Team:EPF Lausanne/Project immuno
From 2010.igem.org
(→B: The P-proteins are not expressed) |
|||
| (7 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
==A: The Immunotoxin is expressed and appears in the supernatant== | ==A: The Immunotoxin is expressed and appears in the supernatant== | ||
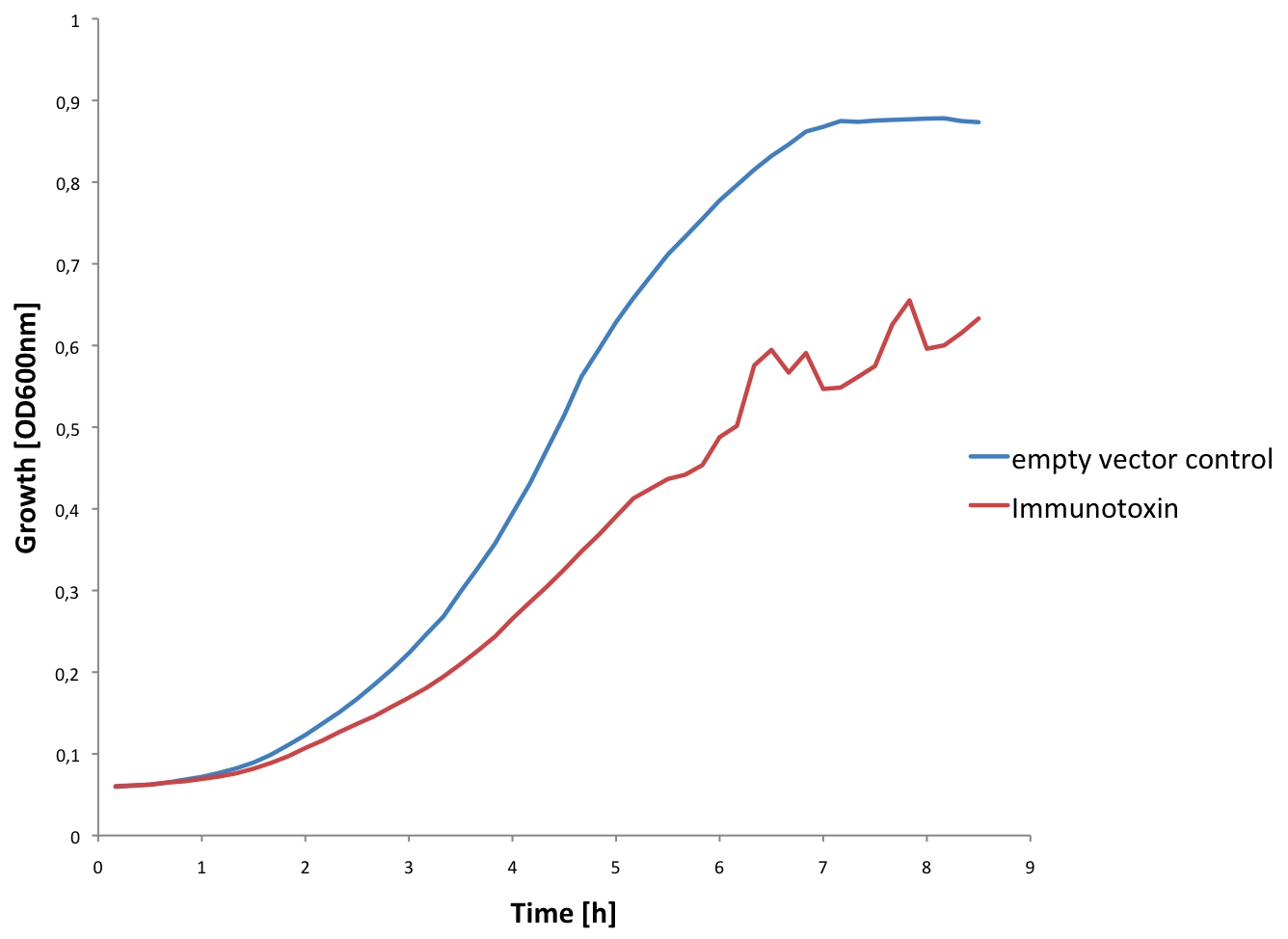
[[Image:EPFL Immuno growth.jpg|300px|thumb|right| <b>Growth curve of ''E. coli'' expressing the Immunotoxin:</b> In blue, we can see the growth curve of ''E. coli'' containing the empty C3 plasmid. In red, we can see the growth of ''E. coli'' transformed with the C3 plasmid containing the Immunotoxin sequence. We could conclude that the expression of the Immunotoxin in high concetrations may prevent ''E. coli'' from growing. ]] | [[Image:EPFL Immuno growth.jpg|300px|thumb|right| <b>Growth curve of ''E. coli'' expressing the Immunotoxin:</b> In blue, we can see the growth curve of ''E. coli'' containing the empty C3 plasmid. In red, we can see the growth of ''E. coli'' transformed with the C3 plasmid containing the Immunotoxin sequence. We could conclude that the expression of the Immunotoxin in high concetrations may prevent ''E. coli'' from growing. ]] | ||
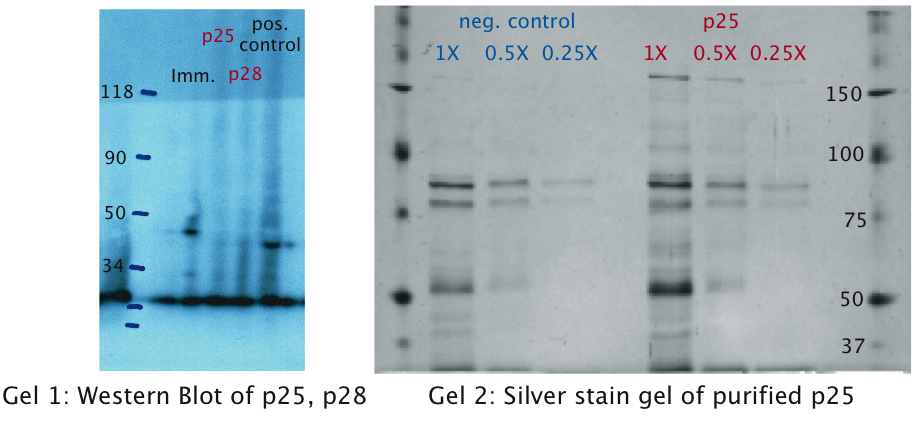
| - | We tested expression of the immunotoxin in ''E. coli'' (see [https://2010.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:EPF_Lausanne/Project/Materials_Methods Materials and Methods] for details). In a western blot analysis of whole cell lysates we could see bands corresponding to full length immunotoxin and possibly degraded fragments of the protein (see | + | We tested expression of the immunotoxin in ''E. coli'' (see [https://2010.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:EPF_Lausanne/Project/Materials_Methods Materials and Methods] for details). In a western blot analysis of whole cell lysates we could see bands corresponding to full length immunotoxin and possibly degraded fragments of the protein (see gel image below). |
| + | |||
| + | The immunotoxin contains a PelB sequence that targets it for secretion into the periplasm. We concentrated the supernatant of both the immunotoxin and a control culture by running it through a filtering device with a 5 kDa cut-off. Running a western blot with these samples (see gel image below) we verified that the immunotoxin was also found in the supernatant. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We observed that the cells containing the immunotoxin plasmid grew a lot slower than the control (see figure). This is probably due to the fact that the cells are producing the immunotoxin. Furthermore at high concentrations the immunotoxin might lyse the cells. | ||
