Team:Slovenia/PROJECT/proof/studies/prod
From 2010.igem.org
| (5 intermediate revisions not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
<style> | <style> | ||
#vsebina_mid{ | #vsebina_mid{ | ||
| - | height: | + | height: 3230px; |
} | } | ||
#lgumb2{ | #lgumb2{ | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
<div id="overhead"> | <div id="overhead"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span style="width:680px;" id="naslov">binding studies - production of binding proteins </span> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div id="thumbsi"> | ||
<a href="/Team:Slovenia/PROJECT/proof/studies/prod"><span style="font-size:15px; | <a href="/Team:Slovenia/PROJECT/proof/studies/prod"><span style="font-size:15px; | ||
| - | width:220px;" id="stopnja3a"> | + | width:220px;" id="stopnja3a">production of binding proteins</span></a> |
<a href="/Team:Slovenia/PROJECT/proof/studies/emsa"><span style="font-size:15px; | <a href="/Team:Slovenia/PROJECT/proof/studies/emsa"><span style="font-size:15px; | ||
width:100px;" id="stopnja3">EMSA</span></a> | width:100px;" id="stopnja3">EMSA</span></a> | ||
| Line 62: | Line 66: | ||
width:100px;" id="stopnja3">SPR</span></a> | width:100px;" id="stopnja3">SPR</span></a> | ||
<a href="/Team:Slovenia/PROJECT/proof/studies/betagal"><span style="font-size:15px; | <a href="/Team:Slovenia/PROJECT/proof/studies/betagal"><span style="font-size:15px; | ||
| - | width:130px;" id="stopnja3"> | + | width:130px;" id="stopnja3">beta-GAL</span></a> |
| - | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
<div id="besedilo"> | <div id="besedilo"> | ||
| Line 77: | Line 80: | ||
Before any <em>in vitro</em> characterisation, DNA-binding proteins had to be obtained. Zinc fingers were firstly tri-point ligated with a particular split GFP and T7 promoter and T7 terminator sequence were added afterwards. T7 promoter enables high production of proteins in<em> E. coli</em> BL21(DE3)pLysS production strain. Zinc fingers were then purified using His tags and used in subsequent experiments.<html> Parts used for production were: <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323001"><span style="color: #810081;">BBa_323001</span></a><a href="/w/page/BBa_323001"></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323015"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323015</span></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323069"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323069</span></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323058"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323058</span></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323004"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323004</span></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323070"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323070</span></a>.</html> | Before any <em>in vitro</em> characterisation, DNA-binding proteins had to be obtained. Zinc fingers were firstly tri-point ligated with a particular split GFP and T7 promoter and T7 terminator sequence were added afterwards. T7 promoter enables high production of proteins in<em> E. coli</em> BL21(DE3)pLysS production strain. Zinc fingers were then purified using His tags and used in subsequent experiments.<html> Parts used for production were: <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323001"><span style="color: #810081;">BBa_323001</span></a><a href="/w/page/BBa_323001"></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323015"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323015</span></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323069"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323069</span></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323058"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323058</span></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323004"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323004</span></a>, <a href="http://partsregistry.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K323070"><span style="color: #0000ff;">BBa_323070</span></a>.</html> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| - | [[Image:SLOSPR_shema.png|thumb|center|700px]] | + | [[Image:SLOSPR_shema.png|thumb|center|700px|'''Figure 1:''' Scheme of cloning for zinc finger protein production.]] |
