Team:KAIST-Korea/Project/Introduction
From 2010.igem.org
(→
Minimal genome fission yeast
) |
(→
Minimal genome fission yeast
(Schizosaccharomyces pombe)) |
||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
=== Yeast? === | === Yeast? === | ||
| - | ====
Minimal genome fission | + | ====
Minimal genome fission yeast, ''Schizosaccharomyces'' pombe ==== |
Porting of cell signal transduction pathway is not easy for wild type organism. Most important reason is unwanted protein degradation. For wild type organism, unfamiliar protein can be harmful because it may be fragmented or misfolded proteins which disturb cellular pathway or viral proteins which may infect organisms. So wild type organism degrade unfamiliar proteins whether it is really harmful or not. And even degradation of at least one element of signal transduction pathway can disconnect whole pathway. So for successful porting of cell signal transduction pathway, inhibition of protease is important. Another problem is signal confusion. Basically, cellular signal transduction pathway is based on the protein-protein interaction(PPI). So unwanted PPI with elements of ported signal transduction pathway can confuse the signal. Of course if origin species of ported pathway is far enough from target species, we can exclude predictable unwanted PPI to avoid homologous proteins. But there are many unpredictable PPIs which can confuse the pathway. To avoid this problems, deletion of unnecessary proteins is required. And fission with minimal genome is made[5]. This yeast have only 1033 necessary genes of 5776 genes from wild type. So it may be useful to port cell signal transduction pathway from other organism(Human) without unwanted protein degradation or signal confusion |
Porting of cell signal transduction pathway is not easy for wild type organism. Most important reason is unwanted protein degradation. For wild type organism, unfamiliar protein can be harmful because it may be fragmented or misfolded proteins which disturb cellular pathway or viral proteins which may infect organisms. So wild type organism degrade unfamiliar proteins whether it is really harmful or not. And even degradation of at least one element of signal transduction pathway can disconnect whole pathway. So for successful porting of cell signal transduction pathway, inhibition of protease is important. Another problem is signal confusion. Basically, cellular signal transduction pathway is based on the protein-protein interaction(PPI). So unwanted PPI with elements of ported signal transduction pathway can confuse the signal. Of course if origin species of ported pathway is far enough from target species, we can exclude predictable unwanted PPI to avoid homologous proteins. But there are many unpredictable PPIs which can confuse the pathway. To avoid this problems, deletion of unnecessary proteins is required. And fission with minimal genome is made[5]. This yeast have only 1033 necessary genes of 5776 genes from wild type. So it may be useful to port cell signal transduction pathway from other organism(Human) without unwanted protein degradation or signal confusion | ||
Revision as of 10:23, 16 July 2010
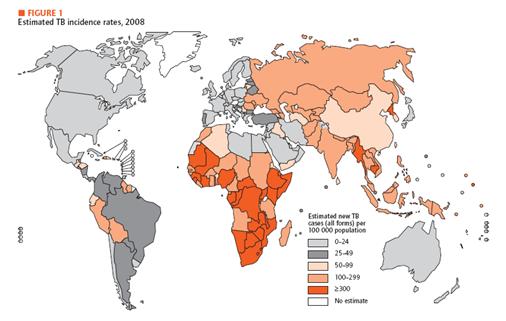
Motivation There are many kinds of diseases that mankind is suffering. When we talk about this topic, we can think easily three issues which are malaria, HIV and tuberculosis. Malaria is a disease that is transmitted from human to human by mosquitoes. Each year, malaria causes nearly one million deaths and the majority of them occur in developing countries. And this disease is high-risk in children, pregnant women, travelers, refugees, displaced persons, and laborers entering endemic areas. In case HIV, there are 33 million people infected in the world and 95 percent of them are living in developing countries. At last, for tuberculosis, it caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis which affects lungs most. Until now, more than 2 billion people are infected with tuberculosis bacilli and 90 percent of them are in developing countries. As we can see, all of these diseases are very problematic in developing country.There are many kinds of diseases that mankind is suffering. When we talk about this topic, we can think easily three issues which are malaria, HIV and tuberculosis. Malaria is a disease that is transmitted from human to human by mosquitoes. Each year, malaria causes nearly one million deaths and the majority of them occur in developing countries. And this disease is high-risk in children, pregnant women, travelers, refugees, displaced persons, and laborers entering endemic areas. In case HIV, there are 33 million people infected in the world and 95 percent of them are living in developing countries. At last, for tuberculosis, it caused by mycobacterium tuberculosis which affects lungs most. Until now, more than 2 billion people are infected with tuberculosis bacilli and 90 percent of them are in developing countries. As we can see, all of these diseases are very problematic in developing country.