[[Image:EPFL Gel1 western.jpg|400px|thumb|center| <b>Gel1 (Lysates):</b> We can see distinct molecular fragments in the immunotoxin lane: The upper fragments (marked with red and purple arrows) match the molecular size of the immunotoxin of about 39 kDa. For the shorter of the two fragments the export tag pelB may have been cut off. The smaller sized fragment (green arrow) of about 20 kDa is most probably part of the degraded immunotoxin. | [[Image:EPFL Gel1 western.jpg|400px|thumb|center| <b>Gel1 (Lysates):</b> We can see distinct molecular fragments in the immunotoxin lane: The upper fragments (marked with red and purple arrows) match the molecular size of the immunotoxin of about 39 kDa. For the shorter of the two fragments the export tag pelB may have been cut off. The smaller sized fragment (green arrow) of about 20 kDa is most probably part of the degraded immunotoxin. | ||
| - | <b>Gel2 (Supernatants):</b> A fragment of the correct size is detected in the supernatant. The smaller fragments (green and yellow arrows) probably correspond to smaller parts of the degraded immunotoxin. ]] | + | <b>Gel2 (Supernatants):</b> A fragment of the correct size is detected in the supernatant. The smaller fragments (green and yellow arrows) probably correspond to smaller parts of the degraded immunotoxin. The band present in all lanes corresponds to a biotinylated protein which is detected by the secondary antibodies.]] |
==B: The P-proteins are not expressed == | ==B: The P-proteins are not expressed == | ||
| - | The same experiments were conducted for the p-proteins [https://2010.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:EPF_Lausanne/Project/Background p25 and p28]. No bands were detected on the western blots (see figure) which leads us to the conclusion that these proteins were only very weakly expressed or not at all. This might be explained by the fact that we took the native sequence from <i>Plasmodium falciparum </i>. The genome of <i>Plasmodium falciparum </i> is very A-T-rich ([http://areslab.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgGateway UCSC Malaria Genome Browser]). | + | The same experiments were conducted for the p-proteins [https://2010.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:EPF_Lausanne/Project/Background p25 and p28]. No bands were detected on the western blots (see figure) which leads us to the conclusion that these proteins were only very weakly expressed or not at all. This might be explained by the fact that we took the native sequence from <i>Plasmodium falciparum</i>. The genome of <i>Plasmodium falciparum</i> is very A-T-rich ([http://areslab.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgGateway UCSC Malaria Genome Browser]). |
