Team:Kyoto/Project/Goal C
From 2010.igem.org
(→Experiment 2:Check the role of TMD1 of S gene) |
(→Goal C: Characterization of the anti-killer gene) |
||
| (23 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
==Goal C: Characterization of the anti-killer gene== | ==Goal C: Characterization of the anti-killer gene== | ||
===Introduction=== | ===Introduction=== | ||
| - | + | As far as we know, there are two anti-killer genes against the killer gene (lysis cassette), S107 and S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub>. | |
| - | + | S107 is expressed by S gene encoded by lysis cassette and S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> is an S allele with the transmembrane domain 1(TMD1) deleted. | |
| - | + | Because TMD1 of S gene is essential for the function of lysis cassette as killer gene, S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> inhibits lysis cassette stronger than S107.([[Team:Kyoto/LearnMore#Lysis Cassette|Learn more]]) | |
| - | + | So, we selected S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> as anti-killer gene. | |
| - | Then, we checked if SΔTMD1 | + | Then, we checked if S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> prevents lysis cassette from causing the cell death. |
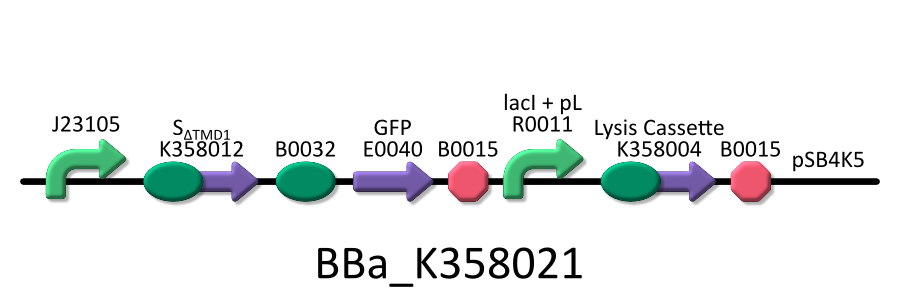
| - | To | + | To investigate the function of S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub>, we used the E.coli transformed with both killer and anti-killer genes ( <partinfo>BBa_K358021</partinfo>). |
| - | Because E.coli | + | Because E.coli will be killed immediately if the killer-gene is constitutively expressed, we constructed the lysis cassette regulated by lac promoter. At first, the E.coli bacteria were grown in the medium without IPTG. After the population of E.coli become enough, they were cultured in the one with IPTG to express lysis cassette. After that, we checked the growth rate of E.coli by measuring the absorbance (OD 550) of the growth medium. Thus, we investigated the possibility whether E.coli that contains both the killer and anti-killer genes could alive due to the constitutive expression of S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub>. |
===Method=== | ===Method=== | ||
====Bacterial strains==== | ====Bacterial strains==== | ||
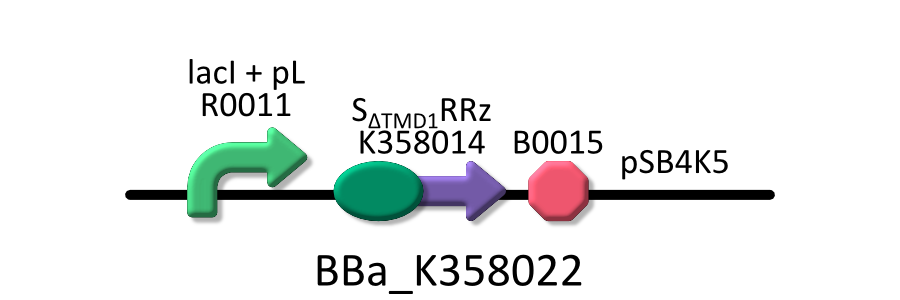
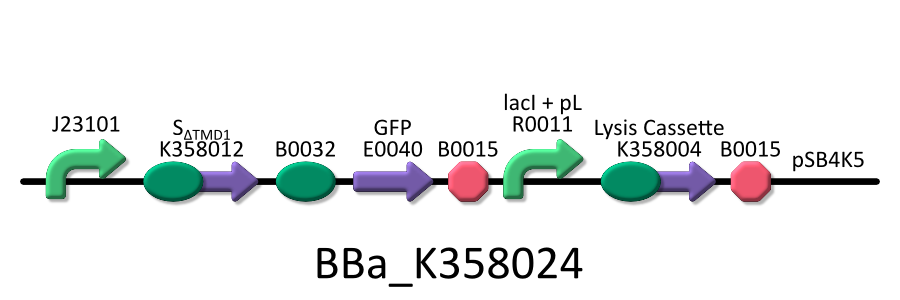
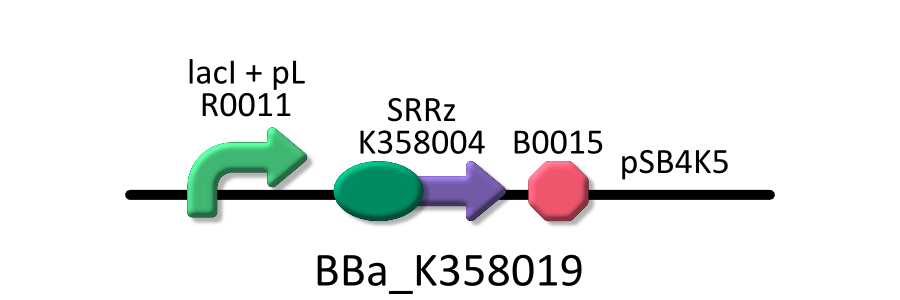
| - | We used four types of E. coli | + | We used four types of E. coli as follows: (1) E. coli KRX transformed with <partinfo>BBa_K358021</partinfo>, (2)KRX transformed with <partinfo>BBa_K358022</partinfo>, (3)KRX transformed with <partinfo>BBa_K358024</partinfo> and (4)KRX transformed with <partinfo>BBa_K358019</partinfo>. |
| - | After this, | + | After this, we call each E.coli to abbreviate in order of name, LB2-1, lacLΔ, LB2-2 and lacL. |
====Construct==== | ====Construct==== | ||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
{{clear}} | {{clear}} | ||
*<partinfo>BBa_K358021</partinfo>:Anti-killergene is induced constitutively and killergene is regulated by lactose promoter. | *<partinfo>BBa_K358021</partinfo>:Anti-killergene is induced constitutively and killergene is regulated by lactose promoter. | ||
| - | It was used in experiment | + | It was used in experiment 2. |