<h2>Protein production</h2> | <h2>Protein production</h2> | ||
| Line 83: | Line 86: | ||
Zinc fingers were produced in <em>E.coli</em> BL21(DE3)pLysS and purified with Ni-NTA column according to our protocols in <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/METHODS_and_PARTS/protocols">Methods & Parts</a>. Their isolation and purity was confirmed with SDS-page and Western blot techniques. Secondary structure of proteins was determined with circular dichroism. Purified proteins were further used for <a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/PROJECT/proof/studies/emsa">electrophoretic mobility shift assay</a> (EMSA) test and <span style="font-size: 115%;"><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/PROJECT/proof/studies/spr">surface plasmon resonance</a> (SPR) experiments.</html><br> | Zinc fingers were produced in <em>E.coli</em> BL21(DE3)pLysS and purified with Ni-NTA column according to our protocols in <html><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/METHODS_and_PARTS/protocols">Methods & Parts</a>. Their isolation and purity was confirmed with SDS-page and Western blot techniques. Secondary structure of proteins was determined with circular dichroism. Purified proteins were further used for <a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/PROJECT/proof/studies/emsa">electrophoretic mobility shift assay</a> (EMSA) test and <span style="font-size: 115%;"><a href="https://2010.igem.org/Team:Slovenia/PROJECT/proof/studies/spr">surface plasmon resonance</a> (SPR) experiments.</html><br> | ||
| - | [[Image:SLOvsi.jpg|thumb|center|700px|'''SDS page of purified zinc fingers. | + | [[Image:SLOvsi.jpg|thumb|center|700px|'''Figure 2:''' SDS page of purified zinc fingers. Purified proteins were loaded on 10 % SDS gel and stained with Coommasie Blue stain. The arrows show the proteins of interest with their expected molecular weight, according to the molecular weight calculated with ProtParam tool.]]<br><br> |
| - | [[Image:SLOvsi-western.jpg|thumb|center|700px|''Western blot confirmed isolated zinc fingers. | + | [[Image:SLOvsi-western.jpg|thumb|center|700px|'''Figure 3:''' Western blot confirmed isolated zinc fingers. We have been able to detect purified proteins with anti-his primary antibodies on Western blot. Arrows indicate each protein and its molecular weight.]]<br><br> |
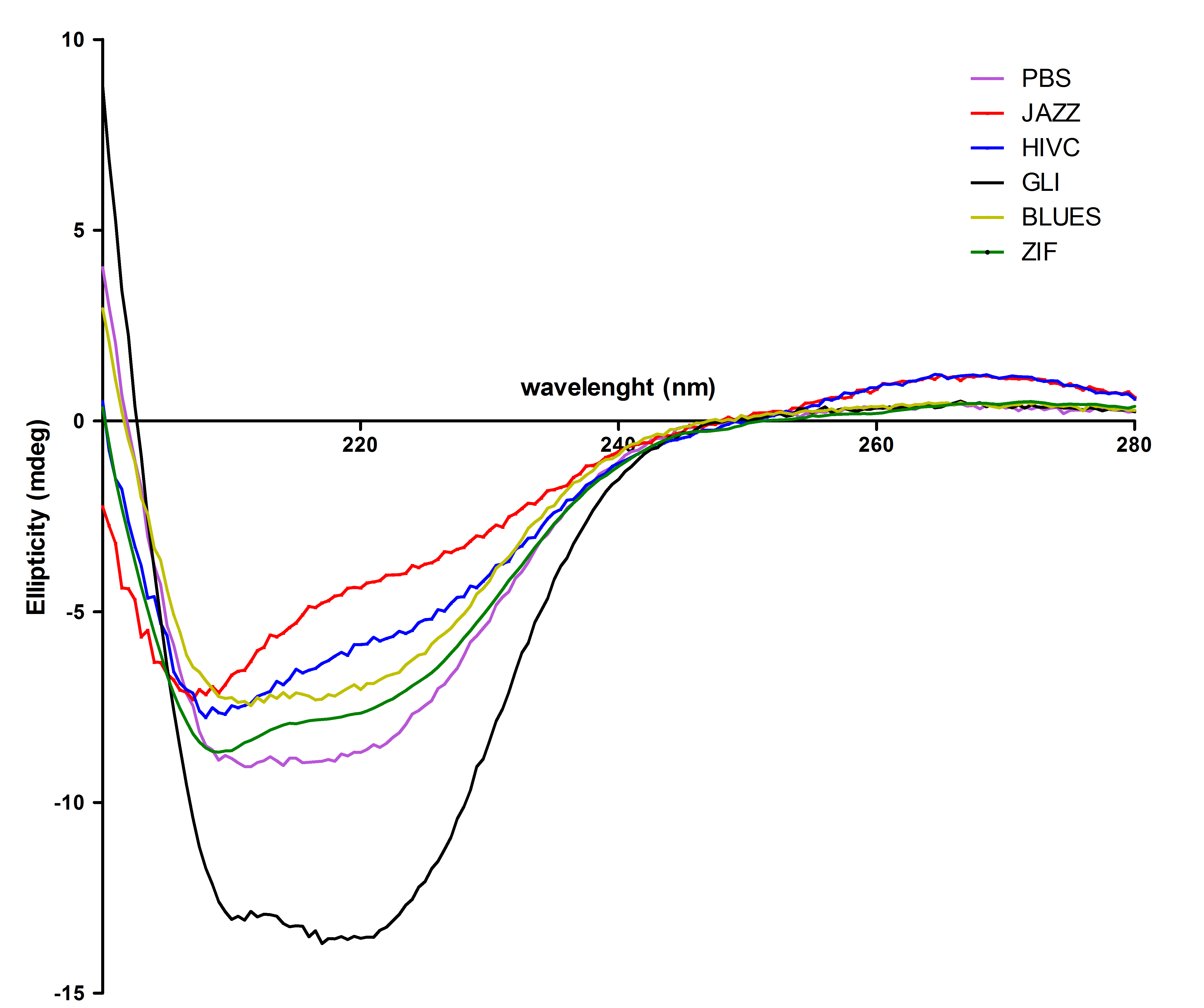
All six proteins were also tested with circular dichorism spectroscopy. Secondary structures were observed successfully: | All six proteins were also tested with circular dichorism spectroscopy. Secondary structures were observed successfully: | ||
| - | [[Image:CDvsiprot(Matej).jpg|thumb|center|700px|''' | + | [[Image:CDvsiprot(Matej).jpg|thumb|center|700px|'''Figure 4:'''Protein secondary structure was studied with CD spectroscopy. From this figure we can see that most of the purified proteins refolded mainly into α-helical structure with a small portion of random coil, except Gli wich contains higher content of α-helical structure.]]<br><br> |
<!--STOP BESEDILO--> | <!--STOP BESEDILO--> | ||
Latest revision as of 01:51, 28 October 2010
Contents |
Cloning scheme
Before any in vitro characterisation, DNA-binding proteins had to be obtained. Zinc fingers were firstly tri-point ligated with a particular split GFP and T7 promoter and T7 terminator sequence were added afterwards. T7 promoter enables high production of proteins in E. coli BL21(DE3)pLysS production strain. Zinc fingers were then purified using His tags and used in subsequent experiments. Parts used for production were: BBa_323001, BBa_323015, BBa_323069, BBa_323058, BBa_323004, BBa_323070.
Protein production
Zinc fingers were produced in E.coli BL21(DE3)pLysS and purified with Ni-NTA column according to our protocols in Methods & Parts. Their isolation and purity was confirmed with SDS-page and Western blot techniques. Secondary structure of proteins was determined with circular dichroism. Purified proteins were further used for electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) test and surface plasmon resonance (SPR) experiments.
All six proteins were also tested with circular dichorism spectroscopy. Secondary structures were observed successfully:
 "
"