| + | |||
We think that expression of p25 and p28 may be improved by codon optimizing it for expression in bacteria like ''E. coli'' and ''Asaia'' as we did with the immunotoxin. | We think that expression of p25 and p28 may be improved by codon optimizing it for expression in bacteria like ''E. coli'' and ''Asaia'' as we did with the immunotoxin. | ||
Additional to the Western Blots, to rule out the possibility that concentration was too low, we attempted a protein purification (following the [http://openwetware.org/wiki/Knight:Purification_of_His-tagged_proteins/Denaturing Knight protocol]) from a large culture volume (see figure) using Ni-NTA columns. | Additional to the Western Blots, to rule out the possibility that concentration was too low, we attempted a protein purification (following the [http://openwetware.org/wiki/Knight:Purification_of_His-tagged_proteins/Denaturing Knight protocol]) from a large culture volume (see figure) using Ni-NTA columns. | ||
| Line 64: | Line 69: | ||
| - | [[Image:EPFL Silver stain wiki.jpg|700px|thumb|center| <b>Gel1 (Western Blot):</b> There are no fragments detected neither for p25 nor for p28. The fragment detected for the positive control around the weight expected verifies the success of the analysis | + | [[Image:EPFL Silver stain wiki.jpg|700px|thumb|center| <b>Gel1 (Western Blot):</b> There are no fragments detected neither for p25 nor for p28. The fragment detected for the positive control around the weight expected verifies the success of the analysis. |
| - | <b>Gel2 (Silver Stain):</b> We tried to purify the proteins in order to exclude the possibility that the proteins were not detected due to low concentration. Protein purification was followed by silver stain analysis. Again, no bands were detected on the gel]] | + | <b>Gel2 (Silver Stain):</b> We tried to purify the proteins in order to exclude the possibility that the proteins were not detected due to low concentration. Protein purification was followed by silver stain analysis. Again, no bands were detected on the gel.]] |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
=References= | =References= | ||
Latest revision as of 00:50, 28 October 2010


Contents |
Proteins
We have chosen two different ways to target the parasite P.falciparum and prevent the malaria transmission through mosquitos. Our engineered bacteria could express either an immunotoxin, or two "p-proteins", or even both for maximum efficiency. We tried to express all of these proteins using the C3 plasmid incorporating the strong promoter, a constitutive sequence for greater level of expression.