| - | *<partinfo>BBa_K358022</partinfo>:lacP + | + | *<partinfo>BBa_K358022</partinfo>:lacP + S<SUB>&DELTA;TMD1</SUB>RRz, TMD1 is deleted from lysis cassette[SRRz]. |
| - | It was used in experiment | + | It was used in experiment 1. |
| - | *<partinfo>BBa_K358024</partinfo>:This part is | + | *<partinfo>BBa_K358024</partinfo>: This part is similar to BBa_K358021, except for its constitutive promoter [BBa_J23101]. This part also induces constitutively S<sub>&DELTA;TMD1</sub> gene, the anti-killer gene, and λ lysis cassette[SRRz], the killer gene is regulated by lacP. |
| - | It was used in the additional experiment | + | It was used in the additional experiment which is not finished. |
| - | *<partinfo>BBa_K358019</partinfo>:Lysis cassette regulated by lacP, Lysis cassette[SRRz] is regulated by lactose promoter. Activating lactose promoter and expressing SRRz gene, it causes the cell lysis. | + | *<partinfo>BBa_K358019</partinfo>: Lysis cassette regulated by lacP, Lysis cassette[SRRz] is regulated by lactose promoter. |
| - | It was used in experiment 1 and 2 | + | Activating lactose promoter and expressing SRRz gene, it causes the cell lysis. Thus, lactose promoter must be repressed when this part is transformed. |
| + | It was used in experiment 1 and 2. | ||
| - | ==== | + | ====Measurement==== |
=====Experiment 1===== | =====Experiment 1===== | ||
| - | We | + | We picked up three colonies from each plate, and cultivated them in the supplemented M9 medium for a night, overnight. The overnight cultures were diluted to 0.1~0.11mM in pre-warmed fresh the supplemented M9 medium. 18h later, we measured OD 550 of the culture containing 0mM or 1mM IPTG. |
=====Experiment 2===== | =====Experiment 2===== | ||
| - | We | + | We picked up three colonies from each plate, and cultivated them in the supplemented M9 medium ~24-30 h (overnight). The overnight cultures were diluted to 0.1~0.11 in pre-warmed fresh the supplemented M9 medium. We measured OD 550 of the culture containing various IPTG at about 100 minute interval. |
===Result=== | ===Result=== | ||
| - | ====Experiment 1: Function check of SΔTMD1==== | + | ====Experiment 1:Check the role of TMD1 of S gene==== |
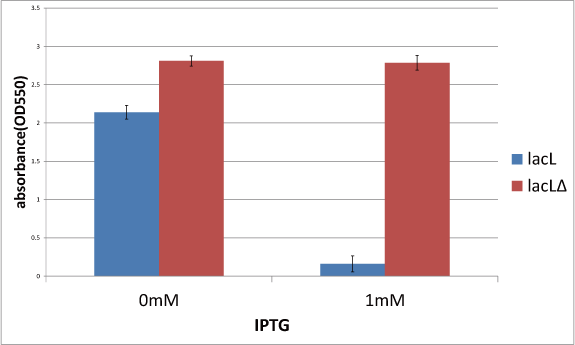
| - | We measured the cell number of | + | [[image:GoalC fig3-2-2.png|450px|right|thumb|Fig.1.the comparison between lacL and lacLΔ. The black lines on bars' edges are error bar.]] |
| - | The result is below(Fig. | + | Then, in order to check if TMD1 of S gene is essential for this killer gene, we measured the cell number of lacLΔ, which does not have TMD1 of S gene and that is, encodes S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> and that of lysis cassette. |
| + | This result is below (Fig.1). | ||
| + | From this result, after IPTG was added, the number of lacLΔ was not decreasing, while the number of lacLΔ was decresing. | ||
| + | It proved that S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> cannot function as killer gene and TMD1 is essential for this killer gene, lysis cassette. | ||
| + | In addition, in the medium without IPTG, the number of lacLΔ is larger than that of lacLΔ. This supports a report <sup>[[#RefL001|[1]]]</sup>, which says that more short proteins are expressed than the ones that are long. | ||
| + | ====Experiment 2: Function check of S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub>==== | ||
