Team:Kyoto/Project
From 2010.igem.org
(→Goal C: Characterization of the anti-killer gene, SΔTMD1) |
(→Project) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{:Team:Kyoto/Header}} | {{:Team:Kyoto/Header}} | ||
==Project== | ==Project== | ||
| + | [[Image:KyotoTop.png|600px|center]] | ||
===Abstract=== | ===Abstract=== | ||
<span class="title">'''The Fantastic Lysisbox:'''</span> | <span class="title">'''The Fantastic Lysisbox:'''</span> | ||
| Line 32: | Line 33: | ||
===Our Goals=== | ===Our Goals=== | ||
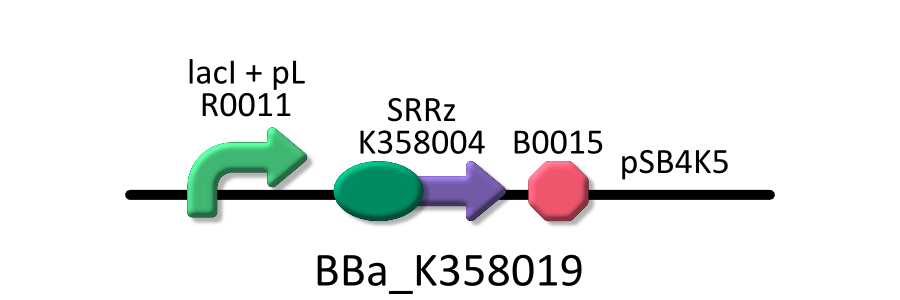
====[[Team:Kyoto/Project/Goal A|Goal A: Characterization of R0011, a strong lactose promoter]]==== | ====[[Team:Kyoto/Project/Goal A|Goal A: Characterization of R0011, a strong lactose promoter]]==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:KyotoGoalA.png|600px|left]] | ||
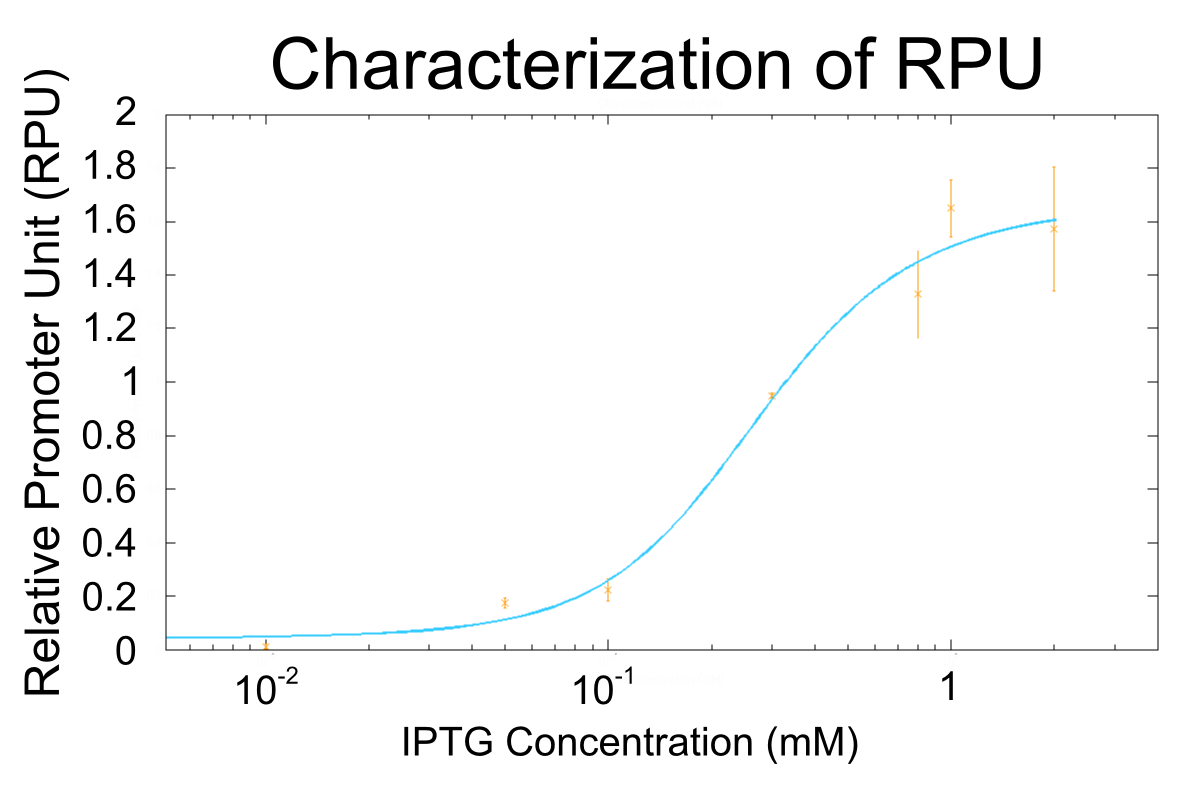
We used R0011, which is one of the most commonly used parts in iGEM, to characterize our genes because the strength of promoter activity is very high. However, in previous iGEM, no teams characterized R0011 with RPU. We tried to determine how the activity of R0011<sup>[[#RefH010|[10]]]</sup> changes.[[Team:Kyoto/Project/Goal A|See the detail of Goal A]] | We used R0011, which is one of the most commonly used parts in iGEM, to characterize our genes because the strength of promoter activity is very high. However, in previous iGEM, no teams characterized R0011 with RPU. We tried to determine how the activity of R0011<sup>[[#RefH010|[10]]]</sup> changes.[[Team:Kyoto/Project/Goal A|See the detail of Goal A]] | ||
