Team:Heidelberg/Modeling
From 2010.igem.org
AlejandroHD (Talk | contribs) |
AlejandroHD (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
Apart from these two options, the user can personalize the binding site to meet their individual requirements. | Apart from these two options, the user can personalize the binding site to meet their individual requirements. | ||
| - | + | ===Seed types=== | |
[[Image:MiRNA_BS_examples_small.jpg]] | [[Image:MiRNA_BS_examples_small.jpg]] | ||
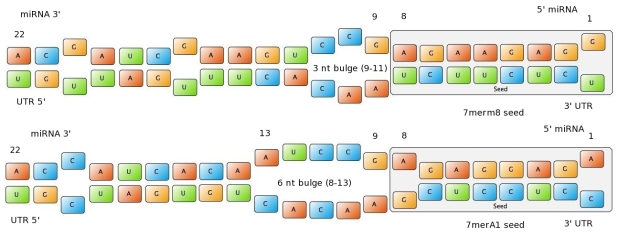
Figure 1: Interactions between two miRNAs and their binding sites. Examples to show different types of seeds. | Figure 1: Interactions between two miRNAs and their binding sites. Examples to show different types of seeds. | ||
| + | |||
In miBS designer, the user can choose between several types of seed for their binding site (ordered by increasing efficacy): | In miBS designer, the user can choose between several types of seed for their binding site (ordered by increasing efficacy): | ||
| Line 47: | Line 48: | ||
The percentages of abundance are calculated among conserved mammalian sites for a highly conserved miRNA (Friedman et al. 2008) | The percentages of abundance are calculated among conserved mammalian sites for a highly conserved miRNA (Friedman et al. 2008) | ||
| - | + | ===Supplementary region=== | |
In miBS designer, the user can choose among several types of supplementary sequences, starting with 3 matching nucleotides (14-16), increasing sequentially until 8 (13-20), and then total matching (from 13-22, leaving a bulge). In case the user needs some other specific supplementary region, he can customize the sequence by inputting the desired matching nucleotides. | In miBS designer, the user can choose among several types of supplementary sequences, starting with 3 matching nucleotides (14-16), increasing sequentially until 8 (13-20), and then total matching (from 13-22, leaving a bulge). In case the user needs some other specific supplementary region, he can customize the sequence by inputting the desired matching nucleotides. | ||
| - | + | ===AU content=== | |
In order to allow the user to improve the efficacy of their binding sites, miBS designer offers options to increase the AU content by adding adenine or uracil to positions around the matches (specifically in -1, 0, 1, 8, 9 and 10). The function is designed so that it varies the AU content without introducing new pairings. | In order to allow the user to improve the efficacy of their binding sites, miBS designer offers options to increase the AU content by adding adenine or uracil to positions around the matches (specifically in -1, 0, 1, 8, 9 and 10). The function is designed so that it varies the AU content without introducing new pairings. | ||
| - | + | ===Sticky ends=== | |
In order to facilitate the task of introducing the binding site into a plasmid, the user can add sequences to both ends of the binding site. Initially, the user can choose among the RFC-12 standard for biobricks BB2, the XmaI/XhoI restriction enzymes used IN WHAT??, or some custom sequences input by the user. In the last case, the output sequences will not be directly ready for cloning: the user has to either digest the construction prior to ligation, or to process the primers before ordering them to remove the extra nucleotides. | In order to facilitate the task of introducing the binding site into a plasmid, the user can add sequences to both ends of the binding site. Initially, the user can choose among the RFC-12 standard for biobricks BB2, the XmaI/XhoI restriction enzymes used IN WHAT??, or some custom sequences input by the user. In the last case, the output sequences will not be directly ready for cloning: the user has to either digest the construction prior to ligation, or to process the primers before ordering them to remove the extra nucleotides. | ||
Revision as of 09:36, 26 October 2010

|
|
||||||||||||
 "
"