Team:UT-Tokyo/Sudoku lab note
From 2010.igem.org
(→Assay) |
(→Main construct) |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
= Main construct = | = Main construct = | ||
| - | [[Image:Sudoku_const_Main_5.png| | + | [[Image:Sudoku_const_Main_5.png|420px|Main construct]] |
If you want to know detail explanation, please read [https://2010.igem.org/Team:UT-Tokyo/Sudoku_construct Construct] section. | If you want to know detail explanation, please read [https://2010.igem.org/Team:UT-Tokyo/Sudoku_construct Construct] section. | ||
Revision as of 10:10, 27 October 2010


Sudoku
Introduction System Lab note [ June / July / August / September - October ] Result Reference
Lab note
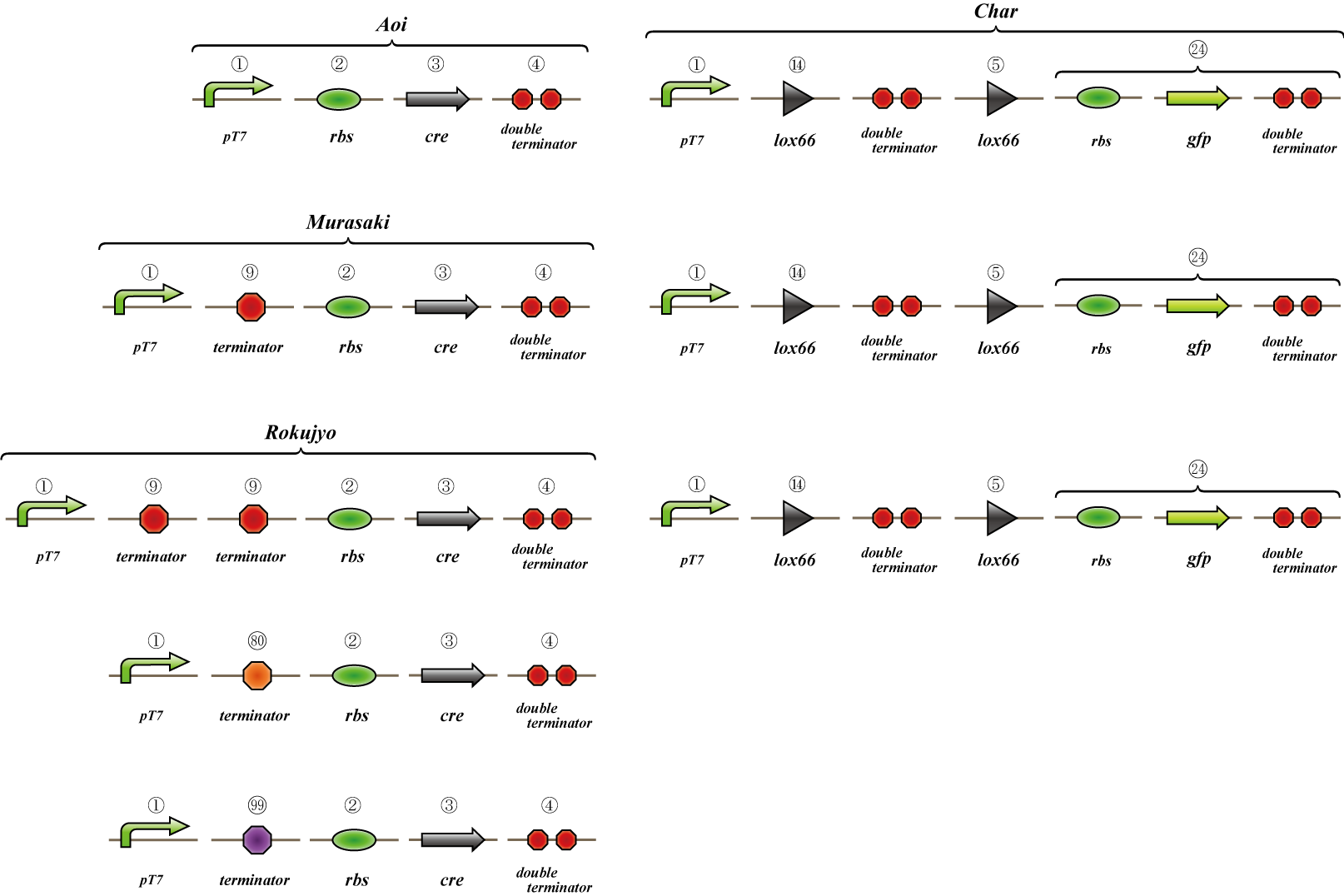
To make main construct, we made several assays.
