Team:Slovenia/PROJECT/proof/studies/betagal
From 2010.igem.org
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
<h2>Introduction</h2> | <h2>Introduction</h2> | ||
| - | Before we started working on our main project (biosynthesis), we had to make sure the zinc finger proteins actually bind to their predicted binding sites. To evaluate binding of zinc finger-enzyme fusion proteins in vitro, we used different methods and techniques, e.g | + | Before we started working on our main project (biosynthesis), we had to make sure the zinc finger proteins actually bind to their predicted binding sites. To evaluate binding of zinc finger-enzyme fusion proteins in vitro, we used different methods and techniques, e.g. surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). In addition, we designed a universal device to measure the binding of DNA binding proteins to the specific DNA sequences <em>in vivo </em>(scheme below). |
[[Image:shemakloniranjaunsistem.png|thumb|center|600px|'''Scheme: construction of a universal device to measure the binding of DNA binding proteins to target DNA sequence <em>in vivo</em>.''']] | [[Image:shemakloniranjaunsistem.png|thumb|center|600px|'''Scheme: construction of a universal device to measure the binding of DNA binding proteins to target DNA sequence <em>in vivo</em>.''']] | ||
| - | The universal device for testing<em> | + | The universal device for testing<em>in vivo</em>binding of DNA binding proteins is composed of several parts (see the scheme): 1) a synthetic promoter, pSYN, into which a DNA binding sequence, specific for each tested DNA binding protein was inserted (between -35 and -10 sites of the promoter); 2) <em>lac</em>Z reporter gene, expression of which is controlled by pSYN; and, 3) the tested DNA binding protein under regulation of the arabinose inducible (pBAD) promoter. The principle of our device is that the binding of a DNA binding protein to its specific target sequence in pSYN promoter would result in decreased basal activity of this promoter. The activity of pSYN was monitored measuring the activity of β-galactosidase as a reporter (see scheme below). <em>E. coli </em>bacteria, containing our device on a low copy plasmid were grown in the presence of increasing concentrations of arabinose to induce expression of the DNA binding protein. After overnight growth in Luria Bertani broth, β-galactosidase activity was measured and results expressed in Miller Units as described in protocols. |
[[Image:shemakloniranjaunsistem.png|thumb|center|600px|'''Scheme: representation of outcome if the correct pair (DNA binding protein and its correct target DNA sequence) are present in the universal device. (A) In the absence of arabinose, small amounts of DNA binding protein are produced, enabling high activity of pSYN promoter that results in high β-galactosidase activity. (B) When arabinose is present in the medium, DNA binding protein expression in the cell is increased, which results in binding to its target DNA sequence in the pSYN promoter. As a consequence, the expression of pSYN is decreased, resulting in lower β-galactosidase activity.''']] | [[Image:shemakloniranjaunsistem.png|thumb|center|600px|'''Scheme: representation of outcome if the correct pair (DNA binding