Team:UNIPV-Pavia/Material Methods/Instruments
From 2010.igem.org
(→NANODROP ND 1000 spectrophotometer) |
|||
| (16 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
<!-- Contenuti --> | <!-- Contenuti --> | ||
| - | <td valign="top" | + | <td valign="top" > |
<table border="0" align="center" width="100%"><tr><td align="justify" valign="top" style="padding:20px"> | <table border="0" align="center" width="100%"><tr><td align="justify" valign="top" style="padding:20px"> | ||
| - | <html><p align="center"><font size=" | + | <html><p align="center"><font size="4"><b>INSTRUMENTS</b></font></p></html><hr><br><br> |
<html><a name="indice"/></html> | <html><a name="indice"/></html> | ||
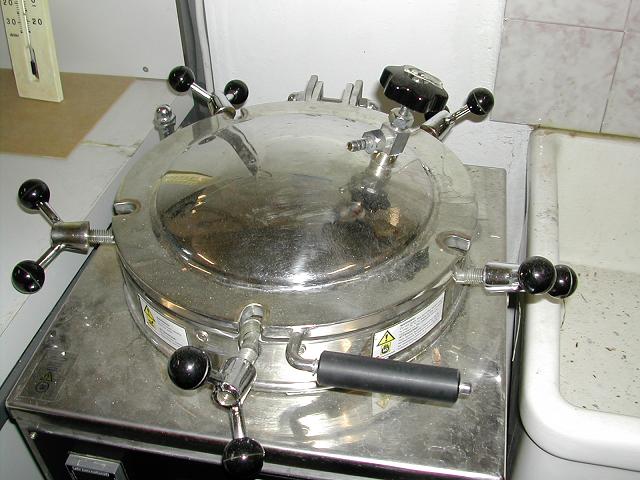
==AUTOCLAVE== | ==AUTOCLAVE== | ||
| - | <table><tr><td valign="top"> | + | <table width="100%"><tr><td valign="top" align="left"> |
<html><p align="justify"> | <html><p align="justify"> | ||
| - | An autoclave is a device to sterilize equipment and supplies by subjecting them to high pressure saturated steam at | + | An autoclave is a device to sterilize equipment and supplies by subjecting them to high pressure saturated steam at 121°C or more, typically for 15 to 20 minutes depending on the size of the load and the contents. It was invented by Charles Chamberland in 1879, although a precursor known as the <i>steam digester</i> was created by Denis Papin in 1679. The name comes from Greek <i>auto</i>, ultimately meaning <i>self</i>, and Latin <i>clavis</i> meaning <i>key</i> — a self-locking device. |
</p></html> | </p></html> | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
| - | <td width="20%" valign='top'> | + | <td width="20%" valign='top' align="right"> |
| - | {| border=" | + | {| border="0" |
| [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_autoclave.jpg | 250px |right|Autoclave]] | | [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_autoclave.jpg | 250px |right|Autoclave]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
|} | |} | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
| Line 49: | Line 33: | ||
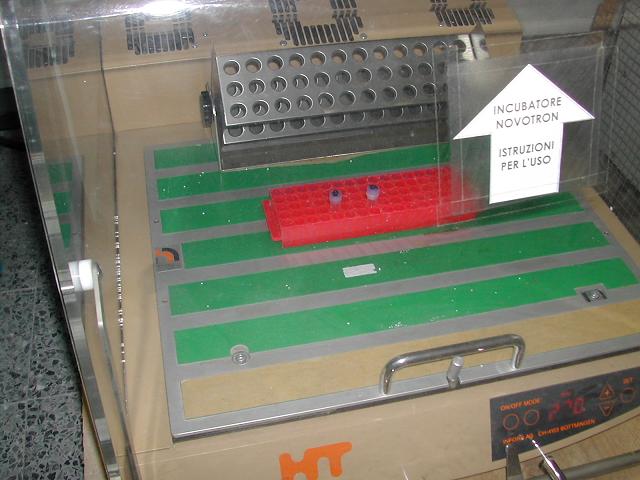
==INCUBATOR FOR PLATES== | ==INCUBATOR FOR PLATES== | ||
| - | <table><tr><td valign="top"> | + | <table width="100%"><tr><td valign="top" align="left"> |
<html><p align="justify"> | <html><p align="justify"> | ||
This is a oven in which plates are kept at 37 C to grow bacteria. | This is a oven in which plates are kept at 37 C to grow bacteria. | ||
</p></html> | </p></html> | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
| - | <td width="20%" valign='top'> | + | <td width="20%" valign='top' align="right"> |