The Immunotoxin is one of our tools to block transmission of malaria parasite in mosquitos. It is composed of two main parts : The first one is a single-chain antibody fragment (scFv) directed to Pbs2l, which is a surface membrane protein of Plasmodium berghei. The second part is a lytic peptide, Shiva-1, which acts by forming “pores” on the parasite’s membrane. The immunotoxin is supposed to specifically target and lyse the parasite.
In parallel to the immunotoxin we thought of a different way of blocking the P.falciparum by using
P25 and P28 which belong to a class of important proteins expressed on the membrane of the Plasmodium. We called them the "P-proteins". They are mainly expressed on the mosquito-stage of the parasite (ookinete).
The Plasmodium normally uses these P-protein to interact with the epithelium in order to go through it.
Now if Asaia starts to produce a high amout of these proteins, the interactions will be disrupted and the plasmodium will not propagate through the mosquito's epithelium.
Results
A: The Immunotoxin is expressed and appears in the supernatant
We tested expression of the immunotoxin in E. coli (see Materials and Methods for details). In a western blot analysis of whole cell lysates we could see bands corresponding to full length immunotoxin and possibly degraded fragments of the protein (see gel image below).
The immunotoxin contains a PelB sequence that targets it for secretion into the periplasm. We concentrated the supernatant of both the immunotoxin and a control culture by running it through a filtering device with a 5 kDa cut-off. Running a western blot with these samples (see gel image below) we verified that the immunotoxin was also found in the supernatant.
We observed that the cells containing the immunotoxin plasmid grew a lot slower than the control (see figure). This is probably due to the fact that the cells are producing the immunotoxin. Furthermore at high concentrations the immunotoxin might lyse the cells.

B: The P-proteins are not expressed
The same experiments were conducted for the p-proteins p25 and p28. No bands were detected on the western blots (see figure) which leads us to the conclusion that these proteins were only very weakly expressed or not at all. This might be explained by the fact that we took the native sequence from Plasmodium falciparum. The genome of Plasmodium falciparum is very A-T-rich ([http://areslab.ucsc.edu/cgi-bin/hgGateway UCSC Malaria Genome Browser]).
We think that expression of p25 and p28 may be improved by codon optimizing it for expression in bacteria like E. coli and Asaia as we did with the immunotoxin. Additional to the Western Blots, to rule out the possibility that concentration was too low, we attempted a protein purification (following the [http://openwetware.org/wiki/Knight:Purification_of_His-tagged_proteins/Denaturing Knight protocol]) from a large culture volume (see figure) using Ni-NTA columns.
References
- [http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6T29-42JHDJD-9&_user=10&_coverDate=03%2F31%2F2001&_rdoc=1&_fmt=high&_orig=search&_origin=search&_sort=d&_docanchor=&view=c&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=5f4b78b08a1846e241faaed33bc76cb3&searchtype=a 1. Shigeto Yoshida, Bacteria expressing single-chain immunotoxin inhibit malaria parasite development in mosquitoes, Molecular and Biochemical Parasitology (2001)]
- [http://www.nature.com/emboj/journal/v20/n15/full/7593895a.html 2. Ana M. Tomas, Gabriele Margos, Robert E. Sinden, P25 and P28 proteins of the malaria ookinete surface have multiple and partially redundant functions, The EMBO Journal (2001)]
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1951121/?tool=pubmed 3. Ajay K. Saxena, Yimin Wu, and David N. Garboczi, Plasmodium P25 and P28 Surface Proteins: Potential Transmission-Blocking Vaccines, Eukaryot Cell (2007)]
- [http://www.nature.com/nsmb/journal/v13/n1/full/nsmb1024.html 4. Ajay et al., The essential mosquito-stage P25 and P28 proteins from Plasmodium form tile-like triangular prisms, natures structural & molecular biology, 2005]

 "
"