protein and its correct target DNA sequence) are present in the universal device. (A) In the absence of arabinose, small amounts of DNA binding protein are produced, enabling high activity of pSYN promoter that results in high β-galactosidase activity. (B) When arabinose is present in the medium, DNA binding protein expression in the cell is increased, which results in binding to its target DNA sequence in the pSYN promoter. As a consequence, the expression of pSYN is decreased, resulting in lower β-galactosidase activity.''']] | ||
<h2>Results</h2> | <h2>Results</h2> | ||
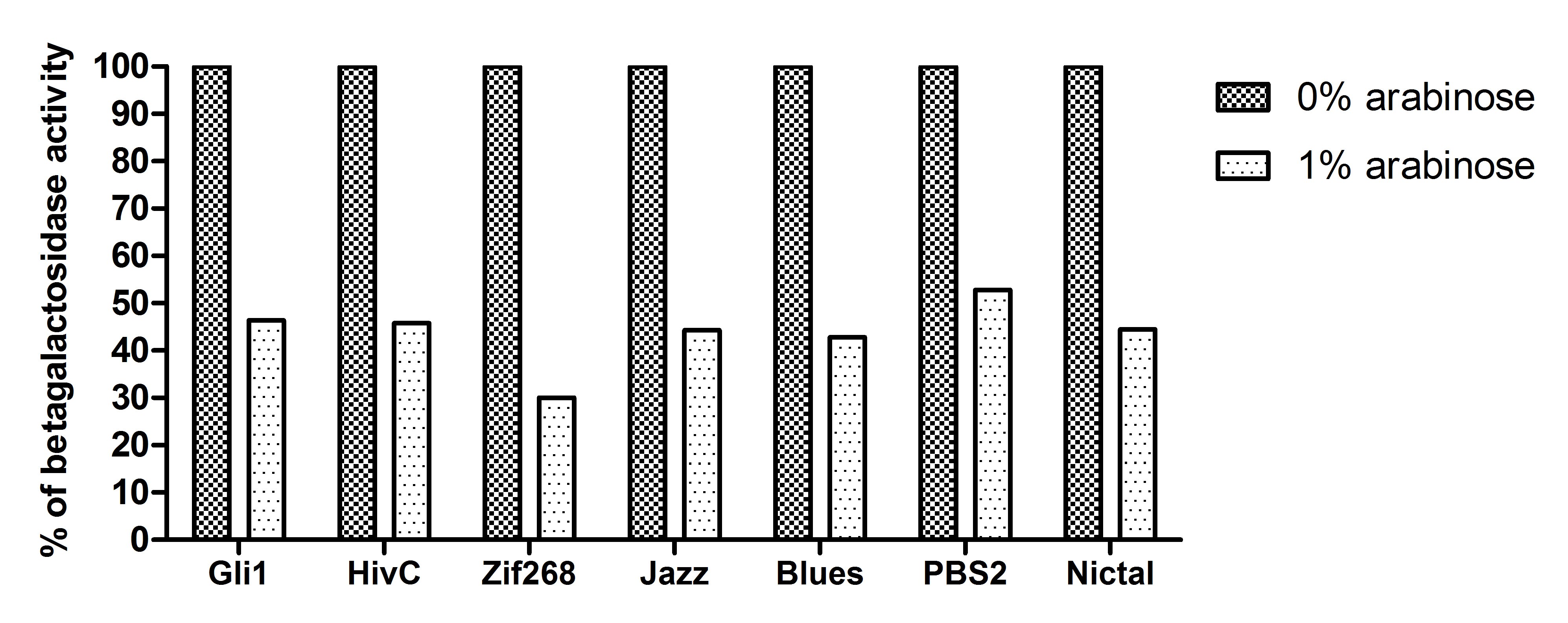
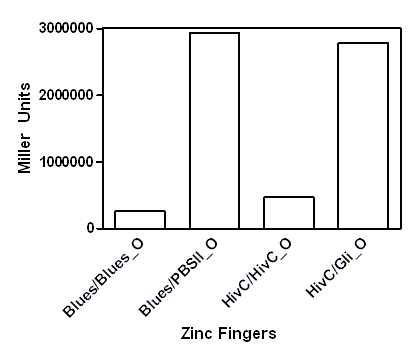
| - | A representative of five experiments of our universal device for testing binding of DNA binding proteins is shown below. A full range of arabinose concentrations | + | A representative of five experiments of our universal device for testing binding of DNA binding proteins is shown below. A full range of arabinose concentrations were tested, however, due to the ease of presentation only results +/- 1% arabinose are presented. To be able to compare β-galactosidase activities of each zinc finger construct among each other, results were expressed as % of 0% arabinose for each zinc finger construct. While 1% arabinose had no effect on β-galactosidase activity of <em>E. coli </em>carrying no plasmid construct (not shown), this concentration of arabinose resulted in ~60 % reduction of β-galactosidase activity in the <em>E. coli </em>containing our device expressing Gli1, HivC, Zif286, Jazz, Blues, PBSII zinc fingers or NicTAL DNA binding protein (see figure A, dotted bars). In contrast, β-galactosidase activity remained unchanged in the control devices, where pSYN promoter contained a binding site of a different zinc finger (compare bars for Blues/Blues_o and Blues/PBSII_O, where the first pair represents β-galactosidase activity of device expressing Blues and containing pSYN with the binding site for Blues, and a device expressing Blues and containing pSYN with the binding site for PBSII, respectively, see figure B). These results suggest that all zinc fingers used in our studies specifically bind to their corresponding DNA binding sites <em>in vivo</em>. Furthermore, we created a universal device that can be customized for testing of binding interactions of any DNA binding protein and its corresponding target DNA sequence. |
[[Image:UniverzalnisistemTinaL.jpg|thumb|center|600px|'''Figure A: Gli1, HivC, Zif268, Jazz, Blues, PBSII and NicTAL DNA binding proteins bind to their specific DNA target sequence <em>in vivo. </em><em>E. coli </em>in Luria Bertani broth were grown overnight in the presence and absence (hatched bars) of 1% arabinose (dotted bars). β-galactosidase was measured as described in protocols. A representative of five independent experiments is shown.''']] | [[Image:UniverzalnisistemTinaL.jpg|thumb|center|600px|'''Figure A: Gli1, HivC, Zif268, Jazz, Blues, PBSII and NicTAL DNA binding proteins bind to their specific DNA target sequence <em>in vivo. </em><em>E. coli </em>in Luria Bertani broth were grown overnight in the presence and absence (hatched bars) of 1% arabinose (dotted bars). β-galactosidase was measured as described in protocols. A representative of five independent experiments is shown.''']] | ||
