Team:TU Delft/Project/solubility/characterization
From 2010.igem.org
(→Emulsifier Assay) |
(→Characterization of the Solubility Parts) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | ==Characterization of the Solubility Parts== | + | ==Characterization of the Hydrocarbon Solubility Parts== |
===Emulsifier Production=== | ===Emulsifier Production=== | ||
Revision as of 14:43, 17 October 2010
Contents |
Characterization of the Hydrocarbon Solubility Parts
Emulsifier Production
The alna gene was induced when the culture reached a density of about 108 bacteria per mL. Bacterial and medium samples were taken for sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-gel electrophoresis to monitor AlnA production. The results shown in Fig. ? indicate that expression of AlnA begins ? min after induction and peaks after ? h.
Emulsifier Assay
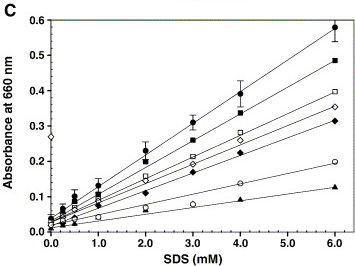
Instead of a colorless hydrocarbon we choose to use the orange Sudan II dye. It stains non-polar molecules and hardly dissolves water. Meanwhile it has a nice absorbance peak at 493 nm, which makes it convenient to measure.
Calibration and Background
Next, the influence of the culture media was determined. We used LB medium for the initial growth of the cells, and induced the production of AlnA in M9 medium. The background influence of the media on the assay were measured, as shown below. It shows that LB medium already has some emulsification effect, but M9 shows very little influence.
 "
"