa_J44000] | plate1-1B | pSB1A2 | 26bp |
| 13 | --- |
--- | --- | --- | --- |
| 14 | lox66 |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_I718016 BBa_I718016] | plate1-17H | pSB1A2 | 34bp |
| 15 | rbs-mRFP1-terminator |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_I13507 BBa_I13507] | plate1-22O | pSB1A2 | 861bp |
| 16 | location sequence(old) |
order | --- | --- | --- |
| 17 | pSP6(rev) |
order | --- | --- | --- |
| 18 | lox2272 |
order | --- | --- | --- |
| 19 | loading sequence(rev) |
order | --- | --- | --- |
| 20 | frt |
[http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J61020 BBa_J61020] | From HQ | pSB1A2 | 34bp |
| 21 | hin(true) |
[http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J31000 BBa_J31000] | From HQ | ??? | 573bp |
| 22 | hin(rev) |
--- | --- | ??? | 573bp |
| 23 | flpe |
--- | --- | --- | about 1.2kbp |
| 24 | gfp unit |
--- | --- | --- | about 1.2kbp |
| 25 | flpe(rev) |
--- | --- | --- | about 1.2kbp |
Detail Note Book
Detail protocols about Sudoku project are:
June.
July.
 "
"