Team:Slovenia/PROJECT/proof/studies/prod
From 2010.igem.org
m |
m |
||
| Line 80: | Line 80: | ||
Before any <em>in vitro</em> characterisation, DNA-binding proteins had to be obtained. Zinc fingers were firstly tri-point ligated with a particular split GFP and T7 promoter and T7 terminator sequence were added afterwards. T7 promoter enables high production of proteins in<em> E. coli</em> BL21(DE3)pLysS production strain. Zinc fingers were then purified using His tags and used in subsequent experiments.<html> Parts used for production were: <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323001"><span style="color: #810081;">BBa_323001</span></a><a href="/w/page/BBa_323001"></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323015"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323015</span></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323069"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323069</span></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323058"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323058</span></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323004"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323004</span></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323070"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323070</span></a>.</html> | Before any <em>in vitro</em> characterisation, DNA-binding proteins had to be obtained. Zinc fingers were firstly tri-point ligated with a particular split GFP and T7 promoter and T7 terminator sequence were added afterwards. T7 promoter enables high production of proteins in<em> E. coli</em> BL21(DE3)pLysS production strain. Zinc fingers were then purified using His tags and used in subsequent experiments.<html> Parts used for production were: <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323001"><span style="color: #810081;">BBa_323001</span></a><a href="/w/page/BBa_323001"></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323015"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323015</span></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323069"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323069</span></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323058"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323058</span></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323004"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323004</span></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323070"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323070</span></a>.</html> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | [[Image:SLOSPR_shema.png|thumb|center|700px|''' | + | [[Image:SLOSPR_shema.png|thumb|center|700px|'''Figure 1:''' Scheme of cloning for zinc finger protein production.]] |
<h2>Protein production</h2> | <h2>Protein production</h2> | ||
Revision as of 23:53, 27 October 2010
Contents |
Cloning scheme
Before any in vitro characterisation, DNA-binding proteins had to be obtained. Zinc fingers were firstly tri-point ligated with a particular split GFP and T7 promoter and T7 terminator sequence were added afterwards. T7 promoter enables high production of proteins in E. coli BL21(DE3)pLysS production strain. Zinc fingers were then purified using His tags and used in subsequent experiments. Parts used for production were: BBa_323001, BBa_323015, BBa_323069, BBa_323058, BBa_323004, BBa_323070.
Protein production
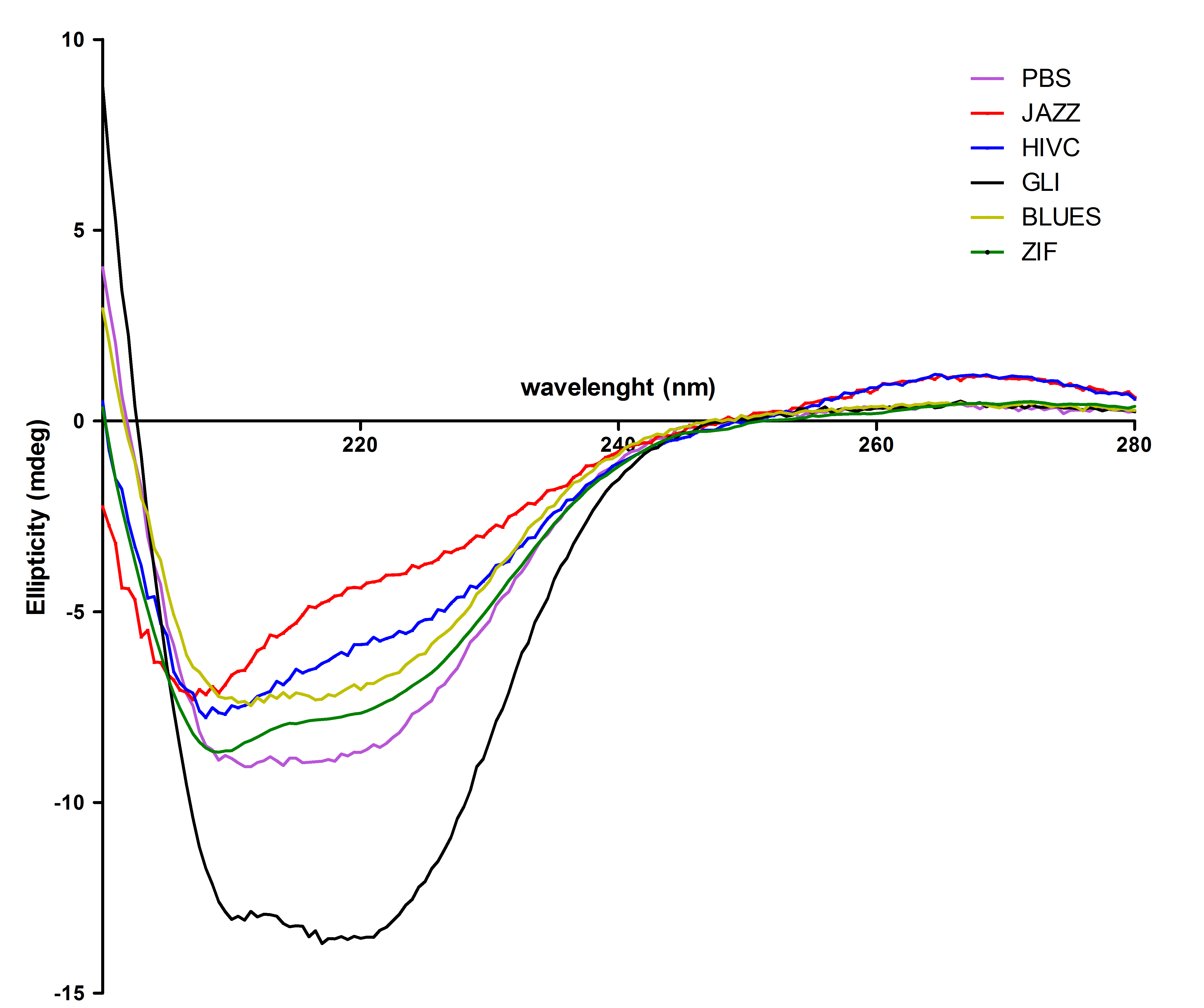
Zinc fingers were produced in E.coli BL21(DE3)pLysS and purified with Ni-NTA column according to our protocols in Methods & Parts. Their isolation and purity was confirmed with SDS-page and Western blot techniques. Secondary structure of proteins was determined with circular dichroism. Purified proteins were further used for electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) test and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) experiments.
All six proteins were also tested with circular dichorism spectroscopy. Secondary structures were observed successfully:
 "
"