| Line 37: | Line 40: | ||
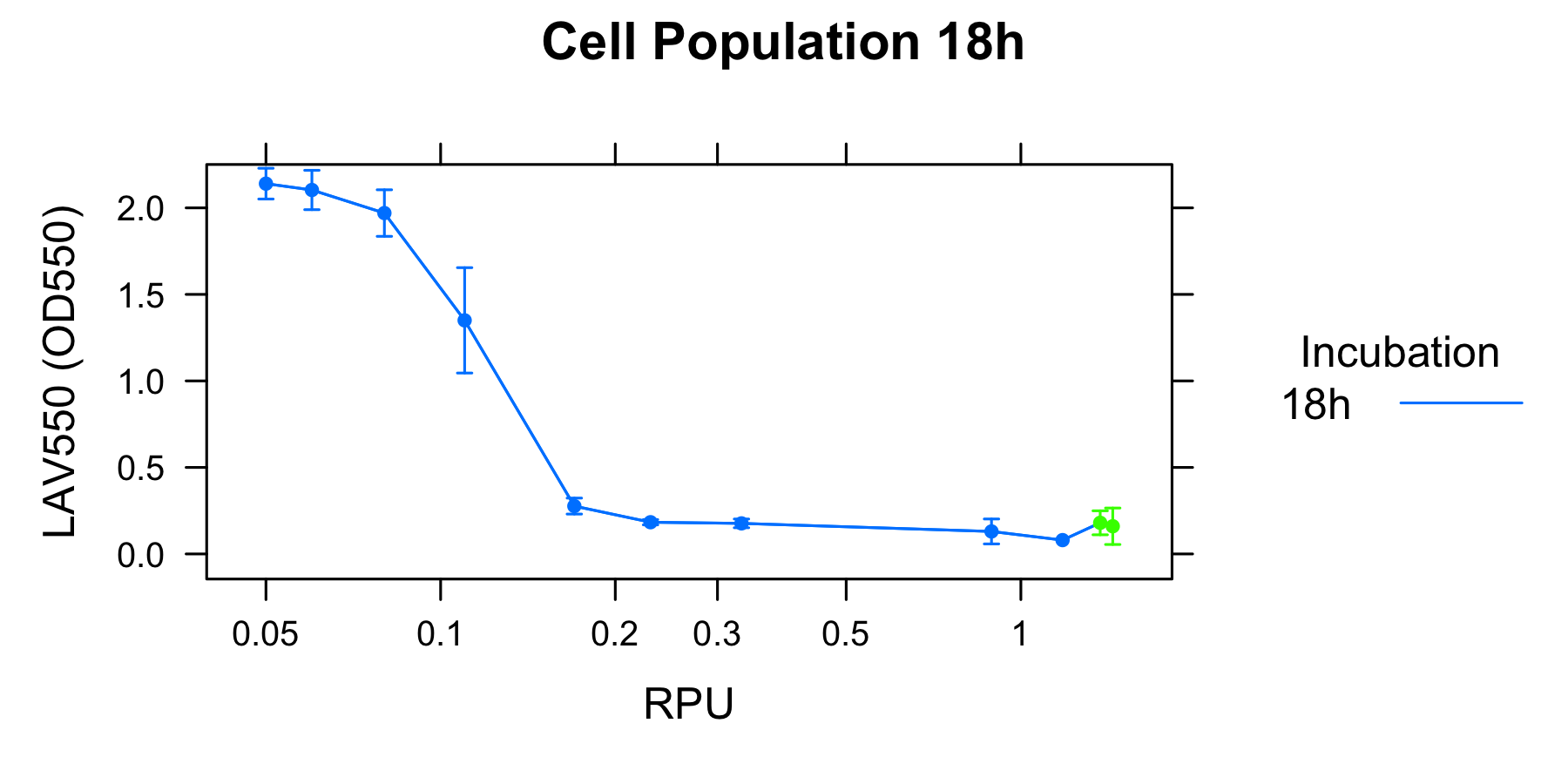
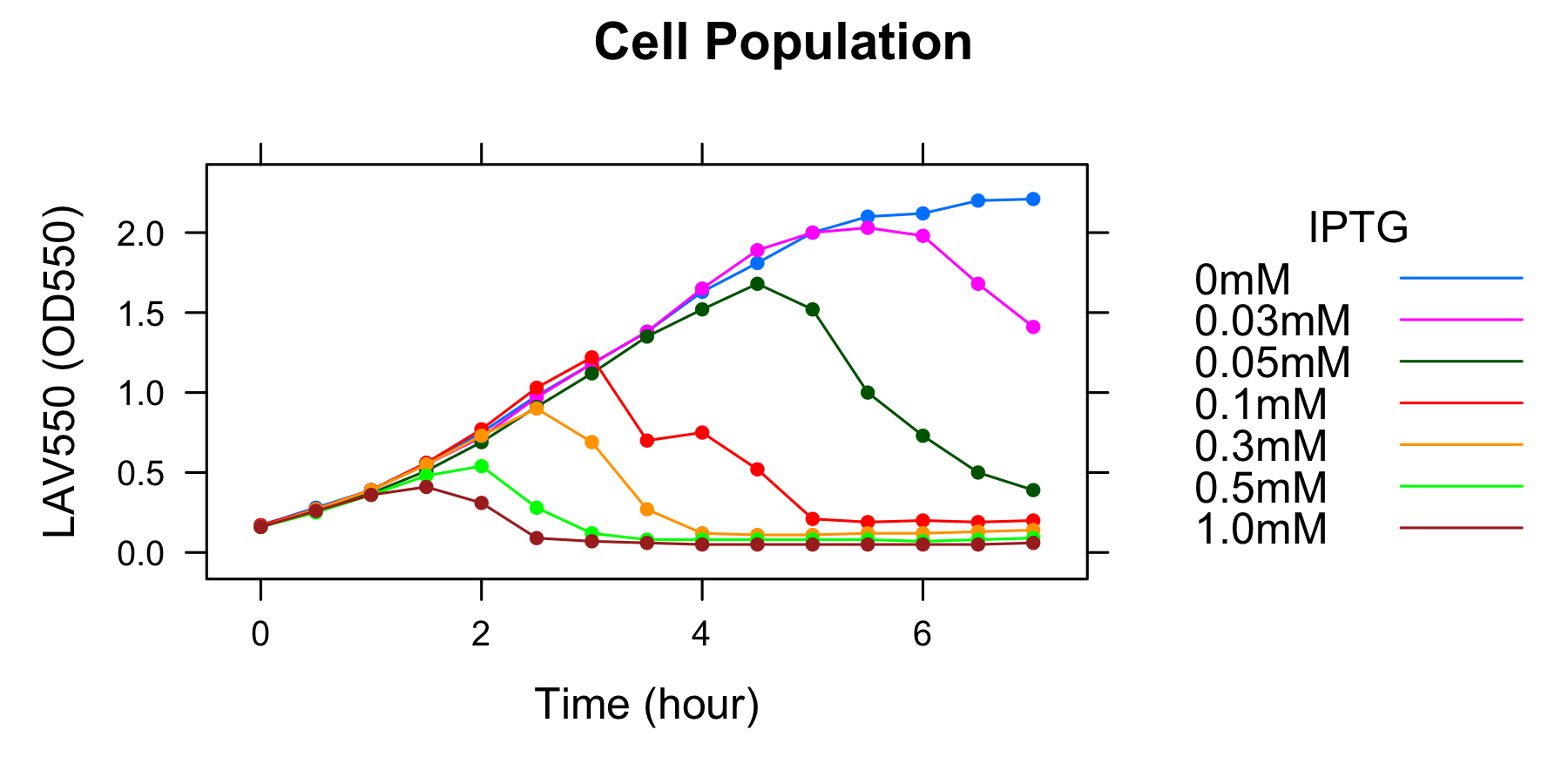
====[[Team:Kyoto/Project/Goal B|Goal B: Quantitative characterization of λ lysis cassette]]==== | ====[[Team:Kyoto/Project/Goal B|Goal B: Quantitative characterization of λ lysis cassette]]==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:KyotoGoalB.png|600px|left]] | ||
[[Image:KyotoFigC004.png|200px|middle]] | [[Image:KyotoFigC004.png|200px|middle]] | ||
| Line 46: | Line 51: | ||
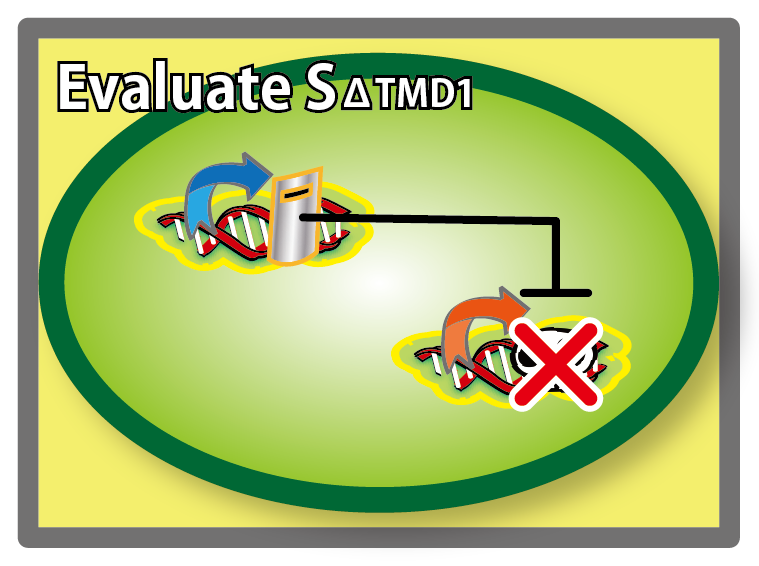
====[[Team:Kyoto/Project/Goal C|Goal C: Characterization of the anti-killer gene, SΔTMD1]]==== | ====[[Team:Kyoto/Project/Goal C|Goal C: Characterization of the anti-killer gene, SΔTMD1]]==== | ||
| + | [[Image:KyotoGoalC.png|600px|left]][[Team:Kyoto/Project/Goal C|[[Image:KyotoArrowC.png|300px]]]] | ||
To check function of the anti-killer gene, first, we made construct and measured A550 of E.coli transformed with the device in medium with IPTG and without IPTG, and we compared this result with that of E.coli transformed with killer gene, lysis cassette. Then, we were able to make sure that Transmembrane domein1 (TMD1) is essential for , lysis cassette. | To check function of the anti-killer gene, first, we made construct and measured A550 of E.coli transformed with the device in medium with IPTG and without IPTG, and we compared this result with that of E.coli transformed with killer gene, lysis cassette. Then, we were able to make sure that Transmembrane domein1 (TMD1) is essential for , lysis cassette. | ||