3. #MS2 virus
4. #flpe
5. #Hin
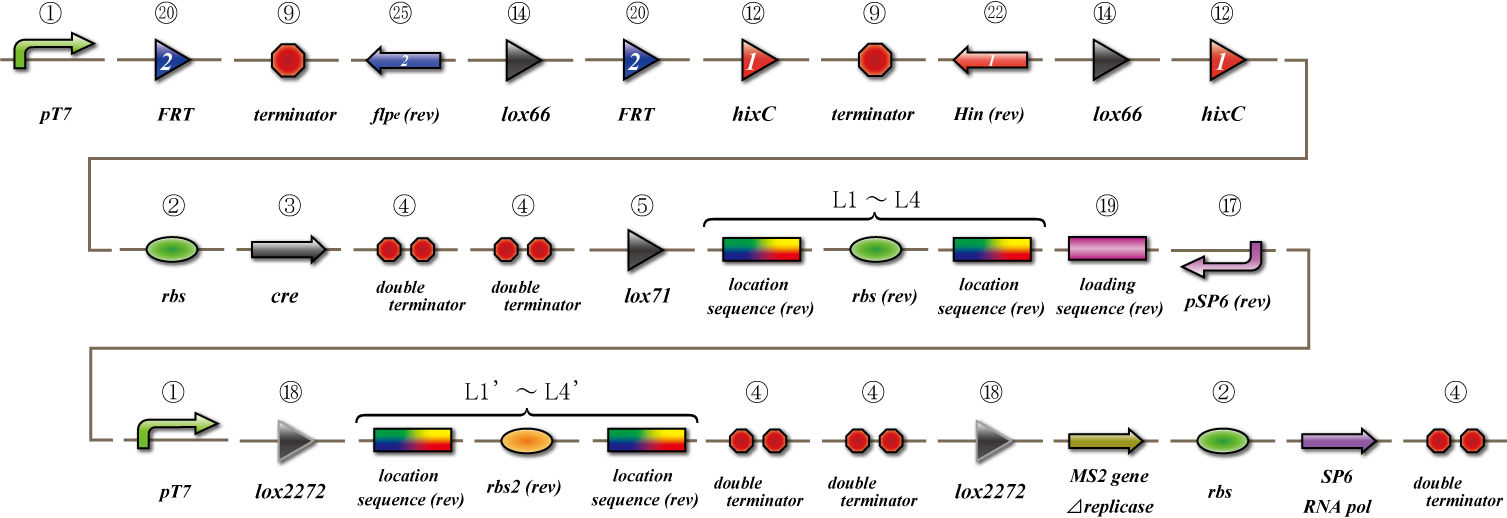
Main construct
If you want to know detail explanation, please read Construct section.
Assay
Terminator leak switch
Location sequence
The object of the assay is to test whether antisense RNA used in our construct works or not. In order to block the unnecessary information transformed by the virus from the other grid, we use antisense RNA to block ribosome to bind the region around the ribosome binding site (rbs) and prevent the expression of protein. In our construct, information is carried by virus and antisense RNA is transcribed constantly inside the cell. Once the unnecessary information was transformed, the antisense will come and shut out all the RNA chain excluded by virus. In this assay, we used pBAD as the promoter to start translating grid information which will be transformed by virus in our construct. The strength of the promoter depends on the concentration of arabinose. On the other hand, we used c-pro as the promoter to start translating antisense RNA. This c-pro is the strongest constitutive promoter submitted in igem parts. In assay I, we examined the relative strength of pBAD (with eight different concentration of arabinose) and c-pro. By using the proper concentration of arabinose which was determined by assay I, in assay II, we inspect observe whether our antisense RNA works or not. In these two assay, gfp was used as a reporter protein.