| - | {| border=" | + | {| border="0" |
| [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_incubatorforplates.jpg | 250px |right|Incubator for plates]] | | [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_incubatorforplates.jpg | 250px |right|Incubator for plates]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 65: | Line 49: | ||
==INCUBATOR AND SHAKER FOR LIQUID CULTURES== | ==INCUBATOR AND SHAKER FOR LIQUID CULTURES== | ||
| - | <table><tr><td valign="top"> | + | <table width="100%"><tr><td valign="top" align="left"> |
<html><p align="justify"> | <html><p align="justify"> | ||
| - | This is a oven where bacteria are kept to grow. In this case you can define temperature | + | This is a oven where bacteria are kept to grow. In this case you can define temperature and rpm. |
</p></html> | </p></html> | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
| - | <td width="20%" valign='top'> | + | <td width="20%" valign='top' align="right"> |
| - | {| border=" | + | {| border="0" |
| [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_incubatorshaker.jpg | 250px |right|Incubator and shaker for liquid cultures]] | | [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_incubatorshaker.jpg | 250px |right|Incubator and shaker for liquid cultures]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
|} | |} | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
| Line 97: | Line 65: | ||
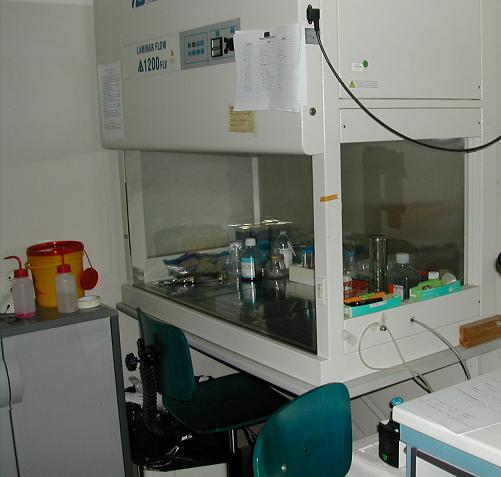
==HOOD== | ==HOOD== | ||
| - | <table><tr><td valign="top"> | + | <table width="100%"><tr><td valign="top" align="left"> |
<html><p align="justify"> | <html><p align="justify"> | ||
It is a laminar flow hood for handling highly toxic products. | It is a laminar flow hood for handling highly toxic products. | ||
</p></html> | </p></html> | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
| - | <td width="20%" valign='top'> | + | <td width="20%" valign='top' align="right"> |
| - | {| border=" | + | {| border="0" |
| [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_hood.jpg | 250px |right|Hood]] | | [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_hood.jpg | 250px |right|Hood]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 113: | Line 81: | ||
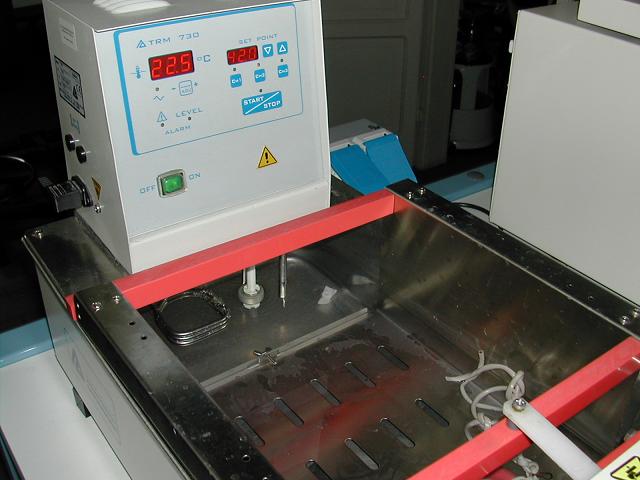
==WATER BATH== | ==WATER BATH== | ||
| - | <table><tr><td valign="top"> | + | <table width="100%"><tr><td valign="top" align="left"> |
<html><p align="justify"> | <html><p align="justify"> | ||
| - | It is a bath in which water is heated to high temperatures for gel extraction and | + | It is a bath in which water is heated to high temperatures for gel extraction and heath shock during bacterial transformation. |