Revision as of 01:15, 28 October 2010
Contents |
Project
Abstract
The Fantastic Lysisbox: Genetically engineered cell death is essential for the application of biotechnology, such as in bioremediation area. In order to control the cell-death, we designed “Lysisbox”, which consists of a pair of modules: “Killer gene” and “Anti-killer gene.” As the Killer gene for Escherichia coli, we noted the lysis cassette [SRRz/Rz1 gene] of lambda phage coding for holin and endolysin. The holin form pores in the inner membrane and the endolysin access and degrade the peptidoglycan passing through the pores, leading the E.coli to death. As the Anti-killer gene, we chose SΔTMD1 coding for a dominant-negative holin that inhibits the formation of the fatal pores. The balance of these two genes' expression level has the key to the E.coli’s life or death. In addition, such controllable membrane pores should show critical functions for all living organisms with lipid membranes and a cell wall. “Lysisbox” will contribute a lot to all the future iGEM projects, thus you must say “FANTASTIC!!!"
Introduction
Background
The cell-death device is required in many fields [1] [2]. In bioremediation, for example, this device can prevent ecosystem disruption by introduced bacteria [3] [4]. Also, it can be applied to other ideas such as E.coli capsules which scatter drug or aroma by cell-lysis responding to a certain signal. Therefore, the cell-death devices based on diverse approaches, including previous iGEM projects have been developed [1] [3] [5] [6]. However, present cell-death devices are not useful because they have two problems as follows:
Therefore, we attempted to solve these problems and design new BioBricks that are better characterized and more applicable cell-death device to contribute to every future projects.
Problems of Present Cell-Death Devices
1.Need for Quantitative Characterization
In previous iGEM, many teams focused on λ lysis cassette, which is a killer-gene derived from λ phage and causes cell lysis. However, they have only characterized its lytic activity qualititatively. Quantitative characterization of its lytic activity is necessary in order to design a universal and applicable cell-death device. For example, we wish to analyze when cell lysis occurs after induction of λ lysis cassette, how many cells lyse, whether all of cells lyse or not, and so on.
2. Solution to the Restriction on Application of Promoters
In constructing a simple circuit consisting of an inducible promoter and λ lysis cassette, the combinations are limited by the promoter's basal expression, strength of killer-function and many other factors. We looked for the solution to this problem and came up with an idea; using both the lysis cassette and its antikiller-gene, SΔTMD1, which lacks the code for trans membrane domain 