Pharge MS2
Parts making
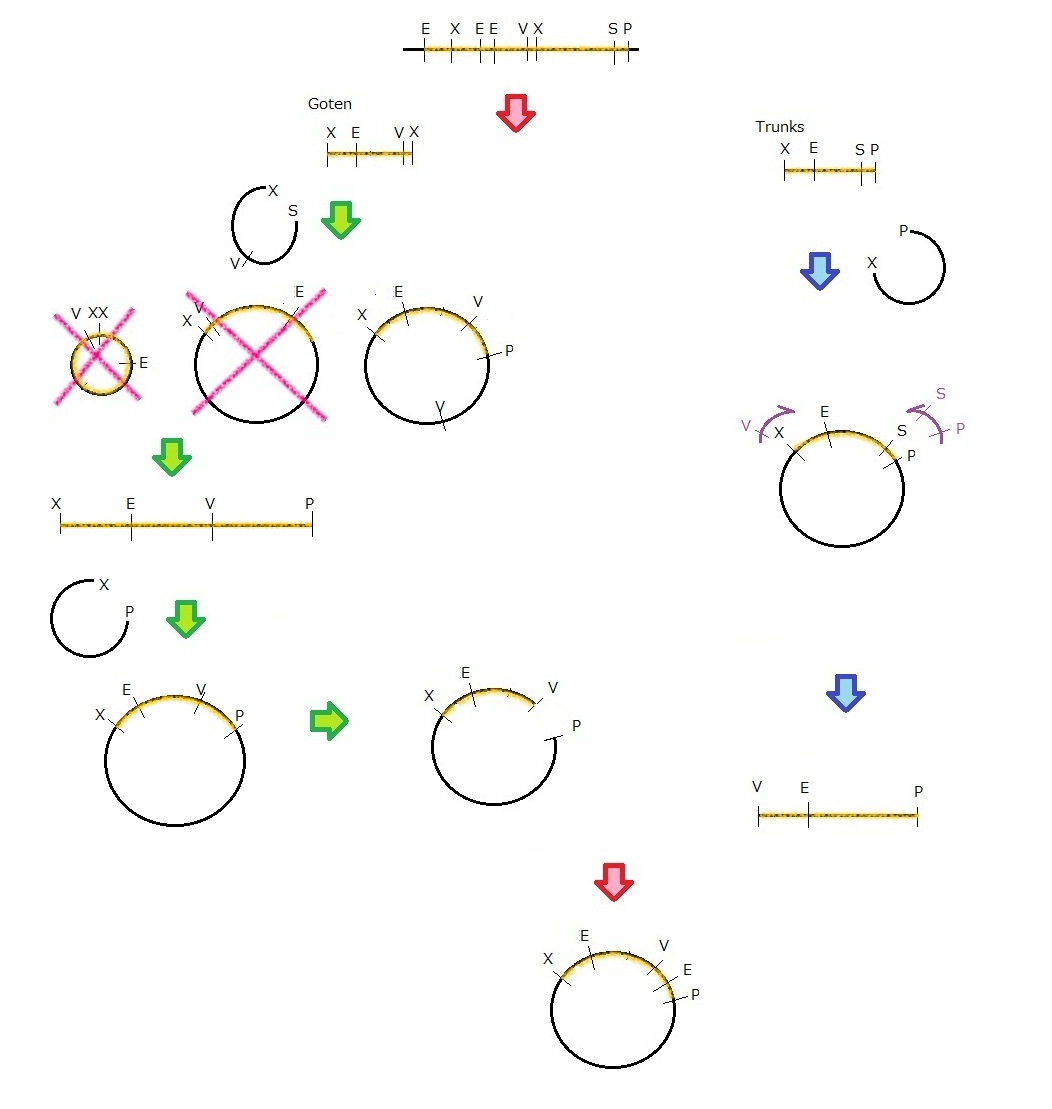
We get MS2 gene RT-PCR product. This original product include a lot of restricted enzyme site: two EcoRI site, two XbaI site and one VspI site.