| + | We measured the cell number of lacLΔ at several time after induction by adding several concentration IPTG. | ||
| + | The result is below (Fig.2). | ||
This result showed that in the medium with more than 0.03mM IPTG, the number of E. coli is decreasing at a certain point. | This result showed that in the medium with more than 0.03mM IPTG, the number of E. coli is decreasing at a certain point. | ||
| - | It demonstrated that In at least more than 0.03mM IPTG, SΔTMD1 can't inhibit lysis cassette | + | It demonstrated that In at least more than 0.03mM IPTG, S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> can't inhibit lysis cassette completely. |
| - | Then, we measured the cell number of lacL in the same way, and compared the result of | + | Then, we measured the cell number of lacL in the same way, and compared the result of lacLΔ with that of lacL to check how S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> inhibited lysis cassette(Fig.2). |
| - | + | From this result, we knew in more than 0.5mM IPTG both lacL and LB2-1 were decreasing in the number at a certain point, or LB2-1 was a little delayed decreasing in the number. | |
| - | From this result, we knew in more than 0.5mM IPTG both | + | This demonstrated that S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> can't correctly inhibit lysis cassette. |
| - | This demonstrated that SΔTMD1 can't correctly inhibit lysis cassette. | + | So, we doubted whether S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> really functioned as anti-killer gene. |
| - | So, we doubted whether SΔTMD1 really functioned as anti-killer gene. | + | Although S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> has no TMD1 of S gene, S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> couldn't show the function as anti-killer gene. |
| - | Although | + | |
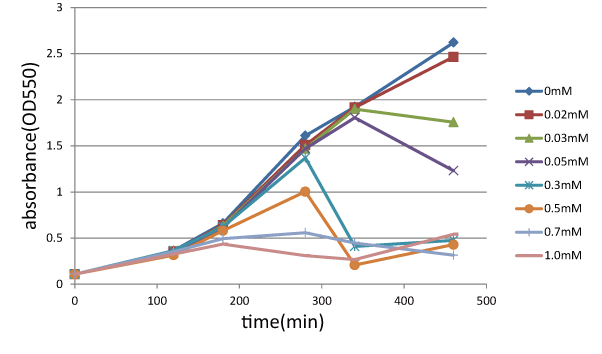
| - | [[image:GoalC fig1.png|440px|Fig.1|left|thumb|Fig. | + | [[image:GoalC fig1.png|440px|Fig.1|left|thumb|Fig.2.the result of function check of S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub>. |
| - | + | We measure OD 550 with various IPTG concentration, 0, 0.02, 0.03, 0.05, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 1.0 (mM). ]] | |
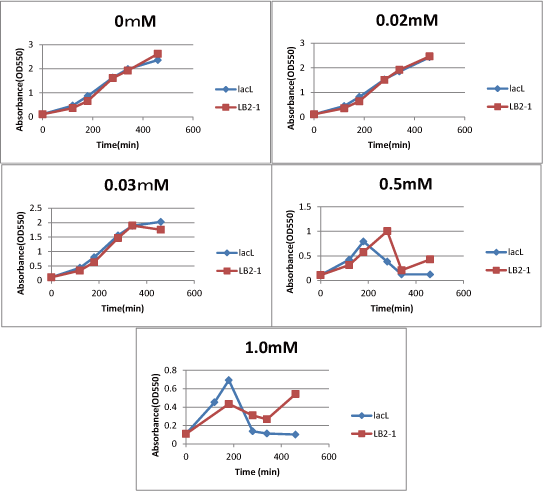
| - | [[image:GoalC fig2-2.png|440px|right|thumb|Fig. | + | [[image:GoalC fig2-3-2.png|440px|right|thumb|Fig.3.Comparison between lacL and LB2-1. |
| - | + | We compared IPTG concentration 0, 0.02, 0.03, 0.5, 1.0. ]] | |
| - | ==== | + | ===Discussion=== |
| - | [[ | + | ====TMD1 of S gene is essential for lysis cassette==== |
| - | + | The result of experiment 1 supports [[#RefL001|Ref.1]]. | |
| - | + | That is, we were able to make sure that TMD1 of S gene is essential for lysis cassette as killer gene. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ====S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> cannot inhibit lysis cassette completely==== | |
| - | ====SΔTMD1 cannot inhibit lysis cassette | + | These results showed that S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> cannot inhibit completely lysis cassette. |
| - | These results showed that SΔTMD1 cannot inhibit completely lysis cassette. | + | This results can't supported a report on lysis <sup>[[#RefL001|[1]]]</sup>, which says that S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> without TMD1 dominant-negatively inhibit lysis cassette. |