1 of killer-gene. We can use two promoters (a constitutive one and an inducible one) for regulating cell-death balance. Into this circuit, we can apply more promoters to this device by using an appropriate constitutive promoter.
We considered that lysis cassette and SΔTMD1 are the most appropriate to killer-gene and anti-killer gene [5]. This was because we found some articles which show the effect of SΔTMD1 in the yeast [9] and also because previous iGEM teams already dealt with lysis cassette.
For further description about lysis cassette and SΔTMD1, go [learn more]
Our Goals
Goal A: Characterization of R0011, a strong lactose promoter
We used R0011, which is one of the most commonly used parts in iGEM, to characterize our genes because the strength of promoter activity is very high. However, in previous iGEM, no teams characterized R0011 with RPU. We tried to determine how the activity of R0011[10] changes.See the detail of Goal A
Goal B: Quantitative characterization of λ lysis cassette
- We found a new fact that cell lysis caused by λ lysis cassette become an apparent equilibrium state, and the value of OD550 depends on the strength of induction of IPTG. We defiend it as LAV (Lytic Activity Value) as a quantitative parameter of lytic activity, and we established a standard method for lytic activity of λ lysis cassette. We characterized the lytic activity of λ lysis cassette quantitatively as our established method, and linked the result to the strength of induction(RPU).