</p></html> | </p></html> | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
| - | <td width="20%" valign='top'> | + | <td width="20%" valign='top' align="right"> |
| - | {| border=" | + | {| border="0" |
| [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_waterbath.jpg | 250px |right|Water bath]] | | [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_waterbath.jpg | 250px |right|Water bath]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 129: | Line 97: | ||
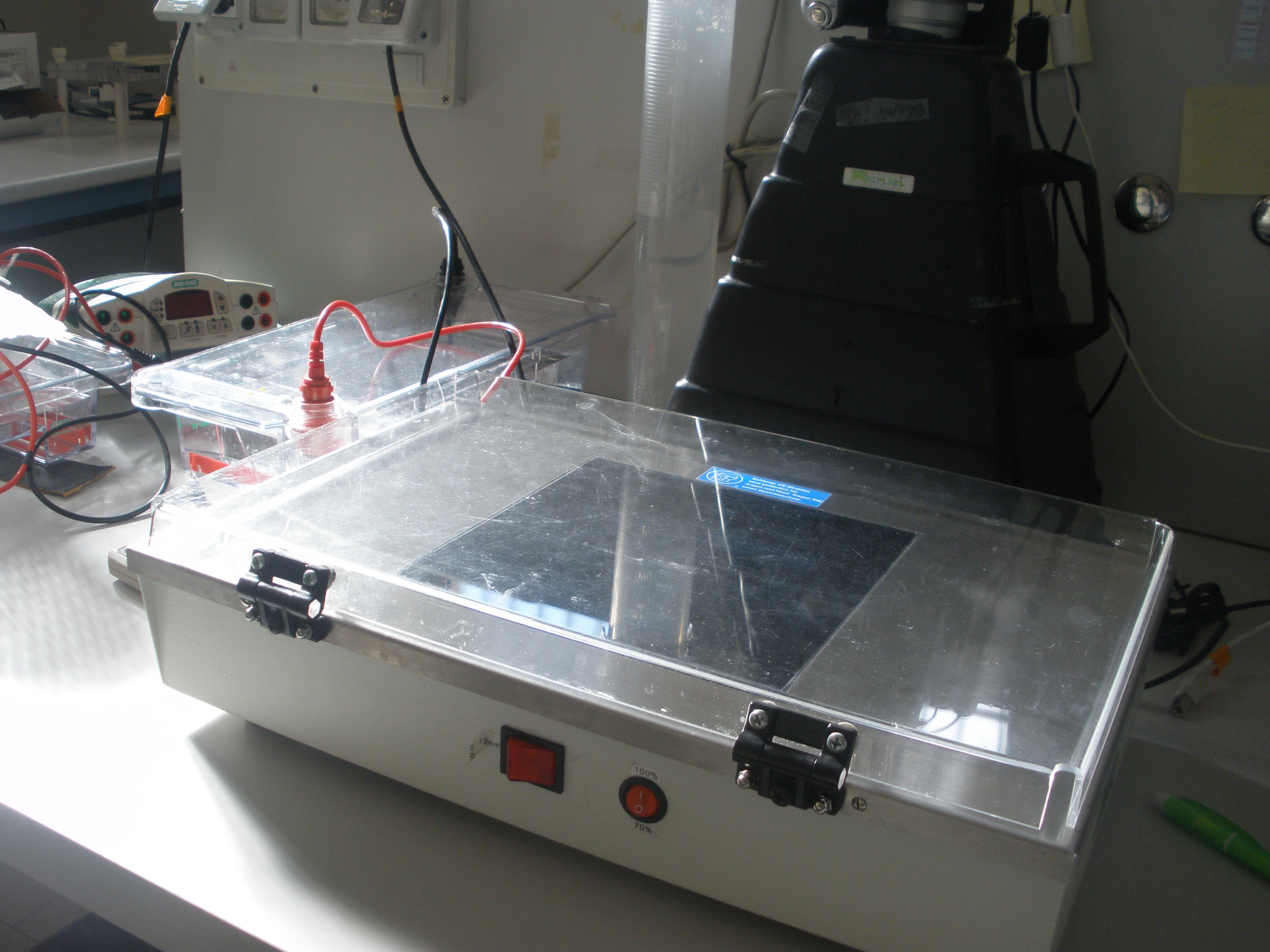
==INSTRUMENTS FOR ELECTROPHORESIS== | ==INSTRUMENTS FOR ELECTROPHORESIS== | ||
| - | <table><tr><td valign="top"> | + | <table width="100%"><tr><td valign="top" align="left"> |
<html><p align="justify"> | <html><p align="justify"> | ||
| - | Gel electrophoresis apparatus - | + | Gel electrophoresis apparatus - Agarose gel is placed in this TBE buffer filled box and electrical field is applied via the power supply to the rear. The negative terminal is the black one while the positive is the red one. In this way DNA, that is naturally negatively charged, migrates to the positive pole. |
</p></html> | </p></html> | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
| - | <td width="20%" valign='top'> | + | <td width="20%" valign='top' align="right"> |
| - | {| border=" | + | {| border="0" |
| [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_electrophoresis.jpg | 250px |right|Instruments for electrophoresis]] | | [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_electrophoresis.jpg | 250px |right|Instruments for electrophoresis]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 145: | Line 113: | ||
==GEL IMAGE ACQUISITION SYSTEM== | ==GEL IMAGE ACQUISITION SYSTEM== | ||
| - | <table><tr><td valign="top"> | + | <table width="100%"><tr><td valign="top" align="left"> |
<html><p align="justify"> | <html><p align="justify"> | ||
It is a UV system with camera used to acquire gel run snapshots. | It is a UV system with camera used to acquire gel run snapshots. | ||
</p></html> | </p></html> | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
| - | <td width="20%" valign='top'> | + | <td width="20%" valign='top' align="right"> |
| - | {| border=" | + | {| border="0" |
| [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_gelacq.jpg | 250px |right|Gel image acquisition system]] | | [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_gelacq.jpg | 250px |right|Gel image acquisition system]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 160: | Line 128: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