To run our project, we don’t have to remove EcoRI site in the region. So we modified XbaI site by PCR as the following method:
1. We divided RT-PCR product into two parts by XP enzyme digestion:
E-X-E-E-V-X -> “Goten”
X-S-P -> “Tranks”
(named from the famous animation, "DRAGON BALL")
2. Insert is ligated with the vector, chloramphenicol-tolerance:
Goten -> EX vector
Tranks -> XP vector
3. Tranks -> PCR adding V-X region
4. Each part -> VP enzyme digestion, ligation each other
Expression check
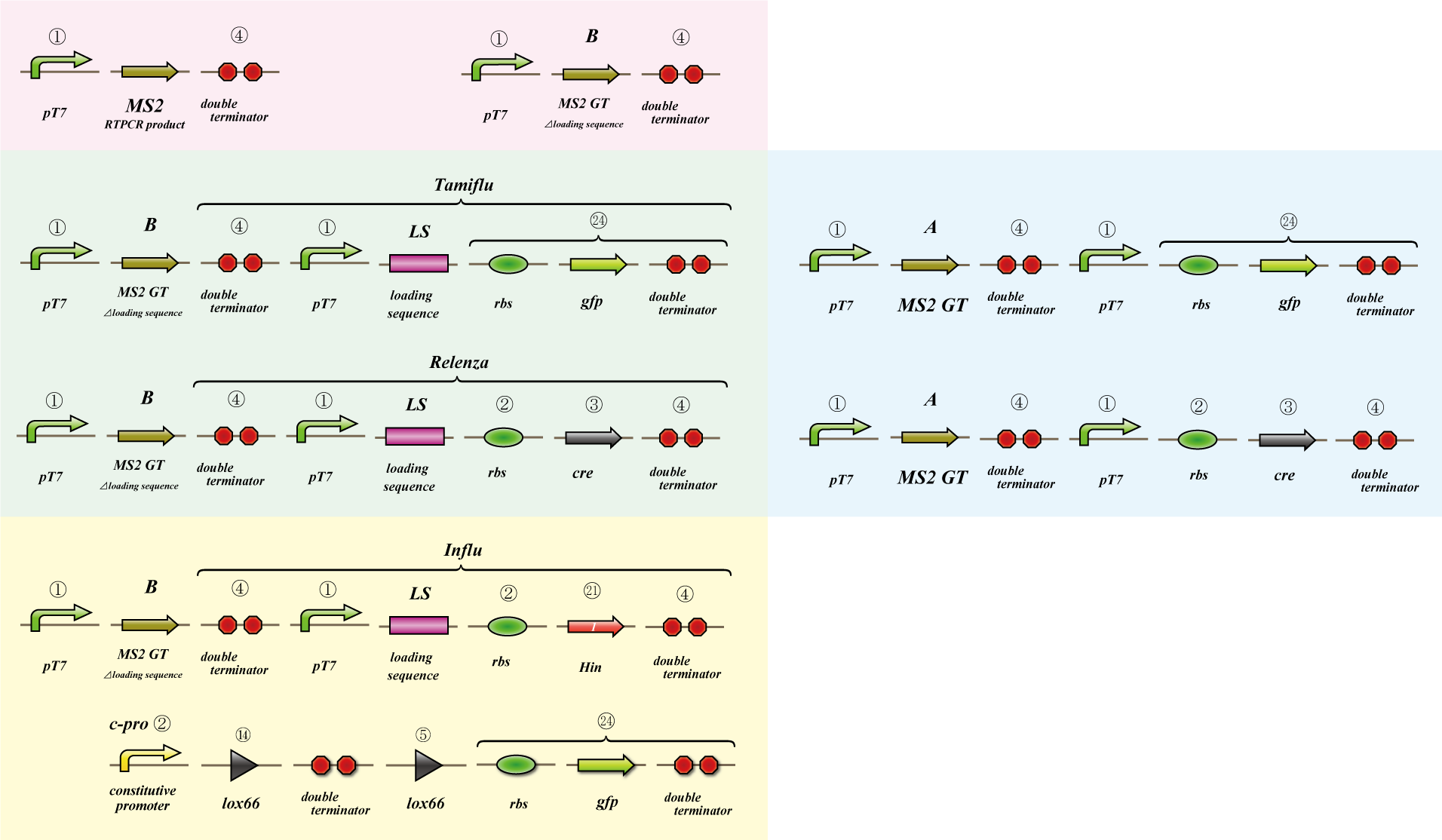
We use MS2 phage to transmit information of location and number. The expression of the phage should start after 4C3 leak switch turns on. MS2 phage transport RNA which has loding sequence, so we knock out self assembly and made our E.coli translate loading seaquence at another point. To check whether transportion go correctly, we made assay.
i. Phage expression assay (red region)
Check whether RT-PCR product can be translated into MS2 phage.
ii. Packaging assay (blue & green region)
MS2 phage package RNA which has loading sequence. Using this character, we check whether RNA which has loading sequence and other coding region (gfp, cre) can be packaged correctly.
iii. Infection assay (yellow & green region)
We make the assay, which express gfp only when cre protein is expressed correctly. By using this part, we check whether E.coli can be infected with the MS2 phage made in assay ii as the fluorescence of gfp.