| - | This results can't supported a report on lysis <sup>[[# | + | |
Why did we get the result against that report? | Why did we get the result against that report? | ||
Probably, there were three reasons below, we thought. | Probably, there were three reasons below, we thought. | ||
| - | *SΔTMD1 in the plasmid did not worked correctly. | + | *S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> in the plasmid did not worked correctly. |
| - | *S | + | *S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> is weaker anti-killer gene than we expected. |
| - | + | *less S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> proteins or more lysis cassette proteins was expressed than we expected. | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | + | =====Reason1:S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> in the plasmid did not work correctly.===== | |
| - | + | To investigate this reason, we sequenced BBa_K358021 we used. | |
| + | The result showed that this construct is inserted into the plasmid correctly, which demonstrated that S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> worked correctly. | ||
| + | So, we assume that the first reason is negative. | ||
| + | =====Reason2: S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> is weaker anti-killer gene than we expected.===== | ||
| + | As anti-killer gene against lysis cassette, there are two genes, S107 and S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> ([[Team:Kyoto/LearnMore#Lysis Cassette|Learn more]]). | ||
| + | S107 is the anti-killer gene. Because it has essential TMD1 of S for function of this killer gene, the anti-killer function of this gene is weak compared with S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub>, which does not have TMD1([[Team:Kyoto/LearnMore#Lysis Cassette|Learn more]]). | ||
| + | Thus, we expected that S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> is a strong anti-killer gene. However, from the result of experiment 2, we could not observe the function of S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> as a strong anti-killer gene under the tested condition. | ||
| + | =====Reason3: Expression balance between the anti-killer and killer genes was not optimized properly===== | ||
| + | In order to investigate the possibility of this reason, we analyzed the expression level of the killer gene, lysis cassette and S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub>. | ||
| + | As a report <sup>[[#RefL002|[2]]]</sup> says, it is necessary for the inhibition of lysis cassette that there are at least ~4.7 times more S107, anti-killer gene than lysis cassette proteins. | ||
| + | So, inhibition of this killer gene needs at least ~4.7 times more expression of the anti-killer gene than that of the killer gene. Thus, we calculated the ratio of the expression levels of the killer and anti-killer gene. The calculation was done under the assumptions that S gene, which includes lysis cassette, produces S105 and S107 at a 2.5:1 ratio([[Team:Kyoto/LearnMore#Lysis Cassette|Learn more]]), and that the strength of function of S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> as anti-killer gene is the same as that of S107. By this calculation, we knew that in LB-1, the anti-killer gene couldn't inhibit killer gene in the medium with more than 0.1246 mM IPTG. So, we assume that S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> was not expressed adequately to inhibit lysis cassette completely. | ||
