|
|
| (9 intermediate revisions not shown) |
| Line 3: |
Line 3: |
| | <div id="subnavi"> | | <div id="subnavi"> |
| | <div id="parts"> | | <div id="parts"> |
| - | == K343004 == | + | __TOC__ |
| - | The FlhDC operon is the master regulator of flagella synthesis. A more detailed description of the operon can be found [https://2010.igem.org/Team:SDU-Denmark/project-t#Hyperflagellation here] <br> | + | == K343005 == |
| - | In our system the purpose of the composite part is to hyper flagellate our cells so that a grater force can be generated in the microtubes. The FlhDC operon is naturally found in the ''E. coli'' strain MG1655 genome. We extracted the operon and inserted a silent mutation (T to C) at position 822 in the operon because without the mutation this site is a Pst1 digestion site and it would therefor constitute problems when assembling the composit part. <br> We have made three FlhDC parts:<br> [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K343100 K343100] is the coding sequence of the native FlhDC operon with the Pst1 digestion site <br> [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K343000 K343000] is the coding sequence of the mutated FlhDC operon <br> [http://partsregistry.org/Part:BBa_K343004 K343004] is the composite part containing the TetR repressable promoter (constitutive when no TetR is pressent) + RBS (J13002), the K343000 part and the double terminator (B0015). <br>
| + | ===UV-Vis determination of beta-carotene and retinal production=== |
| - | The composite part is caracterized firstly by using a motility assay and secondly by measuring plasmid stability and cell growth. <br><br> | + | Both beta-carotene and retinal have unique and characteristic spectres when studied by UV-vis spectrometry. The spectra can be obtained by harvesting beta-carotene- and retinal-producing cells, re-suspending them in acetone and lysing them, which we chose to do by sonication. Afterwards, the cell debris can be pelleted and the supernatant can be examinated. <br> |
| | + | The acetone suspension of beta-carotene and retinal can then be subjected to spectrophotometry, and the obtained values and spectra can be compared to those of pure beta-carotene or retinal in known concentrations. This method provides both a qualitative answer to whether or not the desired compound is present and a qualitative indication of the concentration in the cells. <br> |
| | + | In this experiment cells were prepared and harvested according to protocol [https://2010.igem.org/Team:SDU-Denmark/protocols#EX1.1 EX1.1]. This experiment was performed with six different strains of ''E. coli'':<br> <br> |
| | + | Wild type TOP10<br> |
| | + | Wild type MG1655<br> |
| | + | TOP10-pSB1A2-K274210 <br> |
| | + | MG1655-pSB1A2-K274210<br> |
| | + | TOP10-pSB1A2-K274210/pSB1C3-K343005 (double transformants)<br> |
| | + | MG1655-pSB1A2-K274210/pSB1C3-K343005 (double transformants)<br> |
| | + | Both K343005 and K274210 were constitutively expressed.<br><br> |
| | + | Since the first experiment showed no or small amounts of product in cells grown to exponential phase the measurements were performed on cells incubated for 20 hours at 37 degrees Celcius. The graphs obtained from the experiment are presented below:<br> <br> |
| | + | [[Image: Team-SDU-denmark-Samples form top10 mg1655 and control.png |thumb|400px|center|'''Figure 1:''' UV-VIS spectre of six ''E. coli'' strains: Wild type TOP10, Wild type MG1655, TOP10-pSB1A2-K274210, MG1655-pSB1A2-K274210, TOP10-pSB1A2-K274210/pSB1C3-K343005 (double transformants), MG1655-pSB1A2-K274210/pSB1C3-K343005 (double transformants)]] |
| | + | <br><br> |
| | + | In the spectrum a sudden drop between 330 and 320 nm occurs, this can be caused when the samples was auto zeroed according to acetone which is the solvent used in the extraction of the beta-carotene and Retinal.<br> |
| | + | The graph also shows that cell material interferes with the UV-vis measurement where the retinal has the strongest absorption. Therefore, an organic separation is required prior to the measurements.<br> |
| | + | In order to assess the results, standard dilutions of beta-carotene and retinal were made and measured. The concentrations were 1mM, 100 µM, 50 µM, 25 µM, 10 µM, 5 µM, 1 µM, 100 nM and 10 nM. The standard dilutions were measured on the spectrophotometer. The resulting graphs are presented below:<br><br> |
| | + | [[Image: Team-SDU-denmark-Beta-carotene standarts.png|thumb|350px|left|'''Figure 2:''' UV-VIS of beta-carotene at different concentrations. The spectre looks reliable]][[Image: Team-SDU-denmark-Retinal standarts.png|thumb|315px|center|'''Figure 3:'''UV-VIS of retinal at different concentrations. The spectre does not look reliable]] |
| | + | <br> |
| | + | The spectrum for the Beta-carotene looks normal and reliable, the standards for retinal however doesn’t look reliable. The spectra for the three lowest concentrations appears to be distorted and implies that something is interfering with the measurement.<br> |
| | + | The measurement jumps rapidly from nearly nothing to the maximum absorbance, this might be because the concentration of retinal is to low to be measured as a spectrum, but the concentration of the individual derivates of retinal might be high enough to be measured.<br> |
| | + | It might also just be that the concentrations are to low and something else is influencing the measurements.<br> |
| | + | Because of the error in the UV-vis spectra concerning retinal detection in both the standards and samples the next characterization experiments is preformed on a HPLC.<br> |
| | + | |
| | + | All data can be seen under [https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/7/7d/Team-SDU-Denmark-UV-Vis_determination_of_Carotenoids_and_polyene_chromophores_.zip Raw data] |
| | | | |
| - | ===Motility assay=== | + | ==K343006== |
| - | The purpose of this experiment is to test the motility of the transformed cells containing either pSB1C3-K343004 or pSB3K3-K343004. We also want to test if it makes a difference in the motility whether the bacteria contain low-medium- or high-copy plasmids. <br><br>
| + | === HPLC determination of beta-carotene and retinal production === |
| - | For the motility assays we added 5ul of an ON culture to petridishes containing motility agar (LB media with 0.3% agar) instead of regular LA (Luria agar). This semi-solid media lets the bacteria swim more easily. <br>