- We characterized the lytic ativity of λ lysis cassette with time. See the detail of Goal B
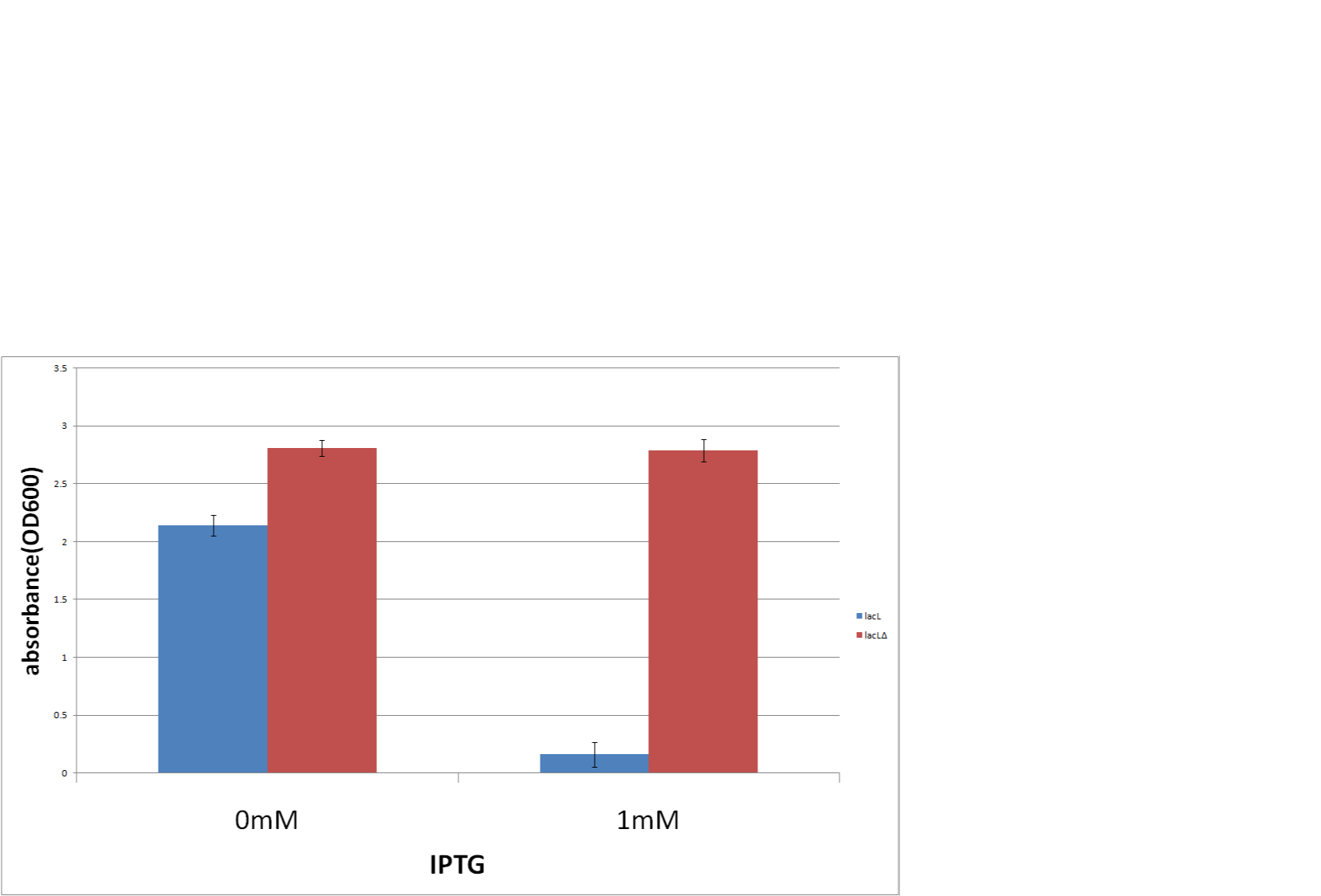
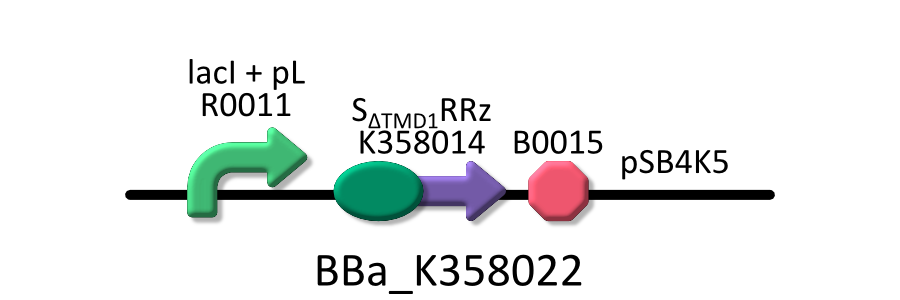
Goal C: Characterization of the anti-killer gene, SΔTMD1
[[Team:Kyoto/Project/Goal C| ]]
]]
To check function of the anti-killer gene, first, we made construct and measured A550 of E.coli transformed with the device in medium with IPTG and without IPTG, and we compared this result with that of E.coli transformed with killer gene, lysis cassette. Then, we were able to make sure that Transmembrane domein1 (TMD1) is essential for , lysis cassette. See the detail of Goal C
Future work
References
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20395970 PMID: 20395970] Khalil AS, Collins JJ., Synthetic biology: applications come of age., Nat Rev Genet. 2010 May;11(5):367-79.
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15832375 PMID: 15832375] Paul D, Pandey G, Jain RK., Suicidal genetically engineered microorganisms for bioremediation: need and perspectives., Bioessays. 2005 May;27(5):563-73.
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15973534 PMID: 15973534] Davison J., Risk mitigation of genetically modified bacteria and plants designed for bioremediation., J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2005 Dec;32(11-12):639-50. Epub 2005 Jun 23.
- https://2009.igem.org/Team:Michigan
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19897658 PMID: 19897658] White R, Tran TA, Dankenbring CA, Deaton J, Young R., The N-terminal transmembrane domain of lambda S is required for holin but not antiholin function., J Bacteriol. 2010 Feb;192(3):725-33. Epub 2009 Nov 6.
