Team:TU Delft/project/modeling/sensing
From 2010.igem.org
(Difference between revisions)
(New page: =Modelling of hydrocarbon sensing= To characterize the hydrocarbon sensing system (AlkS and promotors), a model has to be build that describes ...) |
(→Modelling of hydrocarbon sensing) |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
To characterize the [[Team:TU_Delft/project/genetic_regulation|hydrocarbon sensing system]] (AlkS and promotors), a model has to be build that | To characterize the [[Team:TU_Delft/project/genetic_regulation|hydrocarbon sensing system]] (AlkS and promotors), a model has to be build that | ||
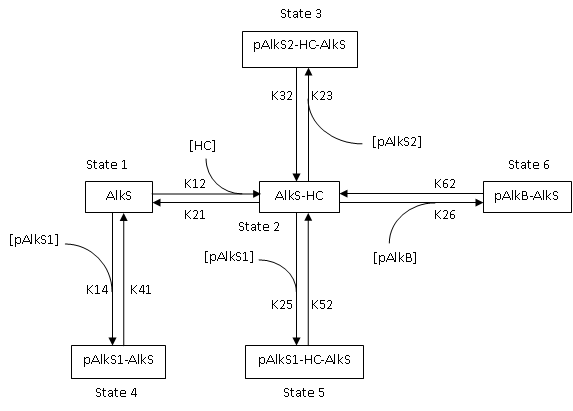
describes the GFP and RFP expression that will be measured with the plate reader. The AlkS protein can bind to various promotors (PAlkS1, PAlkS2, PAlkB) and hydrocarbons. This results in the following protein state diagram: | describes the GFP and RFP expression that will be measured with the plate reader. The AlkS protein can bind to various promotors (PAlkS1, PAlkS2, PAlkB) and hydrocarbons. This results in the following protein state diagram: | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:TUDelft_2010_AlkS_Schema.PNG]] | [[Image:TUDelft_2010_AlkS_Schema.PNG]] | ||
Revision as of 10:49, 12 August 2010
Modelling of hydrocarbon sensing
To characterize the hydrocarbon sensing system (AlkS and promotors), a model has to be build that describes the GFP and RFP expression that will be measured with the plate reader. The AlkS protein can bind to various promotors (PAlkS1, PAlkS2, PAlkB) and hydrocarbons. This results in the following protein state diagram:
Part of the constants will have to be assumed, and hopefully some can be estimated from plate reader expression data.
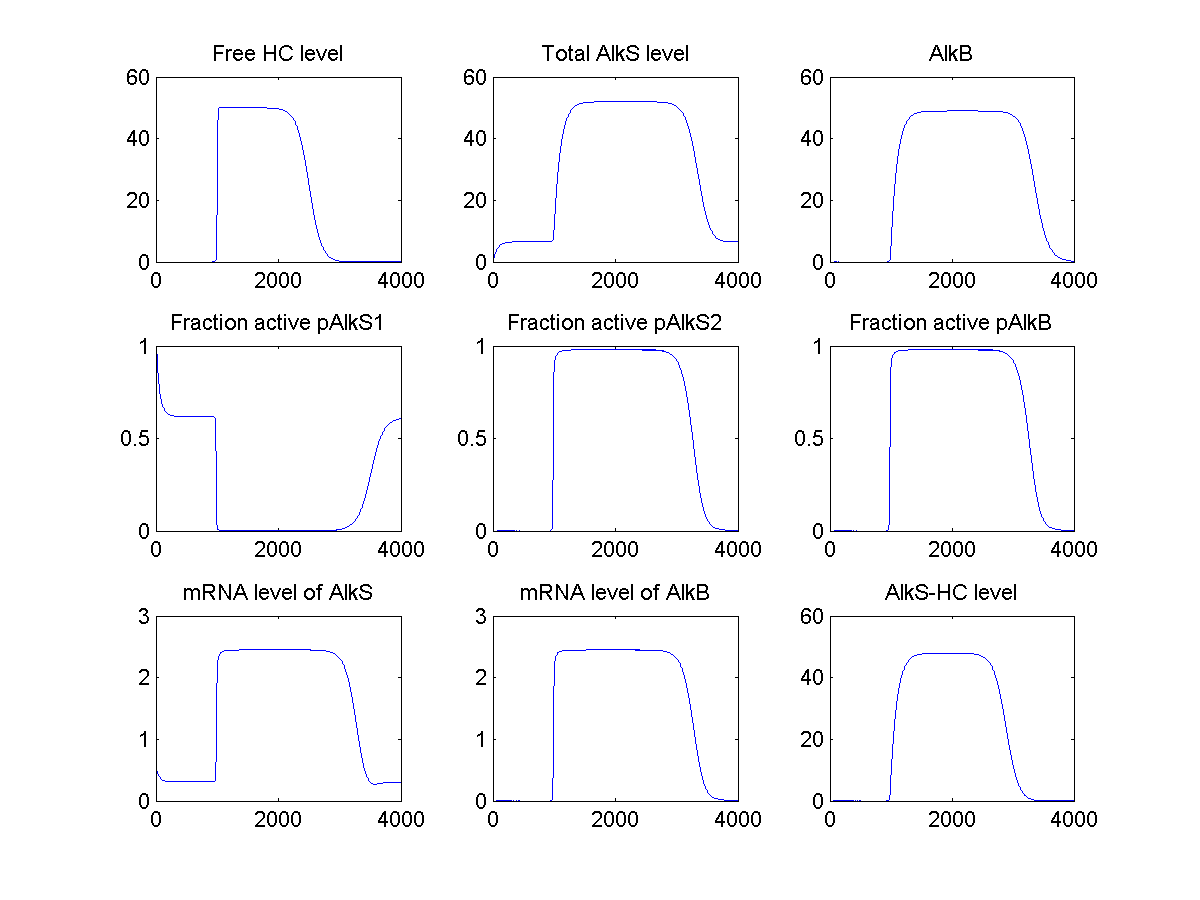
Matlab implementation of this model, and some initial guesses for constants results in the following graphs:
It shows that the model correctly maintains a basal level of AlkS when there are no hydrocarbons (HC), and increases to a high level when HC are added.
 "
"