| + | Apart from spectrophotometry, the resuspension of beta-carotene or retinal in acetone can be subjected to analysis by HPLC. HPLC can be used to separate retinal from beta-carotene, to get a better indication of whether or not our retinal-generating part actually produces retinal from beta-carotene.<br> |
| - | In the assays three control plates were made: A negative control containing ''E. coli'' strain '''DH5alpha''' which does not express flagella and therefore movement in the media should be minimal. A positive control containing ''E. coli'' strain H10407 which is a hyper flagellated class II pathogen, these bacteria should show high motility. And a wild type ''E. coli'' strain '''MG1655''' that has about 4 flagella per cell these cells would be expected to move farther than the DH5alpha but not as far as the positive control. <br><br> | + | In this experiment cells were prepared and harvested according to protocol [https://2010.igem.org/Team:SDU-Denmark/protocols#EX1.2 EX1.2]. This experiment was performed with six different strains of ''E. coli'':<br> <br> |
| - | The plates were incubated at 37 degrees celcius for up to 48 hours. <br>
| + | Wild type TOP10<br> |
| - | The assay was carried out three times. All three times pictures were taken after 24 hours and in two of the assays pictures were also taken after 48 hours. In two of the assays 8.5 cm petridishes was used, the purpose of these assays was to se if the motility of our transformants differed from the control strains. In the third assay we used 13.5 cm petridishes to oberserve the transformants swimming ability compaired to the wild type ''E. coli'' strain MG1655 since the motility of the transformed cells seem to surpass the size of the 8.5 cm petri dishes. <br><br>
| + | Wild type MG1655<br> |
| - | All the pictures taken after 24 hours are shown in the last part of this section while the pictures taken after 48 hours are shown and described. <br>
| + | TOP10/pSB1A2-K274210 <br> |
| - | ''' WT, negative- and positive-control after 48 hours:''' <br>
| + | MG1655/pSB1A2-K274210<br> |
| - | [[Image:Team SDU-Denmark motility exp 3 DH5alpha.JPG|150px|DH5alpha after 48 hours]]
| + | TOP10/pSB1A2-K274210/pSB1C3-K343005<br> |
| - | [[Image:Team SDU-Denmark motility exp 3 MG1655.JPG|150px|MG1655 after 48 hours]]
| + | MG1655/pSB1A2-K274210/pSB1C3-K343005<br> |
| - | [[Image:Team SDU-Denmark motility exp 3 H10407.JPG|150px|H10407 after 48 hours]] <br><br>
| + | Both K343005 and K274210 were constitutively expressed.<br><br> |
| - | [[Image:Team SDU-Denmark motility exp 3 pSB1C3-K343004.JPG|300px|thumb|left|Motility of ''E. coli'' strain MG1655-pSB1C3-K343004 after 48 hours. Cells were grown in a 37 degrees Celcius incubator.]] | + | MG1655 containing PSB1A2 with K274210 or PSB1C3 with K343005 were both under a constitutively active promotor<br> |
| - | [[Image:Team SDU-Denmark motility exp 3 pSB3K3-K343004.JPG|300px|thumb|center|Motility of ''E. coli'' strain MG1655-pSB3K3-K343004 after 48 hours. Cells were grown in a 37 degrees Celcius incubator.]]<br><br> | + | The measurements were preformed on cells after 20 hours of growth. The resulting graphs is presented beneath the text.<br> |
| - | In all three assays we saw that the control plates containing no antibiotics were contaminated with other bacterial colonies. We also saw that the negative control has low motility but they are not immotile. After 24 hours the negative control has not moved much but after 48 hours the length from center to edge of the colony is 1.5cm. The wild type has moved a bit farther than the negative control after 24 hours and after 48 hours the difference from center to edge of the wild type is 2.5cm. The positive control moved about as far in 24 hours as the wild type did in 48 which and after 48 hours it had moved to the edges of the petridish (4.25cm). this was as expected because of their hyper flagellation. <br><br>
| + | [[Image:Team SDU-Denmark-HPLC samples2.png|thumb|center|300px|'''Figure 4:''' HPLC analysis of samples from the 19th oct. 2010 Beta-carotene Peaks are clearly present, but no retinal peaks are observed. Measurements were made after 20 hours of growth]] |
| - | The ''E. Coli'' strain MG1655 cells transformed with pSB1C3-K343004 shows that after 24 hours these bacteria have moved farther than the wild type and the negative control. The ''E. coli'' strain MG1655/pSB3K3-K343004 have moved farthest of all 5 cultures after 24 hours. This mortility pathern are observed in all three assays. The cells containing the pSB3K3 plasmid show a uniform circle whereas the cells transformed with the pSB1C3 plasmid shows a budding-pattern spreading from the center. After 48 hours the pSB1C3 cells are still not covering the entire plate. <br><br> | + | [[Image:Team SDU-Denmark-HPLC samples1.png|thumb|center|300px|'''Figure 5:''' HPLC analysis of samples from the 22nd oct. 2010 Beta-carotene Peaks are clearly pressent, but no retinal peaks are observed. Measurements were made after 20 hours of growth]]<br> |
| - | '''''Pictures of plates after 24 hours''''' <br>
| + | When looking at the retinal and beta-carotene standards analysed on the HPLC, peaks for both chemicals are clearly present. The retinal retention time is 3,480-3,490 minutes and the beta-carotene retention time is 23,300-23,600 minutes.<br> |
| - | '''Experiment 1.''' <br>
| + | The spectra for the first run of samples show large amounts of beta-carotene, smaller amounts of which also are products produced by the K274210 biobrick or absorbed form the media in the cells where the K274210 biobrick is absent.<br> |
| - | [[Image:Team-SDU-Denmark-Flagellamotility-exp1-DH5a.JPG|100px|DH5alpha after 24 hours]] | + | The spectra shows no measurable amounts of retinal in neither of the samples, but the samples produced by bacteria containing the K343006 brick have a lower amount of beta-carotene, which can indicated that either the bacterial production of beta-carotene is lowered or that some of the beta-carotene has been metabolized in the cell, either to a non-measurable concentration of Retinal or some other metabolite. It is also a possibility that the retinal is exported out of the cells.<br> |
| - | [[Image:Team-SDU-Denmark-Flagellamotility-exp1-MG1655.JPG|100px|MG1655 after 24 hours]]
| + | The spectra from the second run of samples again show large amounts of beta-carotene produced by the K274210 biobrick or absorbed form the media in the cells where the K274210 biobrick is absent.<br> |
| - | [[Image:Team-SDU-Denmark-Flagellamotility-exp1-FlhDCmutCP_i_pSB1C3_(LA+chlor).JPG|100px|pSB1C3-FlhDCmutCP after 24 hours.]]