- https://2009.igem.org/Team:UNICAMP-Brazil
- https://2008.igem.org/Team:UC_Berkeley
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18713319 PMID: 18713319] Berry J, Summer EJ, Struck DK, Young R., The final step in the phage infection cycle: the Rz and Rz1 lysis proteins link the inner and outer membranes., Mol Microbiol. 2008 Oct;70(2):341-51. Epub 2008 Aug 18.
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2147680 PMID: 2147680] Garrett J, Bruno C, Young R., Lysis protein S of phage lambda functions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae., J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):7275-7.
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19298678 PMID: 19298678] Kelly JR, Rubin AJ, Davis JH, Ajo-Franklin CM, Cumbers J, Czar MJ, de Mora K, Glieberman AL, Monie DD, Endy D., Measuring the activity of BioBrick promoters using an in vivo reference standard., J Biol Eng. 2009 Mar 20;3:4.
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7768829 PMID: 7768829] Chang CY, Nam K, Young R., S gene expression and the timing of lysis by bacteriophage lambda., J Bacteriol. 1995 Jun;177(11):3283-94.
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11459934 PMID: 11459934] Gründling A, Manson MD, Young R., Holins kill without warning., Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001 Jul 31;98(16):9348-52. Epub 2001 Jul 17.
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9573208 PMID: 9573208] Smith DL, Struck DK, Scholtz JM, Young R., Purification and biochemical characterization of the lambda holin., J Bacteriol. 1998 May;180(9):2531-40.
 "
"