Team:NYMU-Taipei/Project/Speedy switch
From 2010.igem.org
Barry50710 (Talk | contribs) (→Abstract) |
Barry50710 (Talk | contribs) (→Background) |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
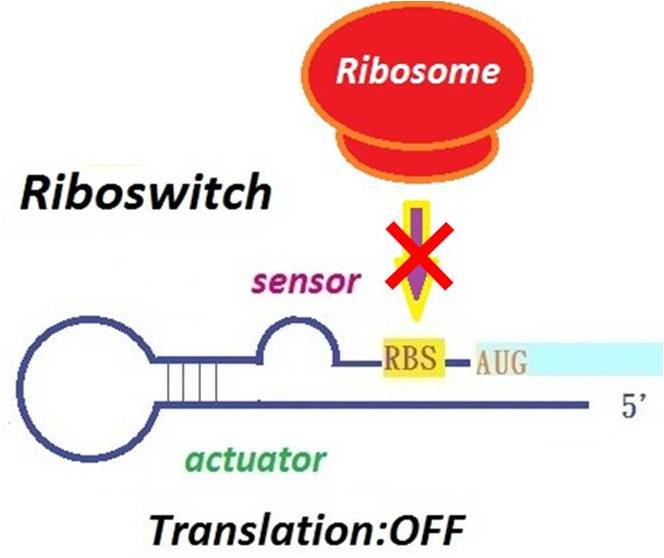
[[Image:NYMU Pre-ribo2.jpg|thumb|right|250px|The riboswitch is turned off. The RBS is hidden by the secondary structure the riboswitch forms. The ribosome is unable to bind to the RBS, suspending translation of the downstream gene.]] | [[Image:NYMU Pre-ribo2.jpg|thumb|right|250px|The riboswitch is turned off. The RBS is hidden by the secondary structure the riboswitch forms. The ribosome is unable to bind to the RBS, suspending translation of the downstream gene.]] | ||
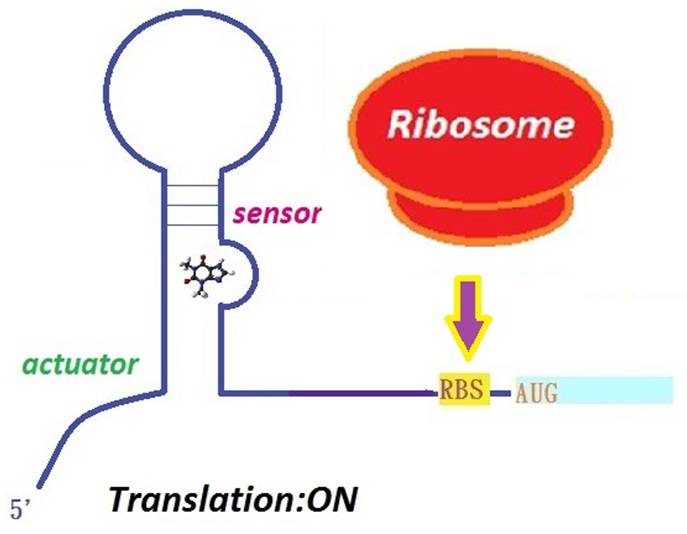
[[Image:NYMU Ribo-2.jpg|thumb|right|250px|The riboswitch is turned on when a specific small molecule binds to it. The ribosome can then bind to the RBS, inducing translation of the downstream gene.]] | [[Image:NYMU Ribo-2.jpg|thumb|right|250px|The riboswitch is turned on when a specific small molecule binds to it. The ribosome can then bind to the RBS, inducing translation of the downstream gene.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Riboswitch is able to control the translation. It is divided into two parts: a '''sensor''' and an '''actuator'''. | ||
Before the discovery of RNA regulatory system , the only way to induce reaction in a cell was through inducible promoters. By turning these promoters on or off, we could control the transcription of the downstream DNA into RNA thus also controlling the translation of RNA to Protein. Yet even with these promoters, the regulation of several metabolic pathways was still unexplainable. | Before the discovery of RNA regulatory system , the only way to induce reaction in a cell was through inducible promoters. By turning these promoters on or off, we could control the transcription of the downstream DNA into RNA thus also controlling the translation of RNA to Protein. Yet even with these promoters, the regulation of several metabolic pathways was still unexplainable. | ||
| - | The discovery of the riboswitch was based on data which described conserved mRNA secondary structure found on 5’-untranslated regions and the creation of small-molecule binding mRNA, | + | The discovery of the riboswitch was based on data which described conserved mRNA secondary structure found on 5’-untranslated regions and the creation of small-molecule binding mRNA, sensors. The function of these riboswitches is similar to the function of inducible promoters in that they both regulate downstream genetic data: their difference is that while promoters regulate transcription of DNA, riboswitches control translation of mRNA. |
| + | |||
| + | A riboswitch is a part of mRNA molecule that can bind a small molecule. When it does, the riboswitch will change its structure to regulate the following gene's activity. | ||
| - | + | A riboswitch have two parts: a sensor and an actuator. These two components work together to form a ‘switch’. The sensor binds to a small molecule inducer, and the actuator structurally changes to regulate gene expression. | |
| - | A riboswitch have two | + | |
(Harbaugh et al.,2008)(Lynch et al., 2006) | (Harbaugh et al.,2008)(Lynch et al., 2006) | ||
Revision as of 11:58, 27 October 2010
| Home | Project Overview | Speedy reporter | Speedy switch | Speedy protein degrader | Experiments and Parts | Applications | F.A.Q | About Us |
Contents |
Abstract
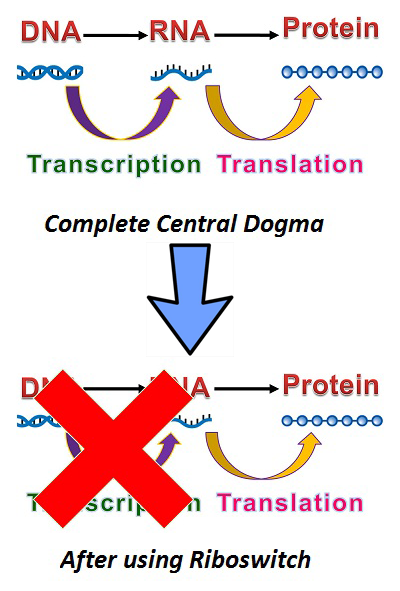
- In our project, speedy switch is a critical "switch" between RNA and protein. We use "Riboswitch" as our speedy switch.