| + | We assume that our experimental results could be due to the 3rd reason (Reason 3) mentioned above, although we cannot rule out the possibility of the second reason. However, it has been reported <sup>[[#RefL001|[1]]]</sup> that S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> inhibits lysis cassette effectively. So, it is reasonable to assume that S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> exhibits enough activity to inhibit lysis cassette. That is why we think that the Reason 3 is the most likely answer. To confirm this possibility, we changed the promoter of S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> to stronger one. The experiment to check the function of S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> using the strong promoter is currently underway. Surely, this result will help us to understand why S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> could not function as we expected and to develop distinct cell-death controllable devices for the further studies. | ||
| + | ===Conclusion=== | ||
| + | 1)We made and registered S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> by deleting TMD1 of S gene and lysis cassetteΔTMD1(S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub>RRz) in BioBrick as new parts. | ||
| + | 2)By the comparison of the function as killer gene between lysis cassette and lysis cassetteΔTMD1, We made sure that TMD1 is essential for fuction of lysis cassette as killer gene. | ||
| + | 3)By co-expressing lysis cassette regulated by a lactose promoter, we characterized the function of S<sub>ΔTMD1</sub> as anti-killer gene. | ||
===Reference=== | ===Reference=== | ||
---- | ---- | ||
# <html><a name="RefL001"></a></html>Rebecca White, Tram Anh T. Tran, Chelsey A. Dankenbring, John Deaton, and Ry Young.2010.The N-Terminal Transmembrane Domain of _ S Is Required for Holin but Not Antiholin Function_. J. Bacteriol. 192: 725–733 | # <html><a name="RefL001"></a></html>Rebecca White, Tram Anh T. Tran, Chelsey A. Dankenbring, John Deaton, and Ry Young.2010.The N-Terminal Transmembrane Domain of _ S Is Required for Holin but Not Antiholin Function_. J. Bacteriol. 192: 725–733 | ||
| - | # <html><a name="RefL002"></a></html>CHUNG-YU CHANG, KIEBANG NAM, AND RY YOUNG1. 1995.2 S Gene Expression and the Timing of Lysis by Bacteriophage | + | # <html><a name="RefL002"></a></html>CHUNG-YU CHANG, KIEBANG NAM, AND RY YOUNG1. 1995.2 S Gene Expression and the Timing of Lysis by Bacteriophage λ. J. Bacteriol. 177: 3283–3294 |
Latest revision as of 03:55, 28 October 2010
Contents |
Goal C: Characterization of the anti-killer gene
Introduction
As far as we know, there are two anti-killer genes against the killer gene (lysis cassette), S107 and SΔTMD1. S107 is expressed by S gene encoded by lysis cassette and SΔTMD1 is an S allele with the transmembrane domain 1(TMD1) deleted. Because TMD1 of S gene is essential for the function of lysis cassette as killer gene, SΔTMD1 inhibits lysis cassette stronger than S107.(Learn more) So, we selected SΔTMD1 as anti-killer gene.
