Team:TU Delft/project/rbs characterization
From 2010.igem.org
(→RBS Characterization) |
(→RBS Characterization) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=RBS Characterization= | =RBS Characterization= | ||
| - | For our RBS characterization project, five different RBS sequences from the [http://partsregistry.org/Ribosome_Binding_Sites/Prokaryotic/Constitutive/Anderson Anderson RBS family] (J61100, J61101, J61107, J61117, J61127) and the standard RBS [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_B0032 B0032] were placed in front of the standard [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_E0040 GFP coding sequence] | + | For our RBS characterization project, five different RBS sequences from the [http://partsregistry.org/Ribosome_Binding_Sites/Prokaryotic/Constitutive/Anderson Anderson RBS family] (J61100, J61101, J61107, J61117, J61127) and the standard RBS [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_B0032 B0032] were placed in front of the standard [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_E0040 GFP coding sequence]. |
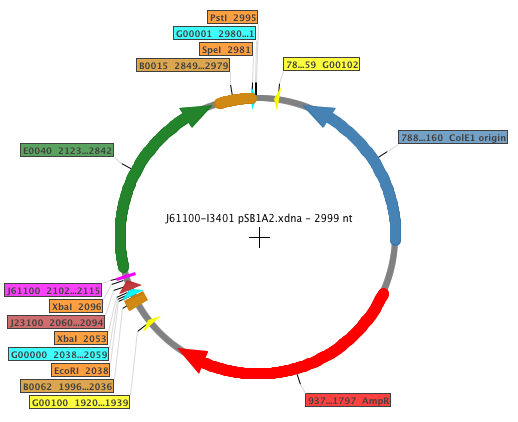
| - | + | The Biobricks generated in order to perform the experiments were: [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K398500 K398500], [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K398501 K398501], [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K398502 K398502], [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K398503 K398503], [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K398504 K398504]. The general map of the construction is shown below, where the RBS is displayed in fucsia. | |
| - | + | ||
[[Image:RBS1.jpg|left|650px]] | [[Image:RBS1.jpg|left|650px]] | ||
{| style="color:black; background-color:white;" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" border="1" | {| style="color:black; background-color:white;" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" border="1" | ||
| Line 39: | Line 38: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
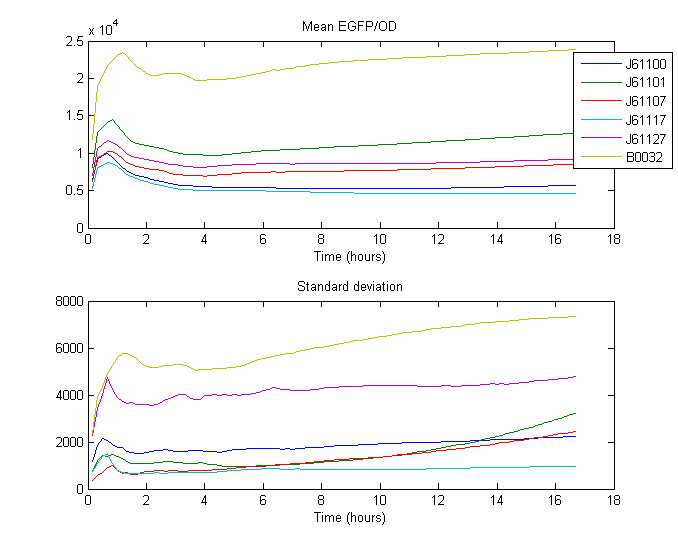
| + | The cells were cultured over 18 hours in 96-well plates using a Gen5 fluorescence and absorbance plate reader, LB with ampicillin was the culture medium used in these experiments. The protein production was measured as fluorescence production. The results are shown below. | ||
[[Image:26_07_2010_Rbs.png|center]] | [[Image:26_07_2010_Rbs.png|center]] | ||
{| | {| | ||
| - | + | The RBS strength was calculated by taking the mean of the ratio between the expression of the standard RBS ([http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_B0032 B0032]) and expression of Anderson RBS over time. Expression being the measured fluorescence divided by measured biomass (absorbance, OD). | |
| + | |||
| + | The measurements were taken from the part of the curve where optimal growth can be assumed; which occurred from 0:40 until 2:30, approximatively. | ||
| + | The result is a simple characterization of the Anderson RBS sequences in relation to the known RBSes. The given strengths are displayed taking the standard RBS [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_B0034 B0034] as reference. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
{| style="color:black; background-color:white;" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" border="1" align="center" | {| style="color:black; background-color:white;" cellpadding="5" cellspacing="0" border="1" align="center" | ||
|'''RBS''' | |'''RBS''' | ||
Revision as of 13:57, 10 August 2010
RBS Characterization
For our RBS characterization project, five different RBS sequences from the Anderson RBS family (J61100, J61101, J61107, J61117, J61127) and the standard RBS B0032 were placed in front of the standard GFP coding sequence. The Biobricks generated in order to perform the experiments were: K398500, K398501, K398502, K398503, K398504. The general map of the construction is shown below, where the RBS is displayed in fucsia.
| Feature | Function |
| AmpR | Ampicillin resistance |
| B0015 | Transcriptional (double) terminator |
| B0062 | Transcriptional terminator |
| E0040 | GFP |
| G00000 | Standard prefix |
| G00001 | Standard suffix |
| G00100 | VF2 primer binding site |
| G00101 | VR primer binding site |
| J61100 | RBS Anderson family |
| J23100 | Promoter |
The cells were cultured over 18 hours in 96-well plates using a Gen5 fluorescence and absorbance plate reader, LB with ampicillin was the culture medium used in these experiments. The protein production was measured as fluorescence production. The results are shown below.
| RBS | Strength |
| J61100 | 0.047513 |
| J61101 | 0.119831 |
| J61107 | 0.065454 |
| J61117 | 0.038518 |
| J61127 | 0.087334 |
| B0032 | 0.300000 |
We've also looked at mRNA folded shapes using mfold to see if there was a common pattern in the Anderson RBS shapes. This might have been usable in predicting RBS strength for the other untested Anderson RBS sequences. Unfortunately, this didn't seem to be the case, as all the tried RBS sequences had very different mfold shapes.
 "
"