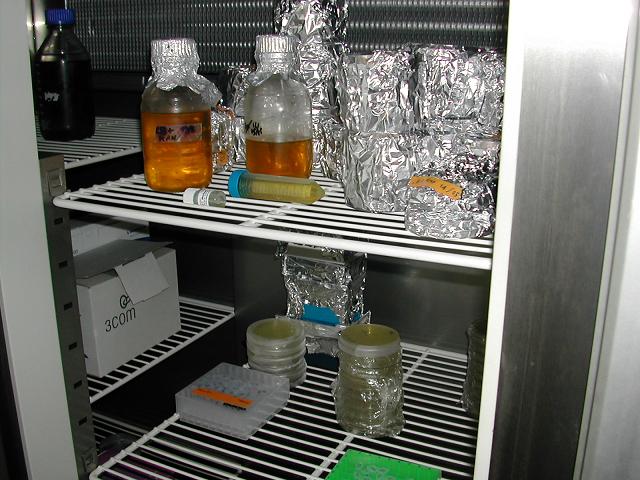
| - | == | + | ==COLD INSTRUMENTS== |
| - | <table><tr><td valign="top"> | + | <table width="100%"><tr><td valign="top" align="left"> |
<html><p align="justify"> | <html><p align="justify"> | ||
| - | + | We have freezers where Dna and bacterial cultures are stocked. In particular we have two -20 C freezers to stock DNA and one -80 C freezer to stock bacteria.<br> | |
| + | We have also a fridge to stock plates and LB medium | ||
</p></html> | </p></html> | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
| - | <td width="20%" valign='top'> | + | <td width="20%" valign='top' align="right"> |
| - | {| border=" | + | {| border="0" |
| - | | [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_freezer.jpg | 250px |right|Freezer | + | | [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_freezer.jpg | 250px |right|Freezer]] |
| + | |} | ||
| + | {| border="0" | ||
| + | | [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_fridge.jpg | 250px |right|Fridge]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
| Line 176: | Line 148: | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | == | + | ==NANODROP ND 1000 spectrophotometer== |
| - | <table><tr><td valign="top"> | + | <table width="100%"><tr><td valign="top" align="left"> |
<html><p align="justify"> | <html><p align="justify"> | ||
| - | + | Nanodrop is a really helpfull instrument used to measure concentration of DNA in a micro-volume of sample and OD in cell cultures.</p></html> | |
| - | </p></html> | + | |
</td> | </td> | ||
| - | <td width="20%" valign='top'> | + | <td width="20%" valign='top' align="right"> |
| - | {| border=" | + | {| border="0" |
| - | | [[Image: | + | | [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_nanodrop.gif | 150px |right|Nanodrop]] |
|} | |} | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
| Line 193: | Line 164: | ||
==TECAN Infinite 2000== | ==TECAN Infinite 2000== | ||
| - | <table><tr><td valign="top"> | + | <table width="100%"><tr><td valign="top" align="left"> |
<html><p align="justify"> | <html><p align="justify"> | ||
Tecan Infinite F200 is a multifunctional microplate filter-based reader with injector option, that provides high performance for the vast majority of microplate applications and research. It has been designed as a general purpose laboratory instrument for professional use, supporting common 6 to 384-well microplates. | Tecan Infinite F200 is a multifunctional microplate filter-based reader with injector option, that provides high performance for the vast majority of microplate applications and research. It has been designed as a general purpose laboratory instrument for professional use, supporting common 6 to 384-well microplates. | ||
