Team:ETHZ Basel/Modeling/Combined
From 2010.igem.org
(→Archeal light switch - Chemotaxis - Movement) |
(→PhyB/PIF3 light switch - Chemotaxis - Movement) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
* Second, the stochastic movement model was combined with the light switch - chemotaxis model. The interface was defined as the dependency CheYp - directed movement probability (or the bias). At every time point of the simulation, the next state (directed movement/tumbling) of the bacterium was selected, based on the value of the input bias. | * Second, the stochastic movement model was combined with the light switch - chemotaxis model. The interface was defined as the dependency CheYp - directed movement probability (or the bias). At every time point of the simulation, the next state (directed movement/tumbling) of the bacterium was selected, based on the value of the input bias. | ||
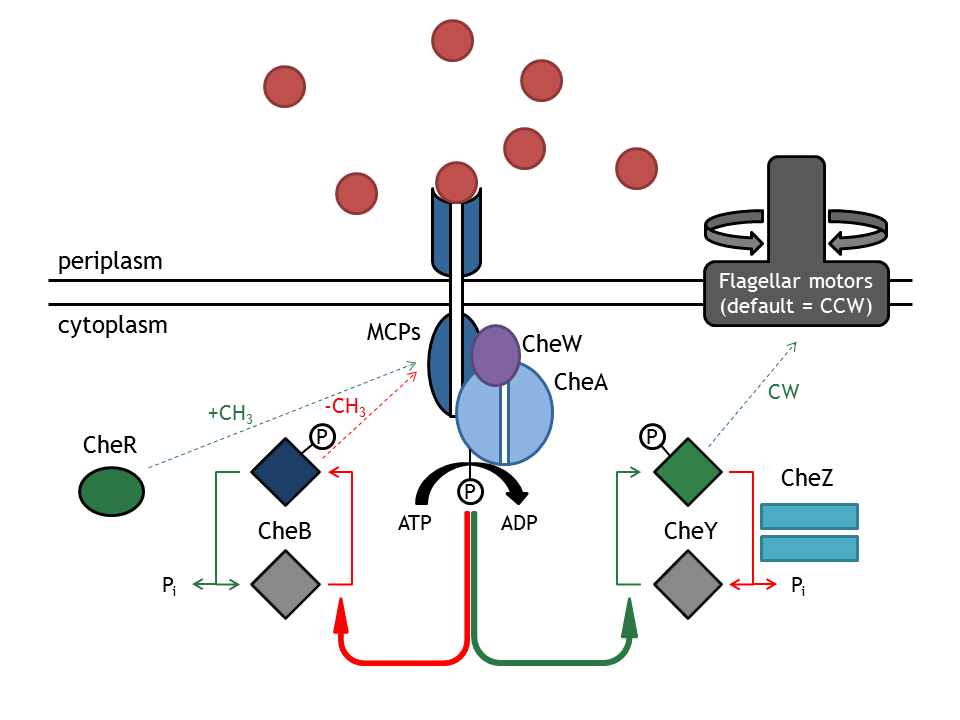
| - | == PhyB/PIF3 light switch - Chemotaxis | + | == PhyB/PIF3 light switch - Chemotaxis == |
[[Image:ETHZ_Basel_chemotactical_network.png|thumb|400px|'''Schematical overview on the chemotaxis pathway.''' MCPs refers to the membrane receptor proteins and Che are the intracellular proteins of the chemotaxis pathway.]] | [[Image:ETHZ_Basel_chemotactical_network.png|thumb|400px|'''Schematical overview on the chemotaxis pathway.''' MCPs refers to the membrane receptor proteins and Che are the intracellular proteins of the chemotaxis pathway.]] | ||
* First, the deterministic light switch and chemotaxis models were combined by assuming a complete removal of a selected Che protein species by the light switch. The interface was defined as the concentration ([LSP1-Che]) of this linked device. | * First, the deterministic light switch and chemotaxis models were combined by assuming a complete removal of a selected Che protein species by the light switch. The interface was defined as the concentration ([LSP1-Che]) of this linked device. | ||
| - | * Second, the stochastic movement model was combined with the light switch - chemotaxis model. The interface was defined as the dependency CheYp - directed movement probability (or the bias). At every time point of the simulation, the next state (directed movement/tumbling) of the bacterium was selected, based on the value of the input bias. | + | * Second, the stochastic movement model was combined with the light switch - chemotaxis model. The interface was defined as the dependency CheYp - directed movement probability (or the bias). At every time point of the simulation, the next state (directed movement/tumbling) of the bacterium was selected, based on the value of the input bias. |
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
== Archeal light switch - Chemotaxis == | == Archeal light switch - Chemotaxis == | ||
[[Image:ETHZ_Basel_archean_chemotactical_network.png|thumb|400px|'''Schematical overview of the chimeric chemotaxis pathway. '''ALR refers to the archeal light receptor, MCPs to the membrane receptor proteins and Che to the intracellular chemotaxis proteins.]] | [[Image:ETHZ_Basel_archean_chemotactical_network.png|thumb|400px|'''Schematical overview of the chimeric chemotaxis pathway. '''ALR refers to the archeal light receptor, MCPs to the membrane receptor proteins and Che to the intracellular chemotaxis proteins.]] | ||
Revision as of 14:08, 27 October 2010
Combined Models
To create the complete model of E. lemming, the individual modules chemotaxis pathway, light switch and movement model were coupled, by defining input - output interfaces. The combination was achieved in two steps:
- First, the deterministic light switch and chemotaxis models were combined by two different ways: The archeal light receptor is linked to the chemotaxis model by replacing the aspartate input. The PhyB/PIF3 is linked by the common LSP1-Che species.
- Second, the stochastic movement model was combined with the light switch - chemotaxis model. The interface was defined as the dependency CheYp - directed movement probability (or the bias). At every time point of the simulation, the next state (directed movement/tumbling) of the bacterium was selected, based on the value of the input bias.
PhyB/PIF3 light switch - Chemotaxis
- First, the deterministic light switch and chemotaxis models were combined by assuming a complete removal of a selected Che protein species by the light switch. The interface was defined as the concentration ([LSP1-Che]) of this linked device.
- Second, the stochastic movement model was combined with the light switch - chemotaxis model. The interface was defined as the dependency CheYp - directed movement probability (or the bias). At every time point of the simulation, the next state (directed movement/tumbling) of the bacterium was selected, based on the value of the input bias.
Archeal light switch - Chemotaxis
Chemotaxis - Movement
The combination of the deterministic and probabilistic models was (first) the biggest challenge and (afterwards) the biggest accomplishment in combining the models. Besides its theoretical complexity, the complete coupling is also conceptually very important. It closes the loop of our E. lemming modeling and it combines two different types of models: deterministic and stochastic, under the same global approach. The two models have different timesteps, the molecular one being much faster than the stochastic one, therefore their combination has been done via Simulink interface. Both models have been independently numerically integrated and the output of the deterministic model was passed as an input to the stochastic one, at every slower time-step. The main assumption we used in the complete coupling was that the mean run length is a function of the bias, while mean tumbling length is bias - independent.
Download
The combined model is included within the Matlab Toolbox and can be downloaded there.
 "
"