| + | The only sample displaying any changes form the first run on the HPLC is TOP10 containing both the K343006 and K274210 biobricks. In the spectrum higher amounts of cell metabolites are still being produced by the K274210 biobrick but also others are produced by the cell. |
| - | [[Image:Team-SDU-Denmark-Flagellamotility-exp1-FlhDCmutCP_i_pSB3K3_(LA+kan).JPG|100px|pSB3K3-FlhDCmutCP after 24 hours]]<br><br>
| + | In this spectra the peak with a retention time of 3,969 is close to the retention time of retinal form the standards but when examining the spectrum of the peak it can be concluded that it is not a retinal peak.<br> |
| - | '''Experiment 2.''' <br>
| + | <br> |
| - | [[Image:Team-SDU-Denmark-Flagellamotility-exp2-DH5a.JPG|100px|DH5alpha after 24 hours]] | + | In order to assess and quantify the results a standard dilution of beta-carotene and retinal was made and measured: 10 µM, 5 µM, 1 µM, 2 µM, 0,5 µM. The standard dilutions were also measured on the HPLC with the same injection volume and program as the samples. The resulting graphs are presented beneath <br> |
| - | [[Image:Team-SDU-Denmark-Flagellamotility-exp2-MG1655.JPG|100px|MG1655 after 24 hours]] | + | [[Image:Team SDU-Denmark-HPLC standards1.png|400px|thumb|center| '''Figure 6:''' HPLC of standard dilutions of beta-carotene and retinal]] |
| - | [[Image:Team SDU-Denmark motility exp 2 FlhDCmutCP in pSB1C3.JPG|100px|FlhDCmutCP in pSB1C3 after 24 hours]]
| + | <br> |
| - | [[Image:Team SDU-Denmark motility exp 2 FlhDCmutCP in pSB3K3.JPG|100px|FlhDCmutCP in pSB3K3 after 24 hours]]
| + | When doing an HPLC analysis it is possible to quantify the amounts of the chemical compounds in the samples.<br> |
| - | [[Image:Team SDU-Denmark exp 2 H10407.JPG|100px|H10407 after 24 hours]]<br><br> | + | This is done by generating a standard curve with known dilutions of the chemical and recording the area under the peaks. The peak area correspond to the concentration of the chemical in the sample.<br> |
| | + | Then the area under the peaks is plotted on the y- axis, the know concentrations of the standards on the x-axis and the regression line is calculated.<br> |
| | + | Now it is possible to calculate unknown concentrations from samples using the regression line from the standard curves.<br> |
| | + | The results for our HPLC analysis can be seen beneath the text.<br> |
| | + | [[Image:Team-SDU-Denmark-Amount of beta-carotene and retinal i standards.png|thumb|400px|center|'''Figure 7:''' Standard curve of area under the HPLC peaks against beta-carotene and retinal concentration. Regression lines were made.]] |
| | + | From the equations for the regression line it is possible to calculate the amount of beta-carotene produced by bacteria grown for 20 hours in LB media.<br> |
| | + | [[Image:Team-SDU-Denmark-Beta-carotene amounts.png|400px|thumb|center|'''Tabel 1:''' Showing calculatet beta-carotene content in samples]] |
| | + | <br> |
| | + | All data can be seen under [https://2010.igem.org/Image:Team-SDU-denmark-HPLC_determination_af_beta-carotene_and_retinal_production.zip Raw data]<br> |
| | | | |
| - | ''' Conclusion''' <br> | + | === Stability assay === |
| - | From the pictures above we can see that the bacteria containing our part is much more motile than the wild type and the negative control. We assume this is caused by overexpression of the FlhDC master flagella operon which leads to hyperflagellation of the cells. <br>
| + | To determine the stability of our pSB1C3-K343006 plasmid, a stability experiment was carried out according to protocol [[https://2010.igem.org/Team:SDU-Denmark/protocols#Stability_assay SA1.1]]. ''E.coli'' MG1655/pSB1C3-K343006 was grown in LB media without chloramphenicol, whereby no selection pressure is exerted on the bacteria. Dilutions of the culture was spreaded onto LA plates and LA plates with 35µg/mL chloramphenicol, respectively, and the colony forming units (CFU) was determined for each plate. The CFU for the LA plates represents the total amount of bacteria in the culture, and the CFU of LA plates with chloramphenicol corresponds to the amount of plasmid carrying bacteria. The percentage of the total amount of bacteria carrying the plasmid was plotted in a semi-logarithmic graph as a function of number of generations.<br><br> |
| - | The pictures taken after 24 hours show that bacteria with pSB1C3-K343004 have not moved as far as the bacteria containing pSB3K3-K343004. pSB1C3 is a high copy plasmid while pSB3K3 is a low-medium copy plasmid. The promoter in K343004 is a constitutive promoter (tetR repressable promoter). Bacteria containing a high copy plasmid with a constitutive promoter are more metabolically challanged than bacteria containing a low- or medium-copy plasmid with a constitutive promoter because of the higher number of plasmids per the cell. Therefore the high copy plasmid bacteria move slower than low- or medium-copy plasmid bacteria. However, after 48 hours there was only a small different in the bacterias migration. <br><br> | + | [[Image:Team-SDU- NinaB stab2.png|400px|thumb|center|'''Figure 8:''' Stability assay of ''E. coli'' strain MG1655-pSB1C3-K343006 showing that almost all cells have shed their plasmids within 20 generations, however some cells kept the plasmids for up to 40 generations.All data can be seen under [https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/3/39/Team-SDU-_NinaB_stability_assay.ZIP Raw data]]]<br><br> |
| | | | |
| - | ===Flagella staining===
| + | As seen in the graph, almost all of the bacteria had lost the plasmid after 20 generations, suggesting that the plasmid is only stable within the cell for a few generations (<20). This is presumably due to the strain brought upon the bacteria by the plasmid. Thereby when the bacteria are carrying a high-copy plasmid like pSB1C3-K343006 it is plausible that the bacteria will quickly lose the plasmid when no longer exposed to a selection pressure. |
| - | <br>
| + | |
| - | When the ''E.coli'' strain MG1655 are transformed with pSB1C3-K343004 an increased flagella production is expected. The idea was to get a quantitative measurement of the increased flagella production by comparing the observed number flagella on the wild type MG1655 and the transformant. We tried to stain the flagella using silver staining and afterwards examined the bacteria under the microscope. The staining procedure was started before the composite part, K343004, was finished so that we could optimize the staining protocol and become really good at staining the flagella. We started with staining of DH5α and H10407; A ''E.coli'' strain which do not express flagella (negative control) and a hyperflagellated ''E.coli'' (positive control), respectively. The bacteria were grown on agar plates ON and stained with this protocol [https://2010.igem.org/Team:SDU-Denmark/protocols#FS1.2 FS1.2]. <br> <br>
| + | |
| - | Unfortunately it was not possible to see a clear and significant difference between the positive and negative control. Though at some places it could look like flagella on the positive control but it was never enough to determine a difference. After repeating the protocol four times, each time with multiple samples, we decided to reject this method, and another approach for characterizing our biobrick was employed. <br>
| + | |
| | | | |
| - | [[Image:Team_SDU-Denmark_Silver_staining_of_H10407_a_positive_control..JPG|300px|thumb|left|Silver staining of ''E. coli'' strain H10407 which should be hyperflagellated. However, no .]][[Image:Team_SDU-Denmark_Silver_staining_of_DH5α_the_negative_control.JPG|300px|thumb|center|Silver staining of DH5alpha: a negative control]]<br>
| + | ===Growth assay=== |
| - | | + | The purpose of this assay is to see if our transformants deviate from the wild type in growth rate. In the growth measurement assay we have measured OD at 550 nm every hour for 12 hours and at hour 24. In the experimental setup we used, no lag phase was observed in any of the measurements. |
| - | === Scanning Electron microscopy ===
| + | The graph below shows the growth of our wild type E. coli strain MG1655 and the MG1655/pSB1C3-K343006, respectively.<br><br> |
| - | <br>