In developing country, there are not much money and technology in medical development for testing and treating diseases. But unfortunately, basic medical tests like blood tests and biopsy and others need certain level of technical development. In addition, at some areas in developing countries doesn’t have electricity or access to high technology equipments. Therefore, we need new diagnosis system for disease test. For our system, we choose tuberculosis as a target. As the history goes on, technology related to diagnosis and treatment of tuberculosis has been developed. Especially for diagnosis, people do Tuberculin Skin Test, X-ray Test for its activation and examination of the sputum today. In addition, people take a blood test that involves ESR, white blood cell, CRP status checking. If necessary, CT and endoscopy can be added. Unfortunately, however, most of these tests require high technology and proper machines to process. Therefore, in developing countries these tests can be very hard to operate. As a solution, we think of a new idea for new diagnosis system.
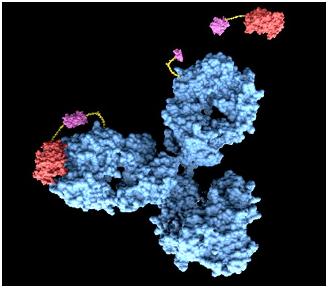
As the advanced version of diagnosis method, we suggest a system using antigen-antibody reaction. Actually, antibody can’t release signals by antigen-antibody reaction. So, we thought of fusion antibody-receptor as solution. Fusion antibody-receptor is a receptor which fused with other functional protein, antibody. In this way, we can get result by gene expression which would generally be GFP expression after our system is triggered by our target antigens. As a result, we can get possibility to make universal sensor by changing only target antigen’s antibody in fusion antibody-receptor. It should be very easy to diagnosis without heavy technology in the future.
Whole Pathway
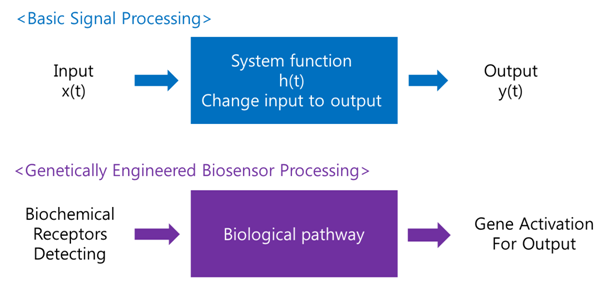
Antibodies for Detecting Mycobacterium tuberculosisMaking Biosensor – Yeast DetectorA biosensor is a device for the detection of an analyst that combines a biological component with a physicochemical detector component.[1] In order to make biosensor with genetically engineered organism, we should consider the following basic sensing process. The ‘Receive input’ part can be alternated by represented receptor, the ‘Process’ part can be signaling pathway which changes input to output, and the ‘Extract output’ part can be something easily detectable by human. Nowadays, pigments or fluorescence proteins are usually used for output, and in order to express these substances, gene expression is made constant use in genetically modified organism. Thus, all engineered biosensors with organisms should be modeled on (consist of) 1) biochemical receptors which can activate gene expression, 2) biological pathway, and 3) gene activation for output.
Yeast?Minimal genome fission yeast, Schizosaccharomyces pombePorting of cell signal transduction pathway is not easy for wild type organism. Most important reason is unwanted protein degradation. For wild type organism, unfamiliar protein can be harmful because it may be fragmented or misfolded proteins which disturb cellular pathway or viral proteins which may infect organisms. So wild type organism degrade unfamiliar proteins whether it is really harmful or not. And even degradation of at least one element of signal transduction pathway can disconnect whole pathway. So for successful porting of cell signal transduction pathway, inhibition of protease is important. Another problem is signal confusion. Basically, cellular signal transduction pathway is based on the protein-protein interaction(PPI). So unwanted PPI with elements of ported signal transduction pathway can confuse the signal. Of course if origin species of ported pathway is far enough from target species, we can exclude predictable unwanted PPI to avoid homologous proteins. But there are many unpredictable PPIs which can confuse the pathway. To avoid this problems, deletion of unnecessary proteins is required. And fission with minimal genome is made[5]. This yeast have only 1033 necessary genes of 5776 genes from wild type. So it may be useful to port cell signal transduction pathway from other organism(Human) without unwanted protein degradation or signal confusion
Biochemical Receptors
Fusion Antibody Receptors
Signal Pathway : JAK-STAT PathwayGene Activation for OutputReferences
|
 "
"