In the past, translating proteins from DNA has followed the central dogma of molecular biology: DNA to RNA to Protein. Normally, after mRNA is transcribed from DNA, ribosomes will bind to the ribosome binding site(RBS) and begin translating mRNA into protein. During this process, we have no way of knowing the location, nor the quantity of mRNA; and after the process, mRNA is quickly degraded. As such, it is very hard to research the detailed roles and implications of mRNA in the central dogma. To resolve this problem, we placed a mRNA level based switch which can be used to control the translation of mRNA: riboswitch
Background
- Riboswitch is able to control the translation. It is divided into two parts: a sensor and an actuator.
Before the discovery of RNA regulatory system , the only way to induce reaction in a cell was through inducible promoters. By turning these promoters on or off, we could control the transcription of the downstream DNA into RNA thus also controlling the translation of RNA to Protein. Yet even with these promoters, the regulation of several metabolic pathways was still unexplainable.
The discovery of the riboswitch was based on data which described conserved mRNA secondary structure found on 5’-untranslated regions and the creation of small-molecule binding mRNA, sensors. The function of these riboswitches is similar to the function of inducible promoters in that they both regulate downstream genetic data: their difference is that while promoters regulate transcription of DNA, riboswitches control translation of mRNA.
A riboswitch is a part of mRNA molecule that can bind a small molecule. When it does, the riboswitch will change its structure to regulate the following gene's activity.
A riboswitch have two parts: a sensor and an actuator. These two components work together to form a ‘switch’. The sensor binds to a small molecule inducer, and the actuator structurally changes to regulate gene expression. (Harbaugh et al.,2008)(Lynch et al., 2006)
Project
In our project, riboswitch serves two main roles. The first is to speed up the cycle from DNA to mRNA to protein. Using a riboswitch we can pretranscribe DNA into mRNA, ready to be translated at a moments notice. In essence, we can create protein without having to wait for transcription. The second role the riboswitch serves is to act as a switch between the mRNA and protein levels. Using a riboswitch, we can control the expression of proteins downstream.
Typically, since translation often occurs the moment mRNA passed into the cytoplasm, protein and mRNA normally exist together. With a riboswitch control, we can study both the expression of mRNA and the expression of protein in the same cells, without the added implication of protein-mRNA interference.
Purpose
- Verification of protein function: we can perform RNA assay & protein assay in the same cell
- Control of protein expression
Design
In order for a riboswitch to work in our experiment, it needs to have the following characteristics:
- The inducer does not naturally exist or metabolize in the target organism.
- The riboswitch does not exist naturally in the target organism.
- The riboswitch does not have EcoRI, XbaI, SpeI, or PstI cutting sites.
- Although we can modify the cutting sites of our riboswitch, this action may cause more problems: the cutting site may mutate the secondary structure and molecule binding sites causing it to cease function.
- Example of speedy switch: We found that the theophylline riboswitch fits all the requirements for use in Escherichia coli DH5α.
- What do we need for the project?