Then, we checked if SΔTMD1 prevents lysis cassette from causing the cell death. To investigate the function of SΔTMD1, we used the E.coli transformed with both killer and anti-killer genes ( <partinfo>BBa_K358021</partinfo>). Because E.coli will be killed immediately if the killer-gene is constitutively expressed, we constructed the lysis cassette regulated by lac promoter. At first, the E.coli bacteria were grown in the medium without IPTG. After the population of E.coli become enough, they were cultured in the one with IPTG to express lysis cassette. After that, we checked the growth rate of E.coli by measuring the absorbance (OD 550) of the growth medium. Thus, we investigated the possibility whether E.coli that contains both the killer and anti-killer genes could alive due to the constitutive expression of SΔTMD1.
Method
Bacterial strains
We used four types of E. coli as follows: (1) E. coli KRX transformed with <partinfo>BBa_K358021</partinfo>, (2)KRX transformed with <partinfo>BBa_K358022</partinfo>, (3)KRX transformed with <partinfo>BBa_K358024</partinfo> and (4)KRX transformed with <partinfo>BBa_K358019</partinfo>. After this, we call each E.coli to abbreviate in order of name, LB2-1, lacLΔ, LB2-2 and lacL.
Construct
- <partinfo>BBa_K358021</partinfo>:Anti-killergene is induced constitutively and killergene is regulated by lactose promoter.
It was used in experiment 2.
- <partinfo>BBa_K358022</partinfo>:lacP + S&DELTA;TMD1RRz, TMD1 is deleted from lysis cassette[SRRz].
It was used in experiment 1.
- <partinfo>BBa_K358024</partinfo>: This part is similar to BBa_K358021, except for its constitutive promoter [BBa_J23101]. This part also induces constitutively S&DELTA;TMD1 gene, the anti-killer gene, and λ lysis cassette[SRRz], the killer gene is regulated by lacP.
It was used in the additional experiment which is not finished.
- <partinfo>BBa_K358019</partinfo>: Lysis cassette regulated by lacP, Lysis cassette[SRRz] is regulated by lactose promoter.
Activating lactose promoter and expressing SRRz gene, it causes the cell lysis. Thus, lactose promoter must be repressed when this part is transformed. It was used in experiment 1 and 2.
Measurement
Experiment 1
We picked up three colonies from each plate, and cultivated them in the supplemented M9 medium for a night, overnight. The overnight cultures were diluted to 0.1~0.11mM in pre-warmed fresh the supplemented M9 medium. 18h later, we measured OD 550 of the culture containing 0mM or 1mM IPTG.
Experiment 2
We picked up three colonies from each plate, and cultivated them in the supplemented M9 medium ~24-30 h (overnight). The overnight cultures were diluted to 0.1~0.11 in pre-warmed fresh the supplemented M9 medium. We measured OD 550 of the culture containing various IPTG at about 100 minute interval.
Result
Experiment 1:Check the role of TMD1 of S gene
Then, in order to check if TMD1 of S gene is essential for this killer gene, we measured the cell number of lacLΔ, which does not have TMD1 of S gene and that is, encodes SΔTMD1 and that of lysis cassette. This result is below (Fig.1). From this result, after IPTG was added, the number of lacLΔ was not decreasing, while the number of lacLΔ was decresing. It proved that SΔTMD1 cannot function as killer gene and TMD1 is essential for this killer gene, lysis cassette. In addition, in the medium without IPTG, the number of lacLΔ is larger than that of lacLΔ. This supports a report [1], which says that more short proteins are expressed than the ones that are long.
Experiment 2: Function check of SΔTMD1
We measured the cell number of lacLΔ at several time after induction by adding several concentration IPTG. The result is below (Fig.2). This result showed that in the medium with more than 0.03mM IPTG, the number of E. coli is decreasing at a certain point. It demonstrated that In at least more than 0.03mM IPTG, SΔTMD1 can't inhibit lysis cassette completely. Then, we measured the cell number of lacL in the same way, and compared the result of lacLΔ with that of lacL to check how SΔTMD1 inhibited lysis cassette(Fig.2). From this result, we knew in more than 0.5mM IPTG both lacL and LB2-1 were decreasing in the number at a certain point, or LB2-1 was a little delayed decreasing in the number. This demonstrated that SΔTMD1 can't correctly inhibit lysis cassette. So, we doubted whether SΔTMD1 really functioned as anti-killer gene. Although SΔTMD1 has no TMD1 of S gene, SΔTMD1 couldn't show the function as anti-killer gene.