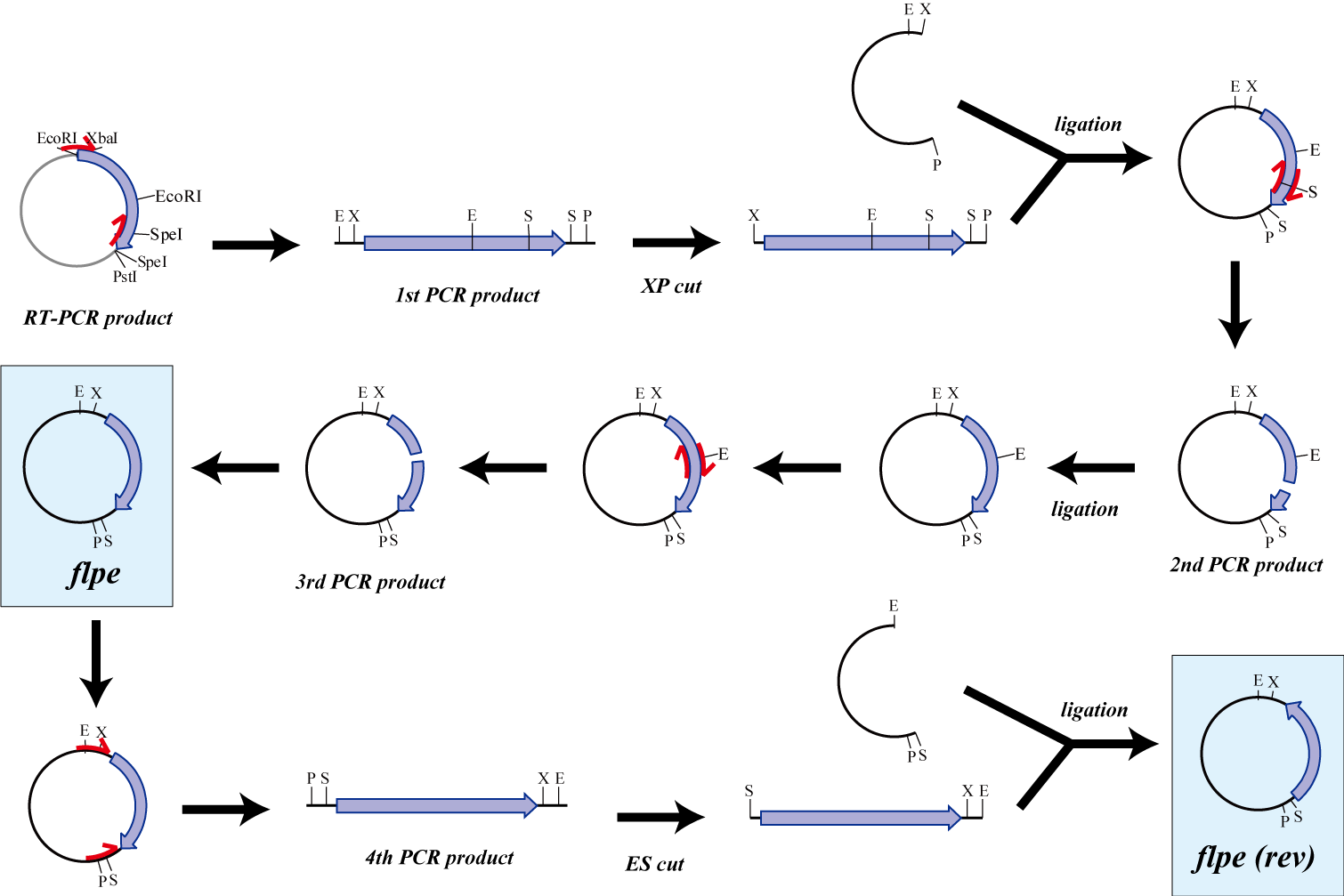
Pharge flpe
The original flpe include two restriction enzyme sites(EcoRI, SpeI).
We modified this flpe by PCR:
1st PCR : cloning
-> ligation with vector
-> 2nd PCR : modified SpeI site
-> 3rd PCR : modified EcoRI site
We use this part as the form of reverse, so we made this part reverse by PCR.
Expression check
To check whether flpe works correctly, we made assay shown in Fig.
The top construct is a nagative control. GFP can't be expressed because of the double terminators.