| + | [[Image: Team SDU-Denmark OD WT+NinaB.JPG|400px|thumb|center|'''Figure 9:''' Growth curve showing measured OD at 550nm. Samples were taken every hour over a 12 hour perion + one sample after 24 hours. In graph ''E. coli'' strain MG1655-pSB1C3-k343006 is compaired with Wild type ''E. coli'' strain MG1655 showing no significant difference between the three graphs. No Lag phase is seen.All data can be seen under [https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/6/68/Team_SDU-Denmark_Growth_rate_assay_no._2_NinaB.zip Raw data]]] <br><br> |
| - | After the failed staning of the flagella we tried to visualize the flagella with scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The bacteria were grown ON in liquid cultures (5 ml LB-media). The bacteria were diluted to approximately 10^6 cells pr 10 µl solution. At that time we did not have our K343004 composite part so therefore we only tried SEM with the negative control strain DH5alpa and wild type MG1655. We did this as a preliminary work so we would be ready to do microscopy on the MG1655 cells containing the composite part when it was ready. Unfortunately the limited resolution and magnitude of the SEM at our disposal made it practically impossible to visualize any flagella in the microscope. Thus if this approach is to be used for characterization, a SEM of higher magnitude and resolution is required.<br>
| + | From our data we see no significant difference between the plasmid carrying bacteria and the wild type. This can be said to be quite contradictory to our results obtained from the stability assay. The transitory stability of pSB1C3-K343006 suggests that it is highly unfavorable for the bacteria, wherefore it might be expected that the growth of the bacteria containing this plasmid would be affected. Thus, however large a disadvantage the plasmid pose to the bacteria, their growth are not significantly influenced by the plasmid. The added reproduction load due to the plasmids, might also prolong the lag phase of the bacteria. Whether this is the case can not be concluded based on this experiment as no lag phase was observed in this experiment. |
| - | The pictures below are SEM pictures the negative control strain DH5alpha and wild type MG1655.<br>br>
| + | |
| - | [[Image:Team SDU-Denmark_DH5alpha_MAG_5.0_kx_and_EHT_7.5_kV.JPG|thumb|left|300px|SEM picture of DH5alpa a negative control that should not express flagella]][[Image:Team_SDU-Denmark_Mg1655_MAG5kx_and_EHT_7.5kV.JPG|thumb|center|300px|SEM picture of the ''E. coli'' strain MG1655 wild type this strain of bacteria should express approximately 4 flagella per cell.However, no flagella are visable]]
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | ===Stability assay===
| + | |
| - | To dertermine the stability of our pSB1C3-K343004 plasmid, a stability experiment was carried out according to protocol[[https://2010.igem.org/Team:SDU-Denmark/protocols#Stability_assay SA1.1]]. ''E.coli'' MG1655/pSB1C3-K343004 was grown in LB media without chloramphenicol, whereby no selection pressure is excerted on the bacteria. Dilutions of the culture was spreaded on LA plates and LA plates with 35ug/mL chloramphenicol, respectively, and the colony forming units (cfu) was determined for each plate. The cfu for the LA plates represents the total amount of bacteria in the culture, and the cfu of LA plates with chloraphenicol corresponds to the amount of plasmid carrying bacteria. The percentage of the total amount of bacteria carrying the plasmid was plotted in a semi-logarithmic graph as a function of number of generation.<br><br>
| + | |
| - | [[Image:Team-SDU-DC stab 2.png|thumb|400px|center| Stability assay of ''E. coli'' strain MG1655-pSB1C3-K343004 showing that almost all cells have shed their plasmids within 20 generations, however some cells kept the plasmids for up to 40 generations. All data can be seen under [https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/0/09/Team-SDU-_flhDC_stability_assay.ZIP Raw data]]]
| + | |
| - | <br><br>
| + | |
| - | As seen in the graph, almost all of the bacteria had shedded the plasmid after 20 generations, suggesting that the plasmid is only stable within the cell for a few generations (<20). This is presumably due to the strain brought upon the bacteria by the plasmid. Thereby when the bacteria are carrying a high-copy plasmid like pSB1C3-K343004 it is to expect that the bacteria will quickly shed the plasmid when no longer exposed to a selection pressure.
| + | |
| - | It is likely to believe that pSB3C5-K343004, since being a low-copy plasmid, will not excert as much strain on the bacteria, and might therefore be stable for more genrations than pSB1C3-K343004. Therefore a stability assay of this plasmid might be of interest.
| + | |
| - | | + | |
| - | ===Growth assay=== | + | |
| - | The purpose of this assay is to see if our transformants deviate from the wild type in growth rate. In the growth measurement assay we have measured OD at 550 nm every hour for 12 hours and at hour 24. In the experimental set-up we used no lag phase was observed in any of the measurements. | + | |
| - | The graph below shows the growth of our wild type E. coli strain MG1655, the MG1655/pSB3K3-K343004 and MG1655/pSB1C3-K343004 respectively.<br><br> | + | |
| - | [[Image:Team SDU-Denmark OD WT+FlhDCmutCP.JPG|400px|thumb|center|Growth curve of ''E.coli'' strain MG1655-pSB1C3-K343004 and MG1655-pSB3K3-K343004 compared with the wild type ''E. coli'' strain MG1655 showing no significant difference between the three curves. No Lag phase observed. All data can be seen under [https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2010/c/c5/Team_SDU-Denmark_Growth_rate_assay_FlhDCmut_CP.zip Raw data]]]<br><br> | + | |
| - | From our data we see no significant difference between the plasmid carrying bacteria and the wild type. This can be said to be quite contradictory to our results obtained from the stability assay. The transitory stability of pSB1C3-K343004 suggests that it is highly unfavourable for the bacteria, wherefore it might be expected that the growth of the bacteria congaing this plasmid would be affected. Thus, however much a disadvantage the plasmid pose to the bacteria, their growth are not significantly influenced by the plasmid. The added reproduction load due to the plasmids, might also prolong the lag phase of the bacteria. Whether this is the case can not be concluded based on this experiment as no lag phase was observed in this experiment. | + | |
| - | <br><br>
| + | |
| | | | |
| - | === Phase contrast of ON cultures===
| + | <br> |
| - | The purpose of the phase contrast microscopy is to see if the transformants are visibly different from the wild type. Since the FlhDC operon is not only an important part of the flagella synthesis but is also coupled to cell metabolism [[https://2010.igem.org/Team:SDU-Denmark/project-p#References 3]], it might be possible to see difference in morphology caused by an alterations in the cell cycle. <br>
| + | <br> |
| - | Phase contrast pictures were taken of wild type MG1655, MG1655/pSB1C3-K343004 and MG1655/pSB3K3-K343004.<br><br>
| + | </div></div> |
| - | [[Image:Team-SDU-Denmark-Flagella-PCM-1.jpg|630px|center|thumb]]<br><br>
| + | |
| - | The pictures clearly show a difference in morphology of the wild type (picture 1) and the two transformants (picture 2-pSB1C3 and 3-pSB3K3). The wild type cells are small cells, while the transformants are obviously larger, which indicates a lower metabolism of the transformants. Cells with impaired metabolism divide slower and are larger than cells with normal metabolism (wild type), since it takes the impaired cells longer to reach the mitotic phase of the cell cycle.
| + | |
| - | </div> | + | |
| - | </div> | + | |
K343005
UV-Vis determination of beta-carotene and retinal production
Both beta-carotene and retinal have unique and characteristic spectres when studied by UV-vis spectrometry. The spectra can be obtained by harvesting beta-carotene- and retinal-producing cells, re-suspending them in acetone and lysing them, which we chose to do by sonication. Afterwards, the cell debris can be pelleted and the supernatant can be examinated.