- We used Green fluorescent protein as our reporter for two main reasons. First, GFP makes a great reporter because it fluoresces when it activates, making it easy to detect. We can use the intensity of the fluorescence to measure the activity of the promoter. The second reason is that the GFP used is a biobrick, thus if another team needed to use this riboswitch circuit, it would be easy for them to attach another biobrick. So we chose biobrick - [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J04630 BBa_J04630] (GFP with terminator)
- Since most riboswitches already have a Ribosome binding site (RBS) in its structure, we did not add another RBS in front of downstream reporter.
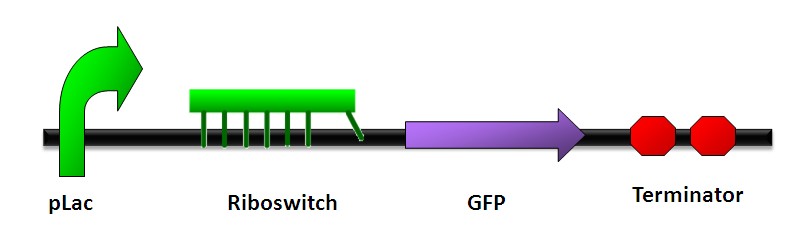
- Our design:
- Promoter [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_R0010 BBa_R0010]
- Riboswitch [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K411001 BBa_K411001]
- GFP+Terminator [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J04630 BBa_J04630]
Transform the whole structure,"promoter+ riboswitch+ GFP+ terminator in plasmid" to Escherichia coli. It will express GFP when theophylline (the inducer) in introduced
Experiment Design
To test our hyposthesis, we needed to construct a circuit that has a promoter, a riboswitch, a reporter, and a terminator. We chose to use the theophylline riboswitch as it suited our requirements.
When the full sequence outlined above is transformed into the bacteria, it waits, inactivated, for the right small molecule inducer, in this case, theophylline. When theophylline is added, it will induce the riboswitch to fold differently to allow the translation of the downstream gene, without waiting for transcription.
By comparing the flourescence intensity data (the speed of GFP production), we can determine the difference in time between the traditional method of inducing promoters, to our method of inducing mRNA.
Since the sequence length of this riboswitch is relatively short, we decided to synthesize the riboswitch directly using two primers (which also contain the biobrick prefix and suffix):
- sequence
ggtgataccagcatcgtcttgatgcccttggcagcaccccgctgcaagacaacaag forward primer : gaattcgcggccgcttctagag ggtgataccagcatcgtcttgatgcccttggcag reverse primer : ctgcagcggccgctactagtacttgttgtcttgcagcggggtgctgccaagggcatcaagac
PCR expected result (99bp)
gaattcgcggccgcttctagagggtgataccagcatcgtcttgatgcccttggcag
gaattcgcggccgcttctagagggtgataccagcatcgtcttgatgcccttggcagcaccccgctgcaagacaacaagtactagtagcggccgctgcag
gtcttgatgcccttggcagcaccccgctgcaagacaacaagtactagtagcggccgctgcag
These two primers anneal atthis common region.
- We then digested the riboswitch PCR product and a plasmid containing the plasmid backbone pSB1A2 with the restriction enzymes XbaI and PstI.
- After gel extraction/PCR purification of the relevant parts, we ligated them and produced the biobrick part [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K411101 BBa_K411101].
- Performed a back insert of [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J04630 BBa_J04630(GFP+terminator)] (digested with XbaI and PstI) into [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K411101 BBa_K411101] (digested with SpeI and PstI) and formed the biobrick [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K411102 BBa_K411102].
- Performed another back insert of [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K411102 BBa_K411102] (digested with XbaI and PstI) into [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_R0010 BBa_R0010(lac promoter)] (digested with SpeI and PstI) and formed the biobrick [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K411103 BBa_K411103].
- Finally we tested this kind of E. coli. We add Theophylline to induce riboswitch and and translate fluorescent GFP.
Result
Reference
- [Svetlana V. Harbaugh et al.,08] Svetlana V. Harbaugh.et al. Riboswitch-based sensor in low optical background. Proc. of SPIE Vol. 7040
- [Lynch06] Sean A. Lynch, Shawn K. Desai, Hari Krishna Sajja, and Justin P. Gallivan1 (2006). A High-Throughput Screen for Synthetic Riboswitches Reveals Mechanistic Insights into Their Function. CELL DOI 10.1016/j.chembiol.
- [Topp07] Shana Topp and Justin P. Gallivan(2007)Guiding Bacteria with Small Molecules and RNA. JACS
- [Mandal03] Maumita Mandal, Benjamin Boese,Jeffrey E. Barrick, Wade C. Winkler, and Ronald R. Breaker1(2003). Riboswitches Control Fundamental Biochemical Pathways in Bacillus subtilis and Other Bacteria. Cell, Vol. 113, 577–586
 "
"