Team:LMU-Munich/ApoControl
From 2010.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
m (Team:LMU-Munich/Apotosis moved to Team:LMU-Munich/ApoControl: wrong name) |
|||
| (One intermediate revision not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
The ApoControl team consists of 12 biology students from the undergraduate school of biology at LMU. We are currently undertaking three subprojects on controllable cell-death. The goal is to develop a system to improve the efficiency and specificity of gene expression in eukaryotic cell-lines and more specifically, to select cells expressing the target gene against cells that do not. Here proapoptotic genes instead of antibiotic resistance are used as selection markers to induce clean cell-death at different stimuli. The project is divided into three parts, each representing different approaches to achieve this goal. | The ApoControl team consists of 12 biology students from the undergraduate school of biology at LMU. We are currently undertaking three subprojects on controllable cell-death. The goal is to develop a system to improve the efficiency and specificity of gene expression in eukaryotic cell-lines and more specifically, to select cells expressing the target gene against cells that do not. Here proapoptotic genes instead of antibiotic resistance are used as selection markers to induce clean cell-death at different stimuli. The project is divided into three parts, each representing different approaches to achieve this goal. | ||
| - | [[Image:cnsZelle.png| | + | [[Image:cnsZelle.png|120px|Logo|right]] |
===Cut'N'Survive System=== | ===Cut'N'Survive System=== | ||
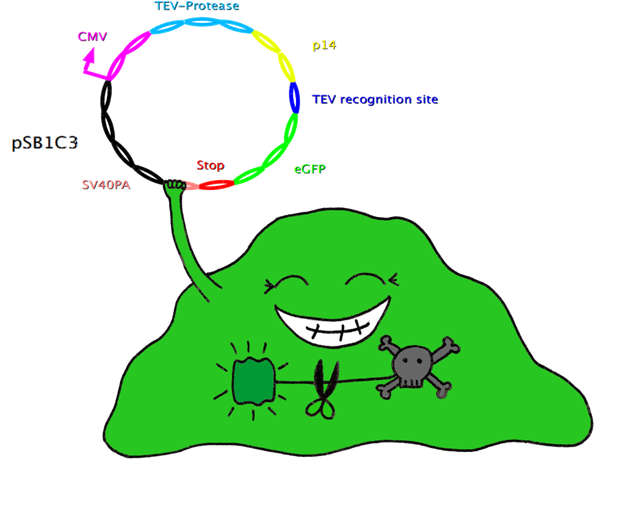
In this system, the apoptosis triggering protein Bak is controlled by the tet-on system for inducible apoptosis. Bak can be degraded when the target gene is successfully expressed, therefore ensuring the survival of the wished cells. Bak is combined with a certain interacting protein p14*, TEV-protease recognition site and N-Degron. This construct should be stably integrated into the cell line genome. The target plasmid consists of eGFP as a target gene, another TEV-protease recognition site, the interaction partner of p14* (SF3B) and the TEV-protease. When the target plasmid is expressed, the interaction proteins bring the TEV-protease together with its recognition site; TEV cuts Bak, together with N-Degron, free from the rest of the protein complex, where N-Degron with its free N-terminal acts as a degradation signal of protease in the cells. Thus this system enables selection of cells expressing the target gene while the not transfected cells undergo induced apoptosis. | In this system, the apoptosis triggering protein Bak is controlled by the tet-on system for inducible apoptosis. Bak can be degraded when the target gene is successfully expressed, therefore ensuring the survival of the wished cells. Bak is combined with a certain interacting protein p14*, TEV-protease recognition site and N-Degron. This construct should be stably integrated into the cell line genome. The target plasmid consists of eGFP as a target gene, another TEV-protease recognition site, the interaction partner of p14* (SF3B) and the TEV-protease. When the target plasmid is expressed, the interaction proteins bring the TEV-protease together with its recognition site; TEV cuts Bak, together with N-Degron, free from the rest of the protein complex, where N-Degron with its free N-terminal acts as a degradation signal of protease in the cells. Thus this system enables selection of cells expressing the target gene while the not transfected cells undergo induced apoptosis. | ||
| - | [[Image:Jumplogo.png| | + | [[Image:Jumplogo.png|120px|Logo|right]] |
===Jump-or-Die System=== | ===Jump-or-Die System=== | ||
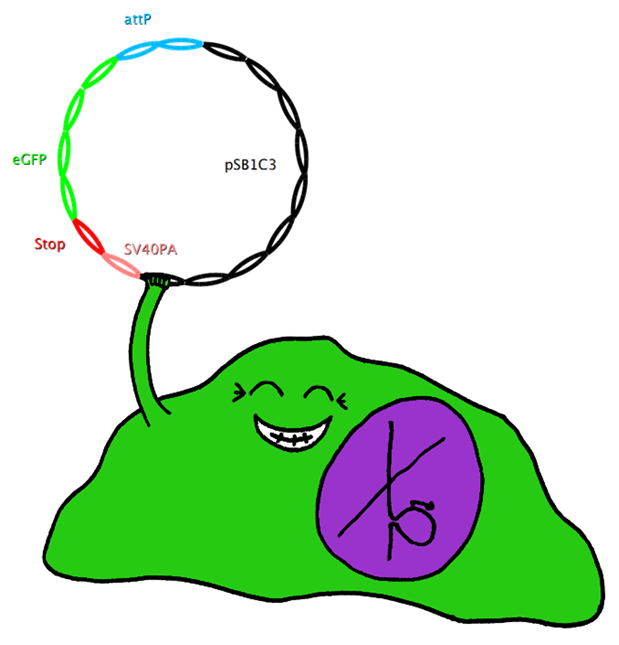
This system also uses Bak as apoptosis inducing selection marker together with the tet-on promoter, which is to be stably integrated in the cell-line genome. However, this construct also includes an upstream bacterial attachment site (attB) and a downstream SV40 polyadenylation site (SV40PA). The target gene eGFP is combined with phage attachment site (attP) and another SV40PA but without promoter. The target plasmid is co-transfected with integrase PhiC31o into the cell line. Therefore the target gene can only be expressed if integrated into the cells’ genome, and the stop-codon and SV40PA following the target gene stop the expression of bak, ensuring the survival of the cell while other cells not expressing the target gene undergo induced apoptosis. | This system also uses Bak as apoptosis inducing selection marker together with the tet-on promoter, which is to be stably integrated in the cell-line genome. However, this construct also includes an upstream bacterial attachment site (attB) and a downstream SV40 polyadenylation site (SV40PA). The target gene eGFP is combined with phage attachment site (attP) and another SV40PA but without promoter. The target plasmid is co-transfected with integrase PhiC31o into the cell line. Therefore the target gene can only be expressed if integrated into the cells’ genome, and the stop-codon and SV40PA following the target gene stop the expression of bak, ensuring the survival of the cell while other cells not expressing the target gene undergo induced apoptosis. | ||
| - | [[Image:prosearchZelle.jpg| | + | [[Image:prosearchZelle.jpg|120px|Logo|right]] |
===ProSearch System=== | ===ProSearch System=== | ||
Latest revision as of 18:54, 26 October 2010


![]()
![]()







![]()
 "
"