The acetone suspension of beta-carotene and retinal can then be subjected to spectrophotometry, and the obtained values and spectra can be compared to those of pure beta-carotene or retinal in known concentrations. This method provides both a qualitative answer to whether or not the desired compound is present and a qualitative indication of the concentration in the cells.
In this experiment cells were prepared and harvested according to protocol EX1.1. This experiment was performed with six different strains of E. coli:
Wild type TOP10
Wild type MG1655
TOP10-pSB1A2-K274210
MG1655-pSB1A2-K274210
TOP10-pSB1A2-K274210/pSB1C3-K343005 (double transformants)
MG1655-pSB1A2-K274210/pSB1C3-K343005 (double transformants)
Both K343005 and K274210 were constitutively expressed.
Since the first experiment showed no or small amounts of product in cells grown to exponential phase the measurements were performed on cells incubated for 20 hours at 37 degrees Celcius. The graphs obtained from the experiment are presented below:
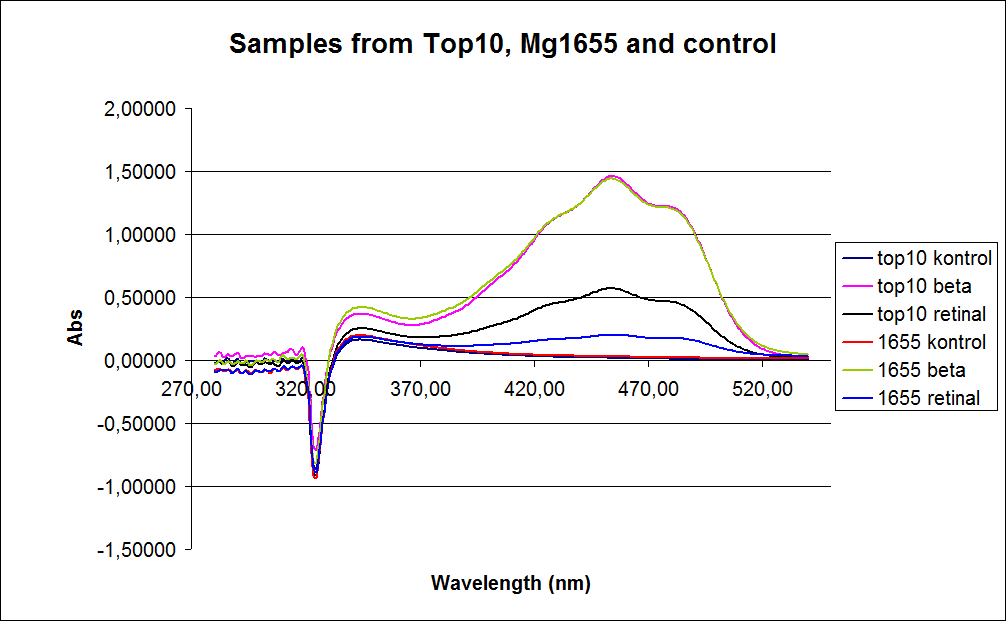
Figure 1: UV-VIS spectre of six
E. coli strains: Wild type TOP10, Wild type MG1655, TOP10-pSB1A2-K274210, MG1655-pSB1A2-K274210, TOP10-pSB1A2-K274210/pSB1C3-K343005 (double transformants), MG1655-pSB1A2-K274210/pSB1C3-K343005 (double transformants)
In the spectrum a sudden drop between 330 and 320 nm occurs, this can be caused when the samples was auto zeroed according to acetone which is the solvent used in the extraction of the beta-carotene and Retinal.
The graph also shows that cell material interferes with the UV-vis measurement where the retinal has the strongest absorption. Therefore, an organic separation is required prior to the measurements.
In order to assess the results, standard dilutions of beta-carotene and retinal were made and measured. The concentrations were 1mM, 100 µM, 50 µM, 25 µM, 10 µM, 5 µM, 1 µM, 100 nM and 10 nM. The standard dilutions were measured on the spectrophotometer. The resulting graphs are presented below:
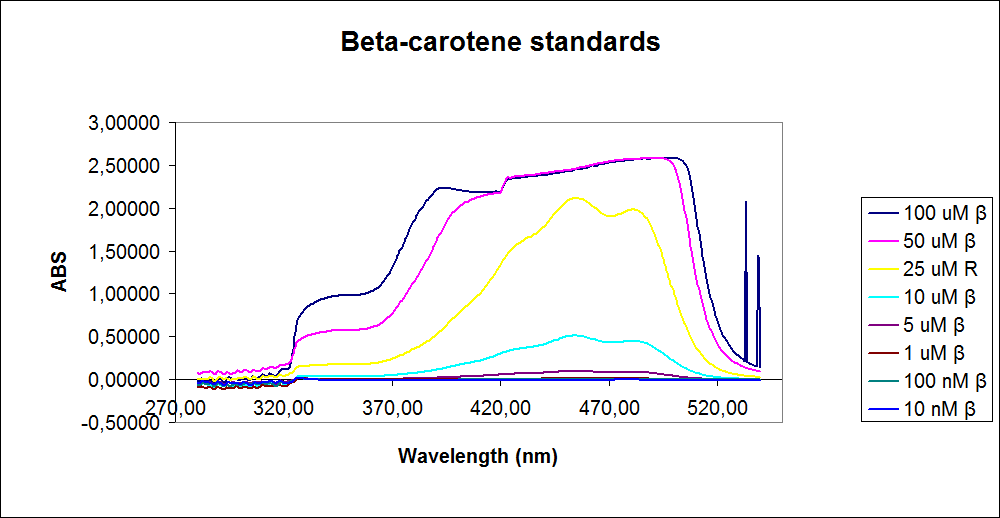
Figure 2: UV-VIS of beta-carotene at different concentrations. The spectre looks reliable
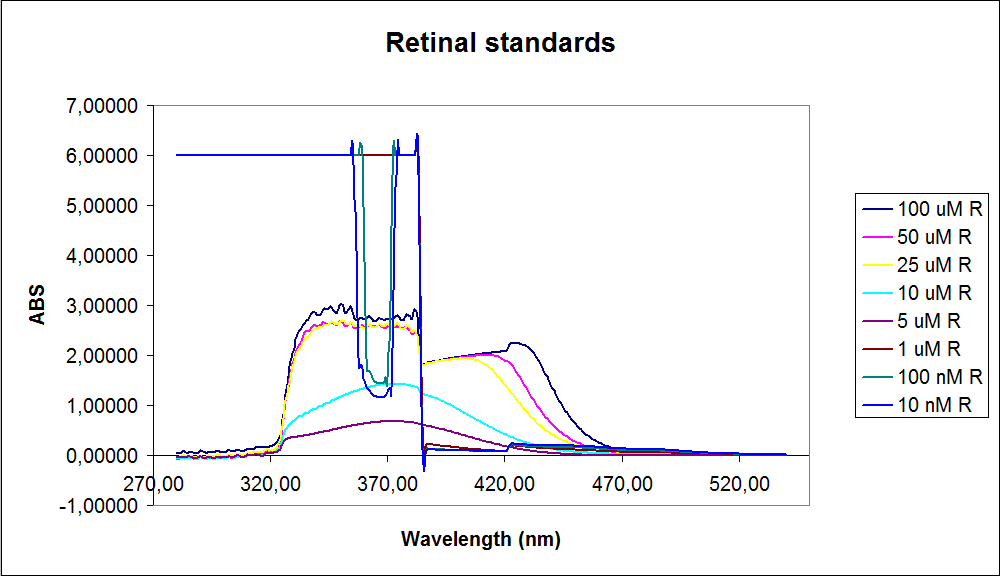
Figure 3:UV-VIS of retinal at different concentrations. The spectre does not look reliable
The spectrum for the Beta-carotene looks normal and reliable, the standards for retinal however doesn’t look reliable. The spectra for the three lowest concentrations appears to be distorted and implies that something is interfering with the measurement.