Revision as of 14:27, 27 October 2010
Contents |
Introduction
Before we started working on our main project (biosynthesis), we had to make sure the zinc finger proteins actually bind to their predicted binding sites. To evaluate binding of zinc finger-enzyme fusion proteins in vitro, we used different methods and techniques, e.g. surface plasmon resonance (SPR) and electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). In addition, we designed a universal device to measure the binding of DNA binding proteins to the specific DNA sequences in vivo (scheme below).
The universal device for testingin vivobinding of DNA binding proteins is composed of several parts (see the scheme): 1) a synthetic promoter, pSYN, into which a DNA binding sequence, specific for each tested DNA binding protein was inserted (between -35 and -10 sites of the promoter); 2) lacZ reporter gene, expression of which is controlled by pSYN; and, 3) the tested DNA binding protein under regulation of the arabinose inducible (pBAD) promoter. The principle of our device is that the binding of a DNA binding protein to its specific target sequence in pSYN promoter would result in decreased basal activity of this promoter. The activity of pSYN was monitored measuring the activity of β-galactosidase as a reporter (see scheme below). E. coli bacteria, containing our device on a low copy plasmid were grown in the presence of increasing concentrations of arabinose to induce expression of the DNA binding protein. After overnight growth in Luria Bertani broth, β-galactosidase activity was measured and results expressed in Miller Units as described in protocols.

Results
A representative of five experiments of our universal device for testing binding of DNA binding proteins is shown below. A full range of arabinose concentrations were tested, however, due to the ease of presentation only results +/- 1% arabinose are presented. To be able to compare β-galactosidase activities of each zinc finger construct among each other, results were expressed as % of 0% arabinose for each zinc finger construct. While 1% arabinose had no effect on β-galactosidase activity of E. coli carrying no plasmid construct (not shown), this concentration of arabinose resulted in ~60 % reduction of β-galactosidase activity in the E. coli containing our device expressing Gli1, HivC, Zif286, Jazz, Blues, PBSII zinc fingers or NicTAL DNA binding protein (see figure A, dotted bars). In contrast, β-galactosidase activity remained unchanged in the control devices, where pSYN promoter contained a binding site of a different zinc finger (compare bars for Blues/Blues_o and Blues/PBSII_O, where the first pair represents β-galactosidase activity of device expressing Blues and containing pSYN with the binding site for Blues, and a device expressing Blues and containing pSYN with the binding site for PBSII, respectively, see figure B). These results suggest that all zinc fingers used in our studies specifically bind to their corresponding DNA binding sites in vivo. Furthermore, we created a universal device that can be customized for testing of binding interactions of any DNA binding protein and its corresponding target DNA sequence.
 "
"