This instrument allows long incubation of the microplate, the chance to set the shaking movements, the duration of all operations, including cycles, and the dispensation of liquid material in the wells. These actions are managed by a user interface operated by i-Control software, ranging from scheduling experiments to the cleaning of injectors. | This instrument allows long incubation of the microplate, the chance to set the shaking movements, the duration of all operations, including cycles, and the dispensation of liquid material in the wells. These actions are managed by a user interface operated by i-Control software, ranging from scheduling experiments to the cleaning of injectors. | ||
| - | We used this instrument for the following measurement techniques: | + | We used this instrument for the following measurement techniques: </p></html> |
| - | + | * fluorescence intensity; | |
| - | + | * absorbance. | |
| - | </p></html> | + | |
</td> | </td> | ||
| - | <td width="20%" valign='top'> | + | <td width="20%" valign='top' align="right"> |
| - | {| border=" | + | {| border="0" |
| [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_tecan.jpg | 250px |right|TECAN Infinite 2000]] | | [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_tecan.jpg | 250px |right|TECAN Infinite 2000]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
| + | <div align="right"><small>[[#indice|^top]]</small></div> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==BACTERIA ROOM AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY ROOM== | ||
| + | <table width="100%"><tr><td valign="top" align="left"> | ||
| + | <html><p align="justify"> | ||
| + | The Molecular Biology room is the place in which we treat DNA.<br> | ||
| + | The Bacteria room is the place in which we work with bacteria. In this room the temperature is 37°C for growth of bacterial culture. | ||
| + | </p></html> | ||
| + | {| border="0" | ||
| + | | [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_bacteriaroom.jpg | thumb | Bacteria room | 250px | right | Bacteria room]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | </td> | ||
| + | <td width="20%" valign='top' align="right"> | ||
| + | {| border="0" | ||
| + | | [[Image:UNIPV_Pavia_molbioroom.jpg | thumb | Molecular biology room | 250px | right | Molecular biology room]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
</td> | </td> | ||
Latest revision as of 21:11, 20 October 2010
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 "
"