The measurement jumps rapidly from nearly nothing to the maximum absorbance, this might be because the concentration of retinal is to low to be measured as a spectrum, but the concentration of the individual derivates of retinal might be high enough to be measured.
It might also just be that the concentrations are to low and something else is influencing the measurements.
Because of the error in the UV-vis spectra concerning retinal detection in both the standards and samples the next characterization experiments is preformed on a HPLC.
All data can be seen under Raw data
K343006
HPLC determination of beta-carotene and retinal production
Apart from spectrophotometry, the resuspension of beta-carotene or retinal in acetone can be subjected to analysis by HPLC. HPLC can be used to separate retinal from beta-carotene, to get a better indication of whether or not our retinal-generating part actually produces retinal from beta-carotene.
In this experiment cells were prepared and harvested according to protocol EX1.2. This experiment was performed with six different strains of E. coli:
Wild type TOP10
Wild type MG1655
TOP10/pSB1A2-K274210
MG1655/pSB1A2-K274210
TOP10/pSB1A2-K274210/pSB1C3-K343005
MG1655/pSB1A2-K274210/pSB1C3-K343005
Both K343005 and K274210 were constitutively expressed.
MG1655 containing PSB1A2 with K274210 or PSB1C3 with K343005 were both under a constitutively active promotor
The measurements were preformed on cells after 20 hours of growth. The resulting graphs is presented beneath the text.
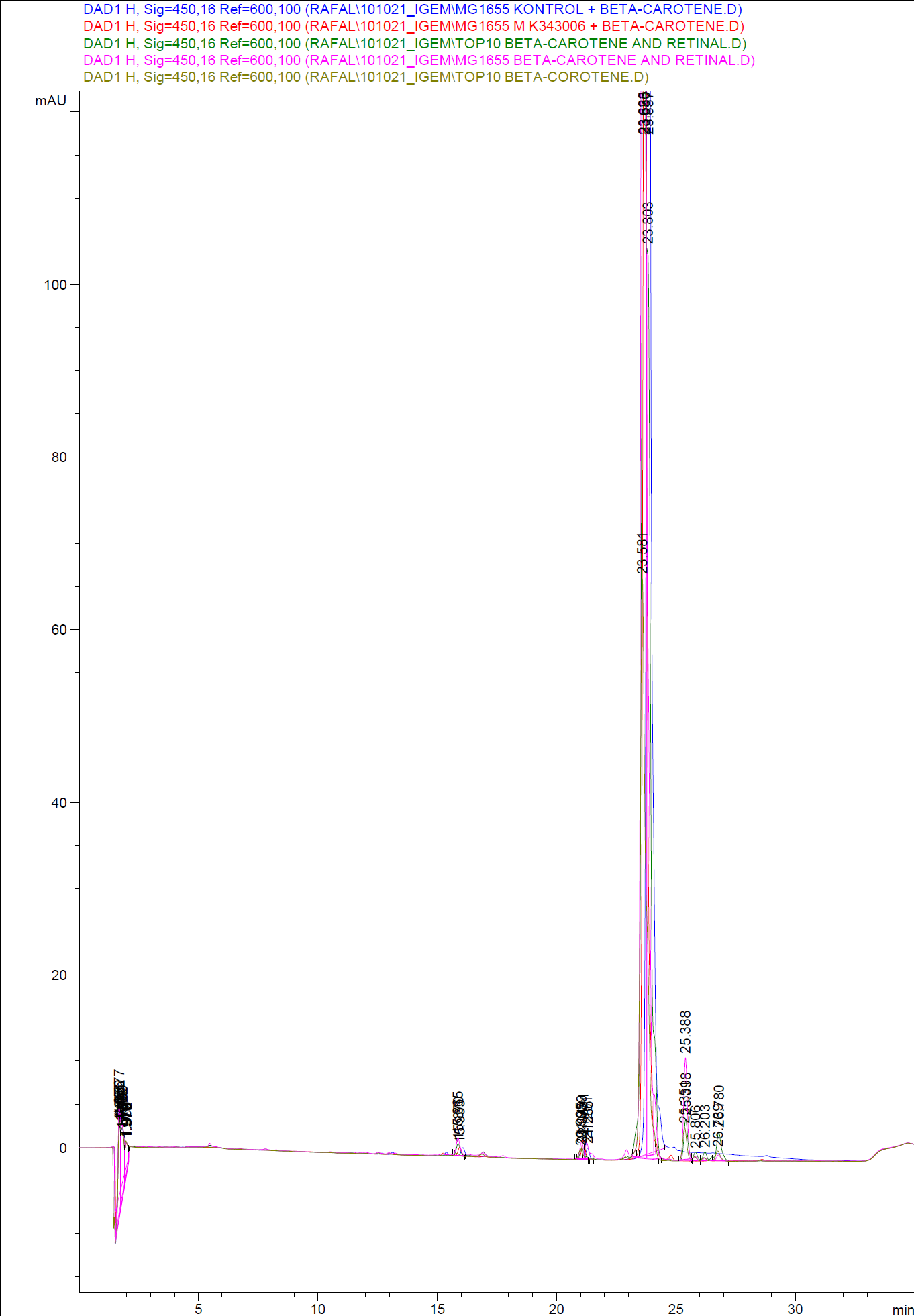
Figure 4: HPLC analysis of samples from the 19th oct. 2010 Beta-carotene Peaks are clearly present, but no retinal peaks are observed. Measurements were made after 20 hours of growth
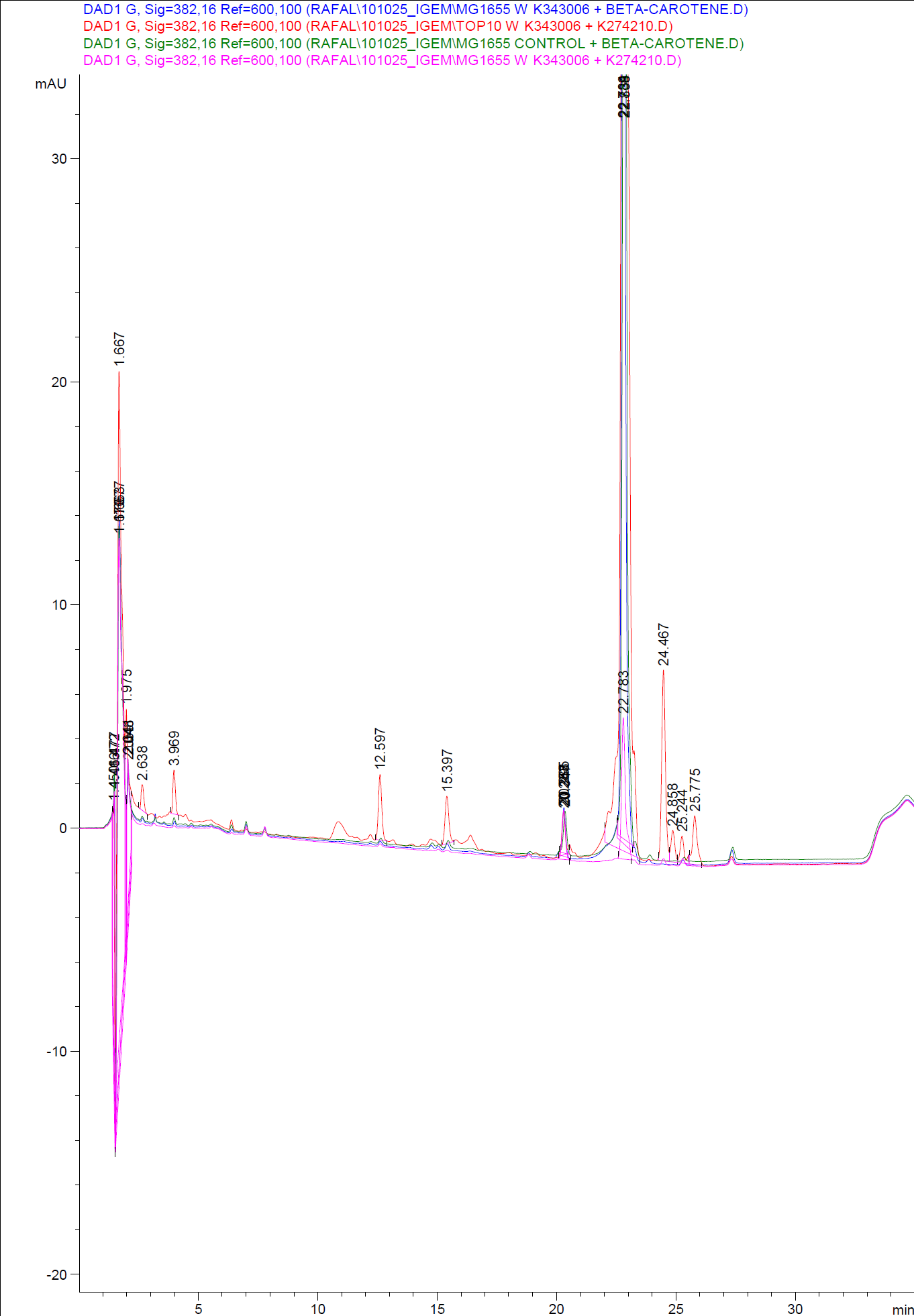
Figure 5: HPLC analysis of samples from the 22nd oct. 2010 Beta-carotene Peaks are clearly pressent, but no retinal peaks are observed. Measurements were made after 20 hours of growth