Discussion
TMD1 of S gene is essential for lysis cassette
The result of experiment 1 supports Ref.1. That is, we were able to make sure that TMD1 of S gene is essential for lysis cassette as killer gene.
SΔTMD1 cannot inhibit lysis cassette completely
These results showed that SΔTMD1 cannot inhibit completely lysis cassette. This results can't supported a report on lysis [1], which says that SΔTMD1 without TMD1 dominant-negatively inhibit lysis cassette. Why did we get the result against that report? Probably, there were three reasons below, we thought.
- SΔTMD1 in the plasmid did not worked correctly.
- SΔTMD1 is weaker anti-killer gene than we expected.
- less SΔTMD1 proteins or more lysis cassette proteins was expressed than we expected.
Reason1:SΔTMD1 in the plasmid did not work correctly.
To investigate this reason, we sequenced BBa_K358021 we used. The result showed that this construct is inserted into the plasmid correctly, which demonstrated that SΔTMD1 worked correctly. So, we assume that the first reason is negative.
Reason2: SΔTMD1 is weaker anti-killer gene than we expected.
As anti-killer gene against lysis cassette, there are two genes, S107 and SΔTMD1 (Learn more). S107 is the anti-killer gene. Because it has essential TMD1 of S for function of this killer gene, the anti-killer function of this gene is weak compared with SΔTMD1, which does not have TMD1(Learn more). Thus, we expected that SΔTMD1 is a strong anti-killer gene. However, from the result of experiment 2, we could not observe the function of SΔTMD1 as a strong anti-killer gene under the tested condition.
Reason3: Expression balance between the anti-killer and killer genes was not optimized properly
In order to investigate the possibility of this reason, we analyzed the expression level of the killer gene, lysis cassette and SΔTMD1. As a report [2] says, it is necessary for the inhibition of lysis cassette that there are at least ~4.7 times more S107, anti-killer gene than lysis cassette proteins. So, inhibition of this killer gene needs at least ~4.7 times more expression of the anti-killer gene than that of the killer gene. Thus, we calculated the ratio of the expression levels of the killer and anti-killer gene. The calculation was done under the assumptions that S gene, which includes lysis cassette, produces S105 and S107 at a 2.5:1 ratio(Learn more), and that the strength of function of SΔTMD1 as anti-killer gene is the same as that of S107. By this calculation, we knew that in LB-1, the anti-killer gene couldn't inhibit killer gene in the medium with more than 0.1246 mM IPTG. So, we assume that SΔTMD1 was not expressed adequately to inhibit lysis cassette completely. We assume that our experimental results could be due to the 3rd reason (Reason 3) mentioned above, although we cannot rule out the possibility of the second reason. However, it has been reported [1] that SΔTMD1 inhibits lysis cassette effectively. So, it is reasonable to assume that SΔTMD1 exhibits enough activity to inhibit lysis cassette. That is why we think that the Reason 3 is the most likely answer. To confirm this possibility, we changed the promoter of SΔTMD1 to stronger one. The experiment to check the function of SΔTMD1 using the strong promoter is currently underway. Surely, this result will help us to understand why SΔTMD1 could not function as we expected and to develop distinct cell-death controllable devices for the further studies.
Conclusion
1)We made and registered SΔTMD1 by deleting TMD1 of S gene and lysis cassetteΔTMD1(SΔTMD1RRz) in BioBrick as new parts. 2)By the comparison of the function as killer gene between lysis cassette and lysis cassetteΔTMD1, We made sure that TMD1 is essential for fuction of lysis cassette as killer gene. 3)By co-expressing lysis cassette regulated by a lactose promoter, we characterized the function of SΔTMD1 as anti-killer gene.
Reference
- Rebecca White, Tram Anh T. Tran, Chelsey A. Dankenbring, John Deaton, and Ry Young.2010.The N-Terminal Transmembrane Domain of _ S Is Required for Holin but Not Antiholin Function_. J. Bacteriol. 192: 725–733
- CHUNG-YU CHANG, KIEBANG NAM, AND RY YOUNG1. 1995.2 S Gene Expression and the Timing of Lysis by Bacteriophage λ. J. Bacteriol. 177: 3283–3294
 "
"