The bottom construct express GFP when flpe works correctly. When flpe is expressed correctly, flpe recognaize the frt site and double terminator which terminates the expression of gfp is removed, so GFP may be expressed.
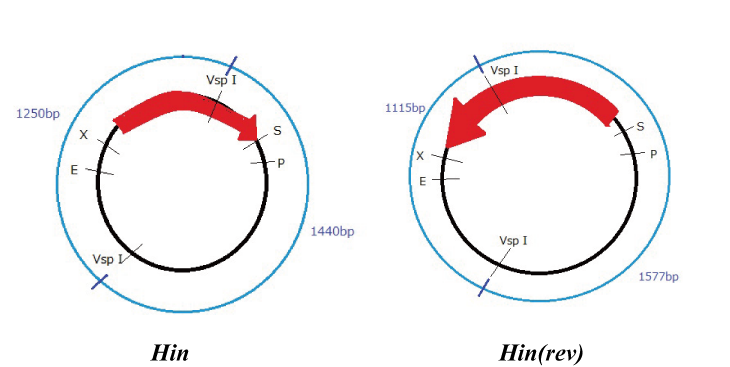
Hin
Parts making (reverse)
We get Hin parts from HQ (BBa_J31000).
We use this part as the form of reverse, so we made this part reverse by PCR.
To check PCR is done correctly, we did VspI digestion.
Expression check
To check whether flpe works correctly, we made assay shown in Fig, similar to the assay of flpe check.
The top construct is a nagative control. GFP can't be expressed because of the double terminators.
The bottom construct express GFP when Hin works correctly. When Hin is expressed correctly, Hin recognaize the hix site and double terminator which terminates the expression of gfp is removed, so GFP may be expressed.
Parts list
| Number | Name | Link to BioBrick | Plate coordinate | Vector | Code length |
| 1 | T7 promoter |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_I712074 BBa_I712074] | plate1-6N | pSB1AK8 | 46bp |
| 2 | rbs |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0030 BBa_B0030] | plate1-1H | pSB1A2 | 15bp |
| 3 | cre recombinase |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_J61047 BBa_J61047] | plate1-5D | pSB1A2 | 1037bp |
| 4 | double terminator |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0014 BBa_B0014] | plate2-24C | pSB1AK3 | 95bp |
| 5 | lox66 recombinase site |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_I718017 BBa_I718017] | plate1-17J | pSB1A2 | 34bp |
| 6 | Kan resistance (rev) |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_J31002 BBa_J31002] | plate1-2K | pSB1A2 | 816bp |
| 7 | rbs (rev) |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B0014 BBa_B0014] | plate1-1J | pSB1A2 | 15bp |
| 8 | lox71 recombinase site |
order-made | --- | --- | 34bp |
| 9 | single terminator |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_B1006 BBa_B1006] | plate1-4H | pSB1AK3 | 39bp |
| 10 | constant express promoter |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_J23119 BBa_J23119] | plate1-18A | pSB1A2 | 35bp |
| 11 | Tet resistance (rev) |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_J31006 BBa_J31006] | plate1-1N | pSB1A2 | 1191bp |
| 12 | hixC |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_J44000 BBa_J44000] | plate1-1B | pSB1A2 | 26bp |
| 13 | --- |
--- | --- | --- | --- |
| 14 | lox66 |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_I718016 BBa_I718016] | plate1-17H | pSB1A2 | 34bp |
| 15 | rbs-mRFP1-terminator |
[http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_I13507 BBa_I13507] | plate1-22O | pSB1A2 | 861bp |
| 16 | location sequence(old) |
order | --- | --- | --- |
| 17 | pSP6(rev) |
order | --- | --- | --- |
| 18 | lox2272 |
order | --- | --- | --- |
| 19 | loading sequence(rev) |
order | --- | --- | --- |
| 20 | frt |
[http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J61020 BBa_J61020] | From HQ | pSB1A2 | 34bp |
| 21 | hin(true) |
[http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_J31000 BBa_J31000] | From HQ | ??? | 573bp |
| 22 | hin(rev) |
--- | --- | ??? | 573bp |
| 23 | flpe |
--- | --- | --- | about 1.2kbp |
| 24 | gfp unit |
--- | --- | --- | about 1.2kbp |
| 25 | flpe(rev) |
--- | --- | --- | about 1.2kbp |
Detail protocols
Detail protocols about this is:
June.
July.
 "
"