When looking at the retinal and beta-carotene standards analysed on the HPLC, peaks for both chemicals are clearly present. The retinal retention time is 3,480-3,490 minutes and the beta-carotene retention time is 23,300-23,600 minutes.
The spectra for the first run of samples show large amounts of beta-carotene, smaller amounts of which also are products produced by the K274210 biobrick or absorbed form the media in the cells where the K274210 biobrick is absent.
The spectra shows no measurable amounts of retinal in neither of the samples, but the samples produced by bacteria containing the K343006 brick have a lower amount of beta-carotene, which can indicated that either the bacterial production of beta-carotene is lowered or that some of the beta-carotene has been metabolized in the cell, either to a non-measurable concentration of Retinal or some other metabolite. It is also a possibility that the retinal is exported out of the cells.
The spectra from the second run of samples again show large amounts of beta-carotene produced by the K274210 biobrick or absorbed form the media in the cells where the K274210 biobrick is absent.
The only sample displaying any changes form the first run on the HPLC is TOP10 containing both the K343006 and K274210 biobricks. In the spectrum higher amounts of cell metabolites are still being produced by the K274210 biobrick but also others are produced by the cell.
In this spectra the peak with a retention time of 3,969 is close to the retention time of retinal form the standards but when examining the spectrum of the peak it can be concluded that it is not a retinal peak.
In order to assess and quantify the results a standard dilution of beta-carotene and retinal was made and measured: 10 µM, 5 µM, 1 µM, 2 µM, 0,5 µM. The standard dilutions were also measured on the HPLC with the same injection volume and program as the samples. The resulting graphs are presented beneath
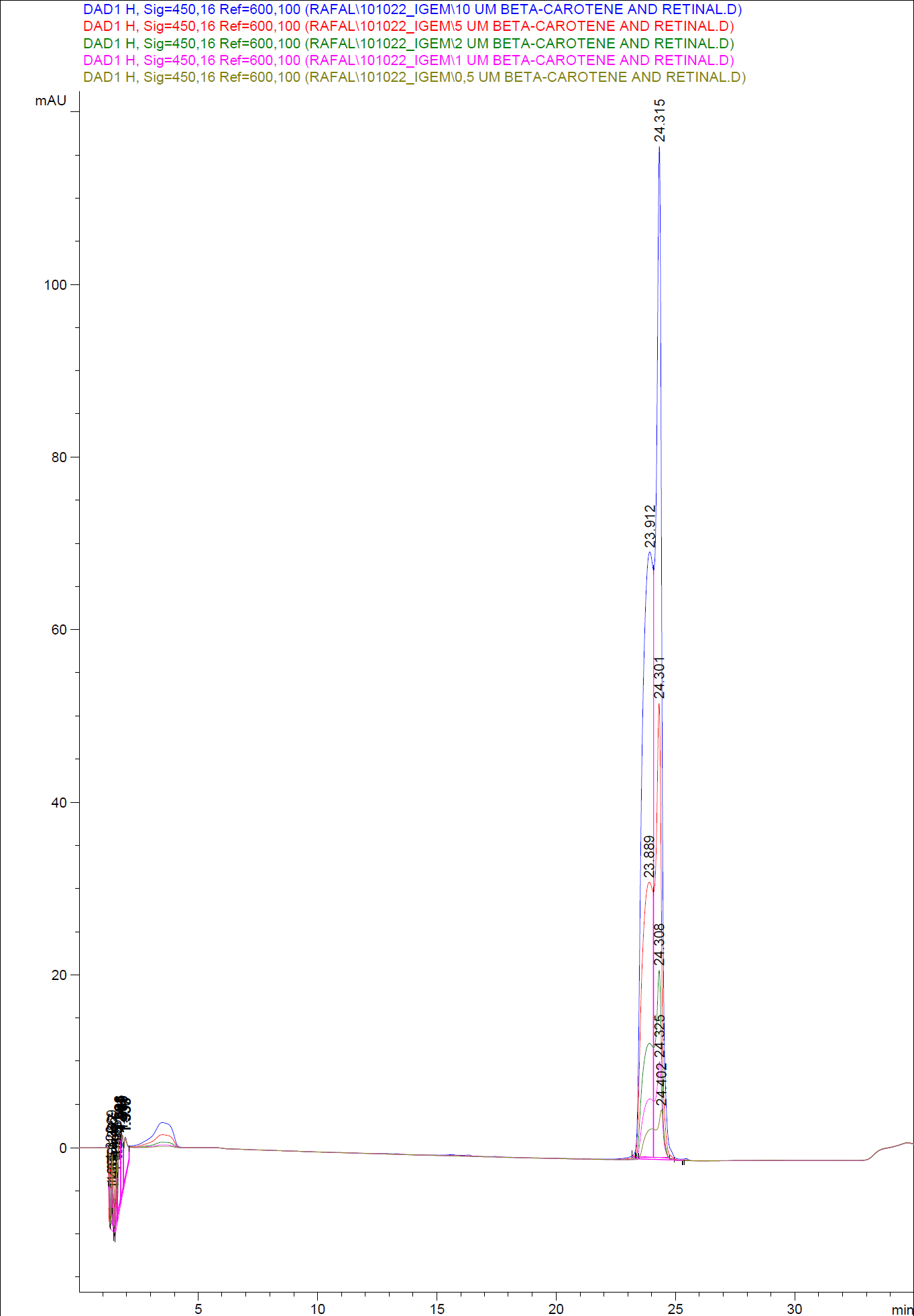
Figure 6: HPLC of standard dilutions of beta-carotene and retinal
When doing an HPLC analysis it is possible to quantify the amounts of the chemical compounds in the samples.
This is done by generating a standard curve with known dilutions of the chemical and recording the area under the peaks. The peak area correspond to the concentration of the chemical in the sample.
Then the area under the peaks is plotted on the y- axis, the know concentrations of the standards on the x-axis and the regression line is calculated.
Now it is possible to calculate unknown concentrations from samples using the regression line from the standard curves.
The results for our HPLC analysis can be seen beneath the text.
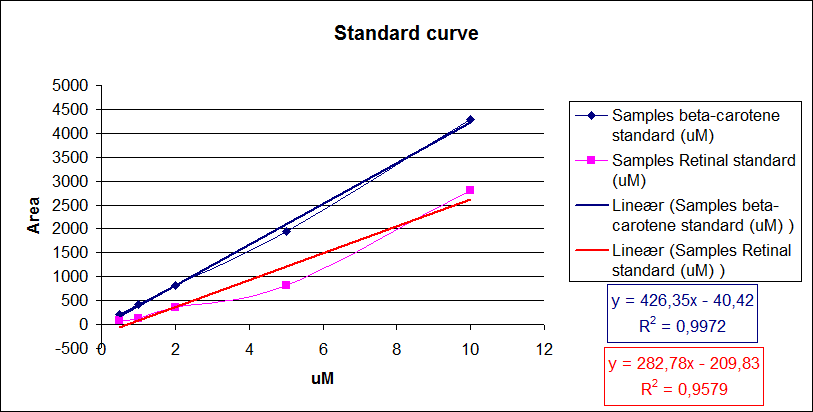
Figure 7: Standard curve of area under the HPLC peaks against beta-carotene and retinal concentration. Regression lines were made.
From the equations for the regression line it is possible to calculate the amount of beta-carotene produced by bacteria grown for 20 hours in LB media.
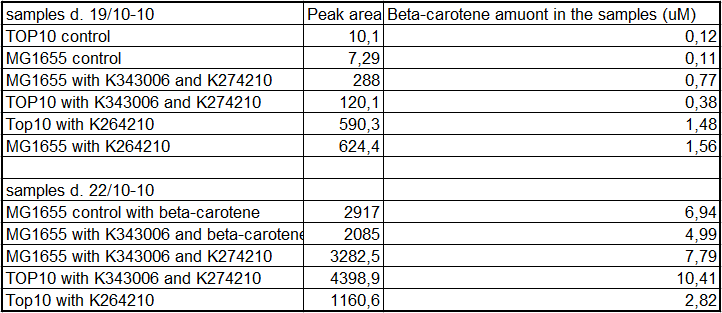
Tabel 1: Showing calculatet beta-carotene content in samples
All data can be seen under Raw data
Stability assay
To determine the stability of our pSB1C3-K343006 plasmid, a stability experiment was carried out according to protocol [SA1.1]. E.coli MG1655/pSB1C3-K343006 was grown in LB media without chloramphenicol, whereby no selection pressure is exerted on the bacteria. Dilutions of the culture was spreaded onto LA plates and LA plates with 35µg/mL chloramphenicol, respectively, and the colony forming units (CFU) was determined for each plate. The CFU for the LA plates represents the total amount of bacteria in the culture, and the CFU of LA plates with chloramphenicol corresponds to the amount of plasmid carrying bacteria. The percentage of the total amount of bacteria carrying the plasmid was plotted in a semi-logarithmic graph as a function of number of generations.
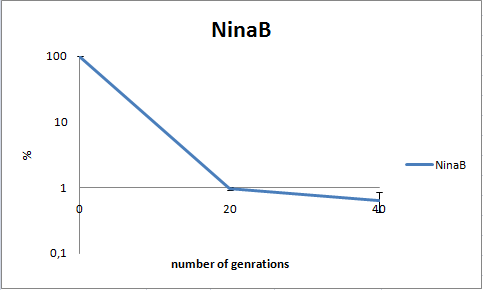
Figure 8: Stability assay of
E. coli strain MG1655-pSB1C3-K343006 showing that almost all cells have shed their plasmids within 20 generations, however some cells kept the plasmids for up to 40 generations.All data can be seen under
Raw data As seen in the graph, almost all of the bacteria had lost the plasmid after 20 generations, suggesting that the plasmid is only stable within the cell for a few generations (<20). This is presumably due to the strain brought upon the bacteria by the plasmid. Thereby when the bacteria are carrying a high-copy plasmid like pSB1C3-K343006 it is plausible that the bacteria will quickly lose the plasmid when no longer exposed to a selection pressure.
Growth assay
The purpose of this assay is to see if our transformants deviate from the wild type in growth rate. In the growth measurement assay we have measured OD at 550 nm every hour for 12 hours and at hour 24. In the experimental setup we used, no lag phase was observed in any of the measurements.
The graph below shows the growth of our wild type E. coli strain MG1655 and the MG1655/pSB1C3-K343006, respectively.

Figure 9: Growth curve showing measured OD at 550nm. Samples were taken every hour over a 12 hour perion + one sample after 24 hours. In graph
E. coli strain MG1655-pSB1C3-k343006 is compaired with Wild type
E. coli strain MG1655 showing no significant difference between the three graphs. No Lag phase is seen.All data can be seen under
Raw data From our data we see no significant difference between the plasmid carrying bacteria and the wild type. This can be said to be quite contradictory to our results obtained from the stability assay. The transitory stability of pSB1C3-K343006 suggests that it is highly unfavorable for the bacteria, wherefore it might be expected that the growth of the bacteria containing this plasmid would be affected. Thus, however large a disadvantage the plasmid pose to the bacteria, their growth are not significantly influenced by the plasmid. The added reproduction load due to the plasmids, might also prolong the lag phase of the bacteria. Whether this is the case can not be concluded based on this experiment as no lag phase was observed in this experiment.
 "
"









